




Key Facts and Applications of Dubnium Explained for Exams
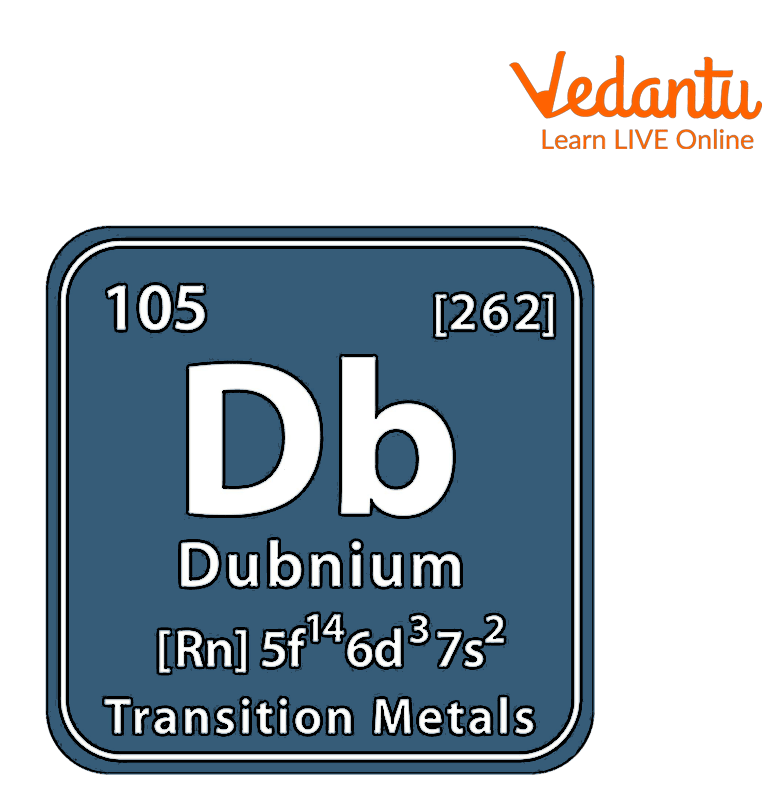
Dubnium is the 105th component of the periodic table. In a periodic table, elements are organized according to their atomic number. The atomic number is the number of protons within the atom's nucleus. Dubnium has an atomic number of a105. It's located in group 5 and period seven of the periodic table of elements and is denoted by the symbol ‘Db’. Dubnium is named after Dubna, a Russian town.
A small quantity of Dubnium has been created by artificial means. The bombardment with the heavy ion linear accelerator can facilitate the making of various isotopes.
Dubnium
What is Dubnium?
Dubnium is a radioactive element created through an experiment with the symbol (Db). The atomic number 105 of the synthetic component Dubnium is represented by its symbol Db.
History of Dysprosium
Element-105 was discovered in 1968 by a team led by Georgy Flerov at Joint Institute for Nuclear Research (JINR). The isotope-261 of the element-105 was created by a team led by Albert Ghiorso at the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory (LBL) in 1970.
At first, both teams gave totally different names to the element-105; the JINR group called it Neilsbhorium and the LBL group called it hahnium; both were named after outstanding scientists. Eventually, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) determined it should be known as Dubnium.
Dubnium doesn't occur naturally in Earth’s crust; it can only be prepared in an artificial manner in particle accelerators. All the isotopes of Dubnium that are characterized to date are obtained synthetically.
Dubnium Electron Configuration
Dubnium atomic number is 105 and electron configuration is \[Rn\] 5f146d37s2 .
Chemical Properties of Dubnium
The chemical properties have only been studied in theory and a few of the properties have been verified in single-atom experiments.
Calculations of solution chemistry indicate that the dubnium compounds that display an oxidation state of ‘+5’ are way more stable than those that show states of ‘+2’ and ‘+3’.
Calculations in solution chemistry additionally dictate that the dubnium compounds that show an oxidation number of ‘+5’ are comparatively more stable than Nb and tantalum compounds of the same state.
