
What are zoospores? Give two suitable examples.
Answer
588.9k+ views
Hint: The term ‘Zoo’ means animals and ‘spores’ means a moment. It has motile spores and uses flagella for locomotion. The reproductive unit is able to give rise to an individual without sexual fusion.
Complete answer:
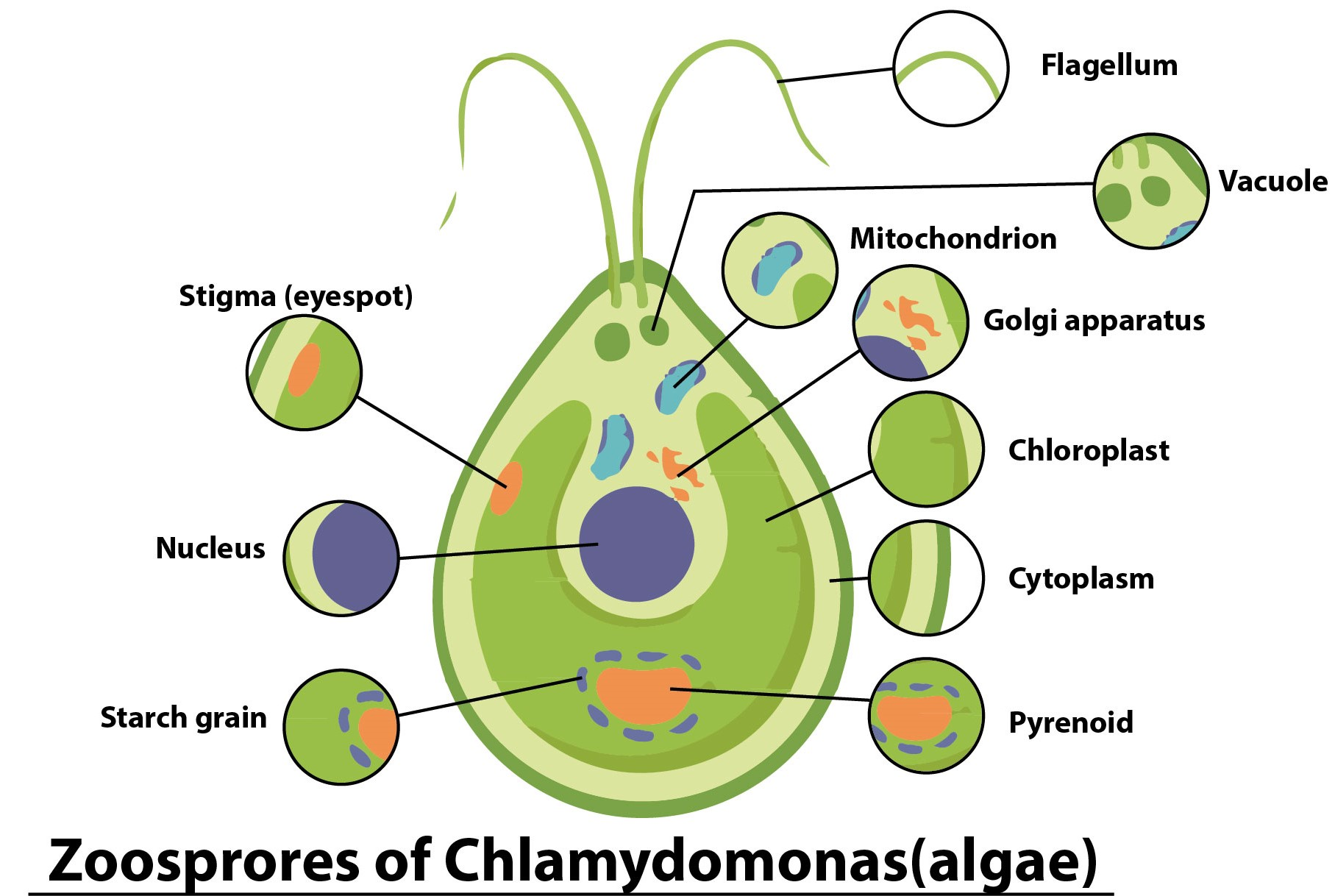
A zoospore is a spore that is motile in nature. They are asexual animals, as they give rise to new individuals without sexual fusion. They are naked and wall-less cells. They use flagella for locomotion. The flagella also help to swim in aquatic habitats for correct dispersal. They swim for several hours, using endogenous food reserves, then encyst by retracting or shedding their flagella and secreting a wall. Under conditions like water scarcity and unfavorable conditions of growth, they will behave as gametes and undergo fusion to make the resting structure called a zygote.
Examples include spores of some algae, fungi, and protozoans i.e. Phytophthora, Saprolegnia, Albugo, Achlya, etc.
Additional Information: In eukaryotes, there are four main types of zoospore are-
-Posterior whiplash flagella, In most of the organisms, there is a single posterior flagellum.
-Biflagellate zoospores with two whip types flagella of unequal length.
-Zoospores have one anterior flagellum of the tinsel type.
-Biflagellate zoospores with both whiplash(smooth) and tinsel type flagella attached anteriorly or laterally.
Note: Zoospores are also called a swarm spore. Zoospores may possess one or more distinct types of flagella that are tinsel and whiplash. The Tinsel flagellum is branched with many mastigonemes and is directed to the forward. The Whiplash flagellum is unbranched with an acute bend at the end and is directed anteriorly or posteriorly.
Complete answer:
A zoospore is a spore that is motile in nature. They are asexual animals, as they give rise to new individuals without sexual fusion. They are naked and wall-less cells. They use flagella for locomotion. The flagella also help to swim in aquatic habitats for correct dispersal. They swim for several hours, using endogenous food reserves, then encyst by retracting or shedding their flagella and secreting a wall. Under conditions like water scarcity and unfavorable conditions of growth, they will behave as gametes and undergo fusion to make the resting structure called a zygote.
Examples include spores of some algae, fungi, and protozoans i.e. Phytophthora, Saprolegnia, Albugo, Achlya, etc.
Additional Information: In eukaryotes, there are four main types of zoospore are-
-Posterior whiplash flagella, In most of the organisms, there is a single posterior flagellum.
-Biflagellate zoospores with two whip types flagella of unequal length.
-Zoospores have one anterior flagellum of the tinsel type.
-Biflagellate zoospores with both whiplash(smooth) and tinsel type flagella attached anteriorly or laterally.
Note: Zoospores are also called a swarm spore. Zoospores may possess one or more distinct types of flagella that are tinsel and whiplash. The Tinsel flagellum is branched with many mastigonemes and is directed to the forward. The Whiplash flagellum is unbranched with an acute bend at the end and is directed anteriorly or posteriorly.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




