Revision Notes on Microbes in Human Welfare for NEET 2024 - Free PDF Download
Students in Class 12 preparing for the NEET exam can now learn how microbes play a crucial role in human welfare from this Class 12 chapter of the Biology subject. The chapter talks about microbes which are diverse in nature and include fungi, bacteria, and protozoa. It also further talks about the infectious agents. All questions and answers in Microbes in Human Welfare Class 12 notes are created by subject matter experts that will help students in preparation for the exam in simple format. Students will have a clear idea about the topics discussed in Microbes in Human Welfare and other aspects.
These Microbes in Human Welfare notes have been curated by top subject matter experts from Vedantu as per the latest NEET syllabus and exam requirement. Students will find the motes very helpful, especially while revising before the NEET exam.
Note: 👉Prepare for Your Future in Medicine with the NEET Rank and College Predictor 2024.
Access NEET Revision Notes Biology Microbes in Human Welfare
Introduction
Microbes are the most essential parts of biological systems on Earth.
They can be found in soil, water, air, our bodies, and the bodies of other animals and plants. They can be found even in places where no other life could possibly exist.
Protozoa, bacteria, fungi, etc are all examples of microbes. They also include microscopic plant viruses, viroids, and prions, which are proteinacious infectious agents.
Bacteria and many fungi can be developed on nutritive media to produce colonies visible with the naked eye. These cultures are beneficial in microorganism research.
Microbes are responsible for a wide range of human diseases. Animal and plant diseases are also caused by them.
However, this should not lead you to believe that all microbes are harmful, many microbes are beneficial too.
Microbes in Vaccination, Antibiotics and Industrial products
Microbes synthesize various products that are beneficial to humans.
Beverages and antibiotics are the most common products derived from microbes.
Fermenters are special vessels used in industries for large-scale microbe cultivation and use.
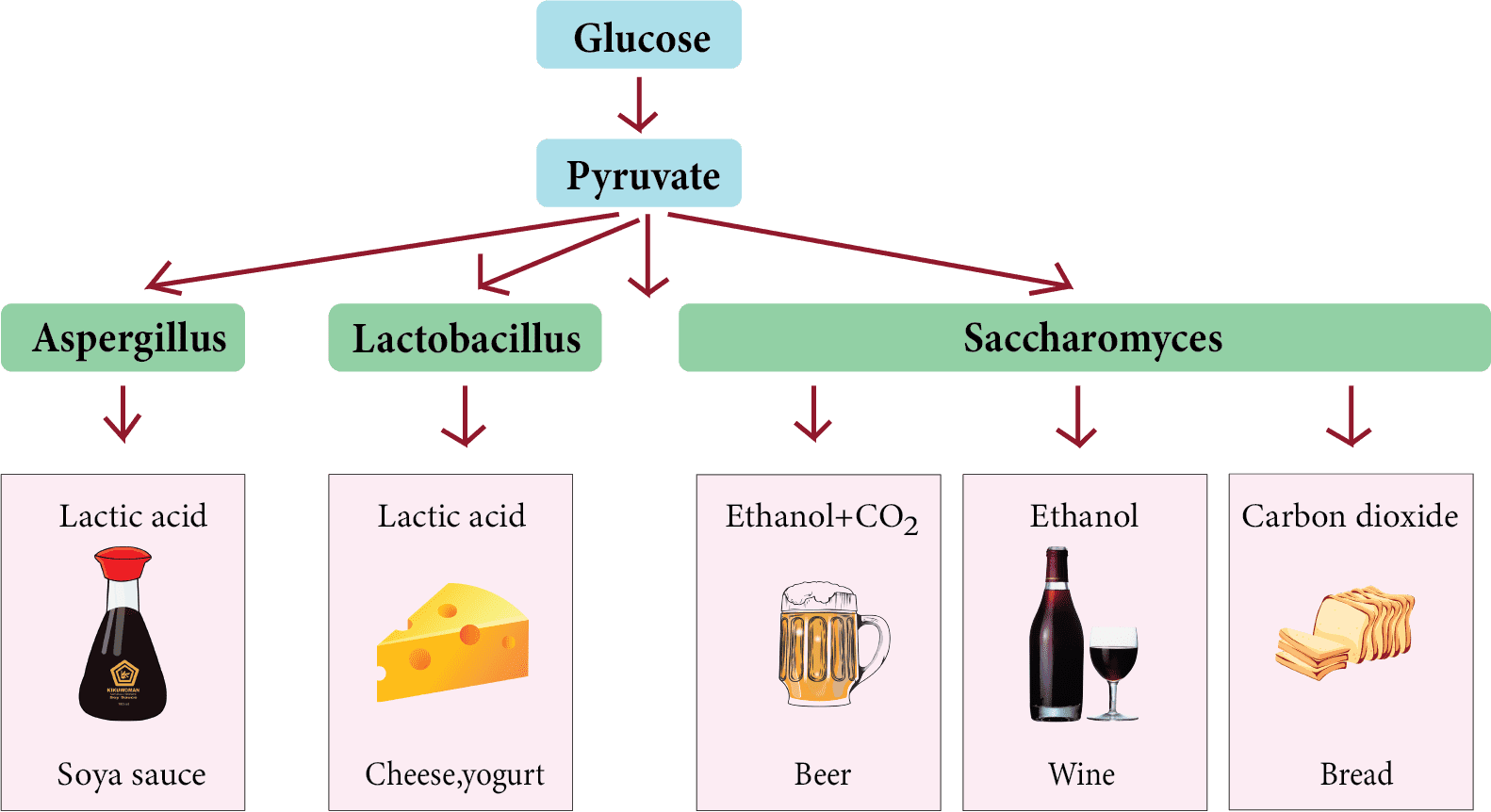
Different Types of Food Items Which are Prepared Using Microbes
Fermentation for Beverage Preparations:
Fermented beverages including wine, whisky, and brandy, are as old as civilization.
