




How to Identify Cathode and Anode in Electrochemical Cells
In electrochemical cells, semiconductor diodes and in some medical devices, electrodes are used as a conductor which conducts electricity from non-metallic parts of the circuits. In other words, we can say that an electrode is a substance which conducts electricity in the electric current, which either enters or leaves the non-metallic medium like an electrolyte. Anode and cathode are the two types of electrodes. An anode is an electrode from which polarized current enters the outer circuit, and a cathode is an electrode from which a conventional current leaves a polarized electrical device. The anode and cathode charge are positive and negative respectively. The anode cathode symbol respectively are A and K.
The word anode originates from the Greek word anodes which means way up, and the word cathode originates from another Greek word, cathodes which means way down.
Electrochemical Cell
What is Anode and Cathode?
Anode and cathode are electrodes used in an electrolytic cell and electrochemical cell. Anode and cathode sign are positive and negative. A and K are the respective symbols of anode and cathode. The details of anode and cathode are given below.
Anode
Generally, the anode is the electrode where oxidation reaction takes place, which means at the anode, electrons are getting released into the external circuit. In the electrolytic cell, the anode is a positive electrode, and in the galvanic cell, the anode is a negative one. the sign of anode is ‘+’
In an electrolytic cell, which uses electrical energy for the propagation of a chemical reaction, In galvanic cells or electrochemical cells, which produce electrical energy by a chemical reaction, the anode is negative since it has a negative potential compared to the solution. The anode of a galvanic cell is zinc metal which is dipped in ZnSO4 solution. The Zn metal oxides to Zn2+ and gives two electrons into the external circuit.
Cathode
Generally, the cathode is the electrode where reduction reaction takes place. This means the cathode gains electrons from the external circuit and gets reduced. The sign of cathode is ‘-’.
In galvanic cells, copper is a cathode which is dipped in CuSO4 solution. Cu2+ ions accept electrons from the external cell and are reduced to Cu metal and deposited on the cathode.
There are two types of cathodes, hot cathode and cold cathode. Cold cathodes are cathodes that are not electrically heated by a filament. Which emits more electrons than can be supplied by thermionic emission. Hot cathodes are heated by electric current passing through the filament. The cold cathode is used in discharge lamps, discharge tubes, and in some vacuum tubes.
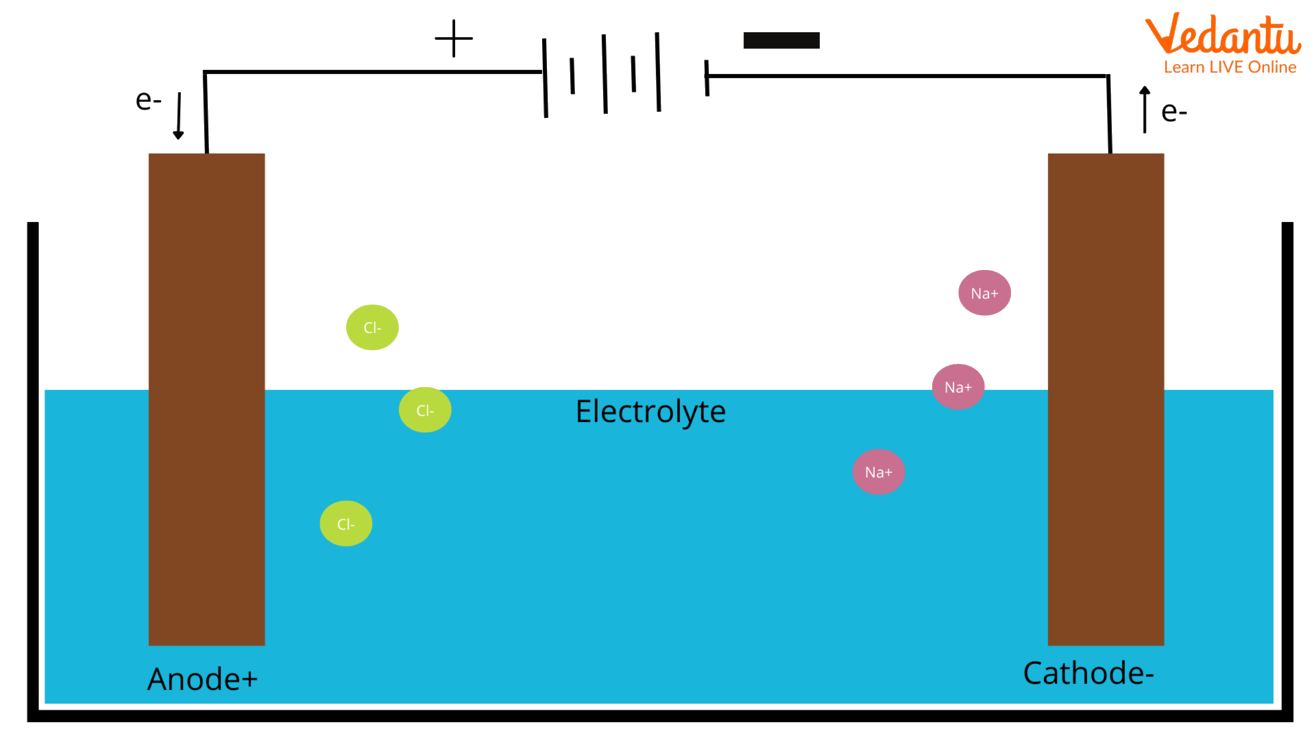
Anode and Cathode in Electrolysis