The complexion tendency and ability of dubnium are expected to be the same as the group-5 elements.
Physical Properties of Dubnium
Dubnium is an artificial element that's quite difficult to characterize.
The atomic mass of the Db is 261.9.
The density, boiling point, and melting point of dubnium are unknown as of now.
The longest-lived isotope of dubnium features a half-life of twenty-eight hours; this makes its estimation of properties very difficult. So far, studies have only been performed on single atoms.
The atoms of the solid-state dubnium square measure expected to arrange themselves in a body-centered cubical structure.
The isotopes that have comparatively long half-lives square measure much harder to produce; this additionally poses challenges within the study of dubnium.
Uses of Dubnium
Since Dubnium isn't produced in high amounts and it doesn't exist even on the earth’s crust. Therefore there are no such practical applications of this metal except the research areas.
The metal has not also proved any harmful effects on health and the surroundings since it tends to decompose within a short period.
Interesting Facts
Dubnium is named for the town in Russia where it was first created, Dubna.
Dubnium doesn't exist naturally on Earth.
Dubnium was first created by bombarding americium-243 with neon-22 atoms.
Conclusion
The valency of Dubnium is five and the dubnium elements have an atomic radius of 139 pm. The element 105 (atomic number) shows the silver color and the dubnium symbol is Db. Dubnium was discovered in 1970 and the melting and boiling point isn't known, however. It's a synthetic component. It is a transuranic element. It's created unnaturally by bombarding Cf 249 isotopes with N 15. It's harmful in nature because of radioactivity.
FAQs on Dubnium: Properties, Uses, and Importance
1. What is Dubnium and what is its chemical symbol?
Dubnium is a synthetic chemical element with the atomic number 105. It is not found naturally on Earth and can only be created in a laboratory setting. Its official chemical symbol is Db.
2. What are the known physical properties of Dubnium?
Dubnium is expected to be a solid metal at room temperature. Since only a very small number of atoms have ever been made, properties like its exact colour or melting point have not been experimentally measured. However, based on its position in the periodic table, scientists predict it would have a silvery-white or metallic grey appearance, similar to other transition metals.
3. Where is Dubnium located on the periodic table?
Dubnium is a transition metal located in Group 5 and Period 7 of the periodic table. It is placed directly below the element Tantalum (Ta). This position is important as it helps scientists predict its chemical behaviour.
4. Why is Dubnium only used for scientific research and not in everyday life?
Dubnium has no commercial or practical uses for two main reasons. Firstly, it is incredibly difficult and expensive to produce. Secondly, it is highly unstable and radioactive. Its most stable known isotope, dubnium-268, has a half-life of only about 28 hours, meaning it decays too quickly for any application outside of scientific study.
5. How can scientists predict Dubnium's chemical properties if it's so unstable?
Scientists predict Dubnium's properties by studying its location in the periodic table, a concept known as periodic trends. Because Dubnium is in Group 5, it is expected to share chemical characteristics with other elements in that group, particularly Tantalum (Ta), which is directly above it. By studying Tantalum's reactions, chemists can make educated predictions about Dubnium's likely chemical behaviour.
6. How is an element like Dubnium, which does not exist naturally, created?
Elements like Dubnium are created in particle accelerators through a process of nuclear fusion. This involves firing a beam of nuclei from a lighter element at a target made of a heavier element. For example, scientists have created Dubnium by bombarding a target of americium-243 with ions of calcium-48. The fusion of these two nuclei results in the temporary formation of a new, heavier element like Dubnium.
7. Why was element 105 called by different names before being named Dubnium?
The naming of element 105 was disputed for many years between the two teams that claimed its discovery. A Soviet team from Dubna, Russia, proposed the name Nielsbohrium (Ns). An American team from Berkeley, USA, proposed Hahnium (Ha). To resolve this conflict, the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) officially named it Dubnium (Db) in 1997, honouring the contributions of the Dubna research institute.
