The most prevalent microbe to use for fermentation is Saccharomyces cerevisiae, also known as brewer's yeast. It has been used to manufacture ethanol by fermenting malt-based food products and fruit juices.
Depending on the fermentation type and raw material used, various alcoholic beverages are produced.
Whisky, brandy, and rum are manufactured by distillation of fermented broth, while both wine and beer are manufactured by fermentation of plant-based food products.
Antibiotics Production:
Antibiotics are the organic chemical compounds produced by microbes that are effective against any disease-producing microbe.
Penicillin was the first antibiotic discovered and is named after the mold Penicillium notatum.
Antibiotics are required for the treatment of various diseases such as whooping cough, diphtheria, leprosy, plague, and others.
Production of other Industrial Products:
Microbes are also used in the manufacturing of certain chemicals such as , organic acids, enzymes, and so on.
Acetobacter aceti, for example, is used to generate acetic acid.
Aspealcoholsrgillus niger yields citric acid.
Lactobacillus creates lactic acid.
Microbes can also be used to produce lipase enzymes.
Streptokinase, which is formed by the bacterium Streptococcus, is very effective at eliminating clots from the patient's blood vessels who have had a myocardial infarction resulting in a heart attack, acting as a 'clot buster.'
Cyclosporin A, an immunosuppressive agent derived from the fungus Trichoderma polysporum, is used for organ transplantation.
Microbes in Household Products
Household Products
Lactobacillus is a bacterium observed in curd. It is utilized to transform milk into curd. This bacterium produces lactic acid by partially digesting milk protein and coagulating it to form curd. A small curd inoculum is necessary for milk for the curd formation process. Vitamin B12 is abundant in curd.
Fermentation is a metabolic process by which alcohol is produced from sugar. There is no need for oxygen in this process. As a result, it is an anaerobic process. The fermentation process was discovered by Louis Pasteur. It is also used to create bread. The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae is responsible for dough fermentation. Many drinks are needed by the same fermentation process.
Bacterial action is also responsible for the formation of dough used in the production of food items such as idli, dosa, and so on. Bacteria are mainly accountable for the fermentation of the dough, which results in the final batter. The release of carbon dioxide causes the dough to puff up.
Propionibacterium sharmanii, a fermenting bacteria, is responsible for the production of cheese. This bacterium is needed for the production of Swiss cheese.
The 'Roquefort cheese' is harvested by growing a specific fungus on it, which gives it a distinct flavor. Cheese is classified according to its texture, taste, and flavor.
Microbes in Sewage Treatment
Human excreta is a significant constituent of wastewater. Thus, municipal wastewater is also referred to as sewage.
It contains a large number of organic substances and microbes. Before releasing it into the environment, excreta should be treated to reduce pollution.
Heterotrophic bacteria, which are generally present in wastewater, are required to treat the sewage.
The sewage treatment procedure is divided into two stages: primary treatment and secondary treatment.
Primary Treatment-
The procedure of primary treatment begins with the manual elimination of small and large particulate via filtration and sedimentation.
To begin with, sequential filtration eliminates debris and then removes the soil and small pebbles.
The remainder, known as effluent, is collected for secondary treatment.
Secondary Treatment-
Effluent is moved through aeration tanks using continuous aeration.
Aerobic microbes can grow rapidly thanks to aeration, which aids in the aerobic degradation of organic matter.
Aerobic microbes combine to form flocs. Flocs are mesh-like structures formed by an association of fungal filaments from masses of bacteria.