During electrolysis a chemical reaction or change takes place by the passage of electricity through the circuit and an electrolytic cell is the device which converts electrical energy to chemical energy. The charge of anion and cation is positive and negative respectively in an electrolytic cell. Consider the electrolysis of molten NaCl.
The anode of the wire or plate is having excessive positive charge because it is connected to the positive terminal of the battery. Hence anions will tend to move towards the anode and give off the electrons to the anode and get oxidized. These electrons are given by anion pass to the external circuit. In the electrolysis of molten NaCl, two inert electrodes are dipped in molten NaCl solution. When the electricity passes, the anode develops an excess positive charge and Cl- ions from the solution move towards the anode, where they become oxidized to sodium metal.
The cathode connects to the negative terminal of the battery, and it contains an excess negative charge. Cations from the solution move towards it and get reduced by accepting the electrons from the external circuit. Conversely, in galvanic cells, the cation is a positive electrode. When molten NaCl is subjected to electrolysis when electricity is passed, Na+ Ions start moving towards the cathode, where it is reduced to become sodium metal.
Difference Between Anode and Cathode
Key Features
Anode and cathode are electrodes used to make electrolytic and electrochemical cells.
Anode is the electrode where oxidation reaction takes place, and in the cathode, reduction takes place.
Anode is the electrode where electricity moves into the external circuit, and cathode is the electrode where electricity is given out.
the charge of anode and cathode are positive and negative in an electrolytic cell and in the galvanic cell it is the opposite
Conclusion
Anode is the positive part of electrolyte where oxidation takes place and cathode is the negative part of the cell where reduction takes place. The symbol of anode and cathode are A and K respectively. In electrolysis anode is positively charged and cathode is negatively charged. Hence the sign of anode and cathode are ‘+’ and ‘-’ respectively.
FAQs on Cathode and Anode Explained: Definitions, Differences & Uses
1. What are the anode and cathode in the context of electrochemistry?
In electrochemistry, the anode is the electrode where oxidation occurs (loss of electrons), and the cathode is the electrode where reduction occurs (gain of electrons). These are the fundamental definitions regardless of the type of electrochemical cell.
2. What is the primary difference between an anode and a cathode?
The primary difference lies in the electrochemical process that takes place at each electrode. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Anode: This is where oxidation happens. It releases electrons into the external circuit.
- Cathode: This is where reduction happens. It accepts electrons from the external circuit.