This lowers biological oxygen demand (BOD). The amount of oxygen ingested by bacteria as well as other microorganisms while decomposing organic matter under aerobic (oxygen present) environments at a specific temperature is referred to as biochemical oxygen demand (BOD). The levels of dissolved oxygen in rivers and other water bodies is directly affected by BOD. The higher the BOD, the faster oxygen is exhausted in the stream. This means that higher groups of aquatic life have less oxygen available to them.
After the BOD of the sewage is lowered, it is carried into a settling tank to allow the bacterial flocs to settle. This sediment is referred to as activated sludge.
A small portion of activated sludge is pumped back into the aeration tank to serve as inoculum.
The remaining sludge is poured into large tanks known as anaerobic sludge digesters.
Various gases are produced during this process, including methane, carbon dioxide, and hydrogen sulfide.
Furthermore, waste can be dumped into rivers, streams, and so on.
The Ministry of Environment and Forests has adopted the Ganga Action Plan and the Yamuna Action Plan to protect our country's major rivers from pollution.
One of the major policy ideas discussed in these plans is the construction of a significant number of sewage treatment plants to ensure that only treated sewage is discharged into rivers.
Microbes in production of Gobar gas
Biogas is a gas mixture with the highest percentage of methane.
Some bacteria that grow anaerobically on cellulose fibers produce a significant amount of methane in addition to CO2 and H2.
These bacteria that generate methane as an outcome of anaerobic respiration are known as methanogens. Methanobacterium is an example of methanogenic bacteria.
Microbes as Biocontrol Agents
The use of natural methods for controlling plant diseases and pests is known as biocontrol.
Pesticides and insecticides have traditionally been used to control diseases and pests. As a result, these chemicals are enormously toxic and hazardous.
Biological Pest and Disease Control:
Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) is a bacterium that is employed as a biocontrol agent against insects and pests.
Endotoxin is produced by this bacterium, which paralyzes the digestive tract of the insect/pest that utilizes it.
Bt cotton is one such plant-produced product.
Trichoderma is a fungus that is used to control plant pathogens.
Baculoviruses are the microbes of insects and other arthropods. The majority of baculoviruses used as biocontrol agents are members of the genus Nucleopolyhedrovirus. These viruses are ideal for narrow-spectrum actions, such as species-specific insecticides. They have been shown to have no negative effects on other organisms such as plants, birds, mammals, and fish, as well as non-target insects.
The Ladybird, a common beetle with red and black markings, and Dragonflies are useful in controlling aphids and mosquitoes, respectively.
Microbes in Biofertilizers:
Microorganisms are also used as bio-fertilizers in some cases.
Rhizobium is a nitrogen-fixing gram-negative bacterium observed as an endosymbiont in plants having root nodules called leguminous plants.
Other free-living bacteria, such as Azospirillum and Azotobacter, can fix atmospheric nitrogen increasing the soil's nitrogen content.
Cyanobacteria are photosynthesis microbes found in both aquatic and terrestrial environments, and many of them, such as Anabaena, Nostoc, and Oscillatoria, can fix atmospheric nitrogen. Cyanobacteria are an important biofertilizer in paddy fields. It also improve soil fertility by adding organic matter.
Microbes in the Human body
Different microbes colonize various parts of the human body, like the gut, skin, reproductive tract, and so on.
The gut is the most significant part where microbes are found in the human body are microflora.
Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and other bacteria are found in the stomach microflora. These microbes are always prepared to stay alive in the stomach's acidic environment.
Enterobacteriaceae is a family of bacteria that make up the intestinal flora. This flora is required for digestion and absorption to function. As a result, the efficiency of digestion is increased, as it is the utility of the gut.
The microbes are preventing another microbe from colonizing.
They also naturally produce certain compounds that are necessary for food digestion.
Viruses are also microbes that are used as a vector in recombinant DNA technology to transmit a required gene.
Microbes as Biofertilizers
Farmers have been forced to shift to organic farming due to the excessive use of chemicals and their damaging effects.
Biofertilizers are used in organic farming.
Biofertilizers are living things that are necessary for soil nutrient enrichment.
Bacteria, fungi, as well as Cyanobacteria, are all found in biofertilizers.
Rhizobium bacteria are observed in leguminous plants such as peas and beans. This bacterium is needed by plants during the nitrogen absorption process.
Azospirillum and Azotobacter are two other bacteria that fix nitrogen.
When fungi form a mutual association with the roots of higher plants like gymnosperms, they are referred to as mycorrhiza.
The fungus absorbs phosphorus from the soil and transports it to the plant.
Autotrophic microbes are Cyanobacteria. They are found in both terrestrial and aquatic environments. For example, Anabaena, Nostoc, Oscillatoria, and others, can fix atmospheric nitrogen.
As a result, an important biofertilizer, Cyanobacteria, is required, particularly in paddy fields.
Blue-green algae add organic material to the soil for increasing its fertility.
Key Points to Remember :
Microbes are an essential part of life on Earth.
Formation of curd is done by bacteria Lactobacillus.
The yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae ferments the dough, which is used to make bread. Idli and dosa are two foods created from dough that has been fermented by bacteria.
To give cheese a specific texture, taste, and flavour, bacteria and fungi are used.
Lactic acid, acetic acid, and alcohol are examples of commercial products made by microbes that are employed in numerous industrial processes.
For more than a hundred years, microbes are being used to treat sewage (waste water) by the process of activated sludge formation and this helps in recycling of water in nature.
Methanogens produce methane (biogas) while degrading plant waste. Biogas produced by microbes is used as a source of energy in rural areas.
Microbes can also be used to kill harmful pests, a process called as biocontrol. The biocontrol measures help us to avoid heavy use of toxic pesticides for controlling pests.
There is a need these days to push for use of biofertilisers in place of chemical fertilisers.
Importance of Ecosystem Class 12 Notes for NEET
When students refer to the notes of the Ecosystem chapter of Class 12 Biology, they will have a complete understanding of the different aspects of our ecological system. The chapter also presents the concept of Ecological Pyramids which is a graphical representation of the ecological parameters presented in the sequence through various trophic levels. There are three different ecological pyramids-
Pyramids of Number
Pyramids of Biomass
Pyramids of Energy
Furthermore, Ecosystem notes also present the idea about ecological succession which is the gradual and fairly predictable change in the composition of species. The ecological succession is further divided into Primary Succession and Secondary Succession. Each aspect of the succession is presented finely in simple words by subject matter experts.
The Ecosystem chapter is very much important for NEET preparation. Students will get to learn about the Nutrient Cycle, Phosphorus Cycle, Carbon Cycle, and others. Upon reading notes, students will become capable of answering questions regarding the Ecosystem chapter that will help scoring high marks.
Benefits of Ecosystem Class 12 Notes From Vedantu
The Ecosystem notes for NEET PDF from Vedantu comes with many benefits. It is quite obvious that students come under a lot of pressure during the NEET exam which requires a lot of preparation. Using the PDF file that comes with handy information, you can prepare for the exam very well. Some of the benefits you will get are-
The Ecosystem notes Class 12 Biology PDF carries detailed explanation about the chapter and each section is finely elaborated.
These practice notes created for students carry the exact portion as per the NEET exam and all questionnaires are similar.
As mentioned above, these notes are created by subject matters of Vedantu who know what students need and how well they can prepare for the exam.
The revision note is compiled as per the latest NCERT syllabus of the chapter.
Download Ecosystem PDF Notes for Free
You can now download the Ecosystem PDF notes which are available for free covering all aspects of the chapter. Students can make use of these notes to understand the format so that you can remember everything. You can even test your exam preparation skills and practice giving answers to questions. To test your replying skills, use this Ecosystem Class 12 notes PDF file of the chapter and get insight of everything you should know to prepare.
Other Important Links
Other Important Links for NEET Microbes in Human Welfare |
NEET Biology Revision Notes - Chapter Pages
NEET Biology Chapter-wise Revision Notes | |
Microbes in Human Welfare Notes | |
FAQs on Microbes in Human Welfare NEET Notes 2024 | Free PDF Download
1. What are the different types of Microbes in Human Welfare?
There are different types of microbes in Human Welfare, including bacteria, protozoa, fungi, certain algae, and prions are all microorganisms. Bacteria, certain algae, and protozoa are single-celled microorganisms, while algae and fungi are multicellular.
2. What do you understand about sewage as discussed in Microbes in Human Welfare?
In municipal sewage, water that contains huge amounts of organic matter is called sewage. Sewage is thus cleaned in sewage treatment facilities (STPs) by heterotrophic bacteria before discharging resulting in less pollution. The treatment of sewage is done in two stages.
3. Are microbes available in biofertilisers?
Biofertilisers are also one form of organisms that improve the soil's nutrient quality. Bacteria, fungus, and cyanobacteria are the most common suppliers.
Rhizobium bacteria generate root nodules on the roots of leguminous plants, which raise the nitrogen level in the soil, which is required for numerous metabolic activities. Azotobacter and Azospirillum are soil-dwelling bacteria that fix nitrogen from the atmosphere into organic forms.
4. Are microbes found in household products?
Lactobacillus and other bacteria often referred to as lactic acid bacteria (LAB) thrive in milk and convert it to curd. The LAB creates acids that partially breakdown and coagulate milk proteins. It also boosts Vitamin B12 levels, which increases nutritional quality.

