Essentially, electrons always flow from the anode to the cathode in the external circuit.
3. Why is the charge of the anode and cathode not always the same?
The charge (positive or negative sign) of the anode and cathode depends entirely on the type of electrochemical cell:
- In a galvanic cell (like a battery), the spontaneous chemical reaction produces energy. The anode is the source of electrons, making it the negative terminal. The cathode is where electrons are consumed, making it the positive terminal.
- In an electrolytic cell, an external power source drives a non-spontaneous reaction. The external source pushes electrons to the cathode, making it the negative terminal. It pulls electrons from the anode, making it the positive terminal.
4. How can you identify the anode and cathode in any electrochemical cell diagram?
To identify the electrodes, ignore the charge signs and focus on the processes:
- Identify the site of Oxidation: The half-reaction showing a species losing electrons (e.g., Zn → Zn²⁺ + 2e⁻) occurs at the anode.
- Identify the site of Reduction: The half-reaction showing a species gaining electrons (e.g., Cu²⁺ + 2e⁻ → Cu) occurs at the cathode.
- Follow the Electron Flow: If the direction of electron (e⁻) flow is shown, electrons always travel from the anode to the cathode.
5. What are the anode and cathode in a common dry cell battery?
In a typical Leclanché cell (a common dry cell), the components serve specific roles:
- The anode is the outer zinc container, which gets oxidised.
- The cathode is the central graphite (carbon) rod surrounded by a paste of manganese dioxide (MnO₂), where reduction takes place.
6. Is there an easy way to remember which process occurs at the anode and cathode?
Yes, a very common and helpful mnemonic is "An Ox, Red Cat".
- An Ox: Anode is for Oxidation.
- Red Cat: Reduction occurs at the Cathode.
Another mnemonic to remember the flow of ions is that cations (positive ions) move towards the cathode, and anions (negative ions) move towards the anode.
7. Why does the material of the anode and cathode sometimes seem to participate in the reaction, and other times not?
This is the difference between active and inert electrodes.
- Active Electrodes: These are made of materials (like zinc or copper) that actively participate in the half-reactions. The anode itself gets oxidised, and the cathode can be the site where ions from the solution plate onto it.
- Inert Electrodes: These are made of materials like platinum or graphite that do not participate in the reaction. They only provide a surface for oxidation or reduction to occur and act as a conductor for electrons. For example, in the electrolysis of water, platinum electrodes are used.
8. How are the concepts of cathode and anode applied in industrial processes like electroplating?
In electroplating, the goal is to coat an object with a thin layer of metal. This process uses an electrolytic cell:
- The cathode is the object you want to plate (e.g., an iron spoon). It is given a negative charge to attract positive metal ions from the solution.
- The anode is made of the metal you want to coat with (e.g., silver). It is given a positive charge and oxidises, replenishing the metal ions in the electrolyte solution.
This ensures a steady supply of metal ions that reduce and deposit onto the cathode, forming a uniform layer.
9. What is the difference between a galvanic cell and an electrolytic cell in terms of anode and cathode?
The main difference relates to energy conversion and electrode polarity:
- Galvanic Cell: Converts chemical energy to electrical energy (spontaneous reaction). The anode is negative and the cathode is positive.
- Electrolytic Cell: Converts electrical energy to chemical energy (non-spontaneous reaction driven by an external source). The anode is positive and the cathode is negative.
Despite the sign change, the rule 'Anode=Oxidation, Cathode=Reduction' remains true for both.
10. How are the anode and cathode represented in standard cell notation?
Standard cell notation follows a specific format: Anode | Anode Ion || Cathode Ion | Cathode. The anode and its corresponding half-cell are always written on the left, and the cathode is on the right. The double vertical line (||) represents the salt bridge. For example, in a Daniell cell, the notation is: Zn(s) | Zn²⁺(aq) || Cu²⁺(aq) | Cu(s). Here, Zinc is the anode and Copper is the cathode.
























