
Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Notes PDF for High Scores in NEET Biology
Class 11 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants is a fundamental chapter that elaborates on how a plant conducts the process of photosynthesis in its cell organelles. It explains the biochemical process of synthesising food by trapping solar energy using pigments and converting simpler molecules to complex ones. The outcome of photosynthesis forms the main source of food for almost all ecosystems. To understand the concepts of this chapter easily, refer to the Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Class 11 notes prepared by the subject matter experts of Vedantu.
Note: 👉Get a Head Start on Your Medical Career with the NEET Rank and College Predictor 2024.
These notes have been designed to offer a concise format of the entire chapter. The fundamental principles and every crucial concept are explained and described using simpler scientific language for NEET aspirants. Using these notes will enable students to complete revising this chapter faster without compromising on preparation quality.
Access NEET Revision Notes Biology Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
Introduction:
Plants are the primary source of food for all animals on Earth, including humans.
Green plants synthesise the food they require, and all other organisms rely on them to meet their energy requirements. They produce the food through photosynthesis and are thus classified as autotrophs because they prepare their own food.
Heterotrophs, which include humans, are species that depend on green plants for nutrition.
All living things on Earth rely on sunlight for energy.
Photosynthesis is a biological process in which plants use light energy from the sun to fuel the formation of organic molecules like glucose.
Photosynthesis is vital for two reasons:
It is the prime source of all food on the planet.
Oxygen is emitted into the atmosphere (which is required for aerobic life to exist on this planet).
Photosynthesis requires three components:
Chlorophyll, which is the green pigment found in leaves
Light
Carbon dioxide.
Early Experiments:
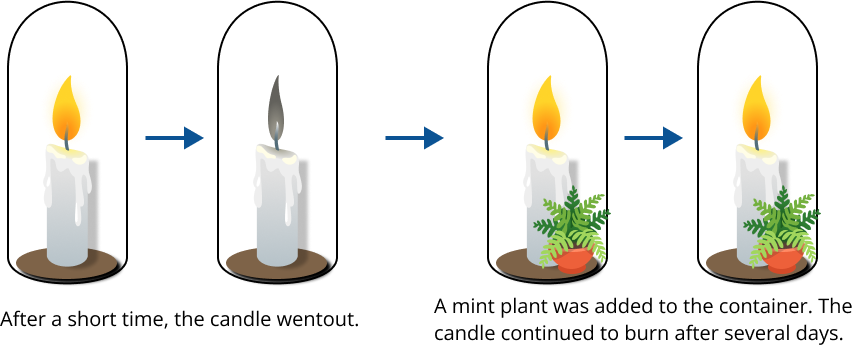
Early Experiment of Photosynthesis Done by Joseph Priestly
Joseph Priestly, in 1774, discovered that plants replenish oxygen in the air which respiratory animals and burning candles eliminate.
Julius von Sachs discovered in 1854 that the green parts of plants are where glucose is produced which is usually saved as starch.
T.W Engelmann (1843-1909) carried out a fantastic experiment. He used a prism to separate light into its spectrum components before lighting a green alga named Cladophora that was dissolved in an anaerobic bacteria solution. The microorganisms were used to discover where O2 originated. He found that germs gathered primarily in the split spectrum's blue and red light areas. So, the first photosynthesis action spectrum was thus defined, resembling the absorption spectra pigments of chlorophyll a and b.
The empirical equation then depicted the entire process of photosynthesis for oxygen-evolving organisms:$\mathrm{CO}_{2}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O} \rightarrow\left[\mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{O}\right]+\mathrm{O}_{2}$
where CH2O is a carbohydrate like glucose (6 carbon sugar).
Cornelius van Neill, a microbiologist, made notable participation in the understanding of photosynthesis by demonstrating that photosynthesis is a light-dependent reaction in which H2 from an appropriate hydrogen compound, i.e. H2O, reduces carbon dioxide to carbohydrates.
The equation can be expressed as,
$2 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{~A}+\mathrm{CO}_{2} \xrightarrow{Light} \mathrm{~A}+\mathrm{CH}_{2} \mathrm{O}+\mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}$
H2O is the H2 donor in green plants and is oxidized to O2. Some life forms do not produce O2 during photosynthesis. As a result, it is deduced that O2 created by plants (green) comes from H2O rather than CO2.
As a result, the photosynthesis equation is as follows:
$6\mathrm{CO}_{2}+12 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}\xrightarrow{Light} \mathrm{C}_{6} \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_{6}+6 \mathrm{H}_{2} \mathrm{O}+6 \mathrm{O}_{2}$
Photosynthesis occurs in the chloroplasts of mesophyll cells of the green leaves, specifically in the green leaves of plants.
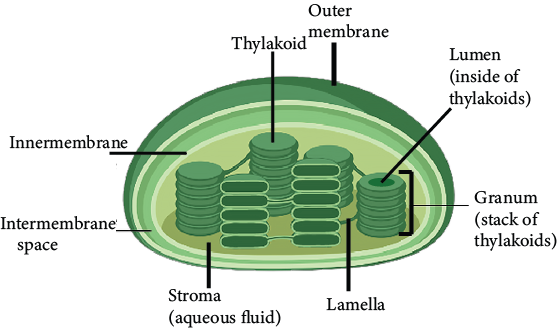
Chloroplast
The membrane system is responsible for capturing solar energy and producing ATP and NADPH; the reactions or set of reactions participating are light-driven and thus referred to as Light reactions.
Enzymes in the stroma are capable of taking CO2 and converting it into sugar, which then forms starch; the reactions are not instantly light-driven but are reliant on the components of light reactions, namely ATP and NADPH, and are referred to as Dark reactions.
How Many Different Kinds of Pigments are Required in Photosynthesis?
In leaves, there are four pigments: chlorophyll-a (bluish-green), chlorophyll-b (yellowish-green), Xanthophylls (yellow), and carotenoids (yellow to yellow-orange).
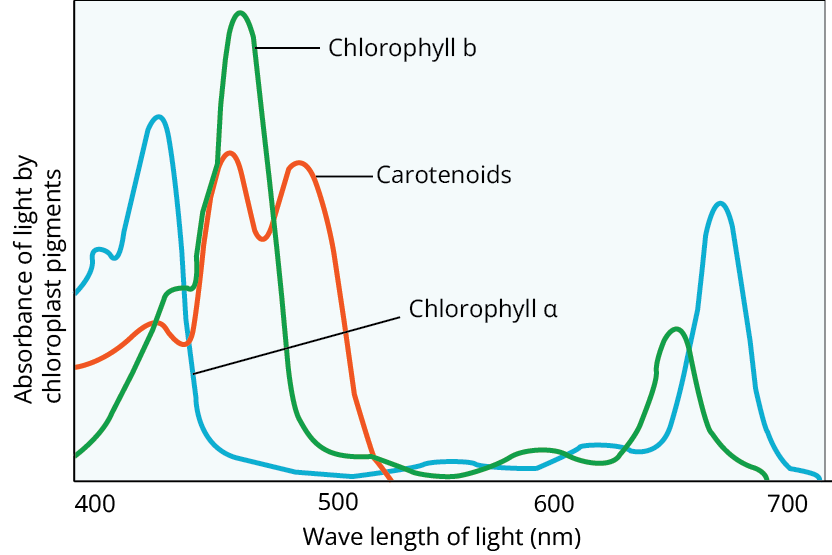
Absorption spectrum of Chlorophyll-a, b, and Carotenoids
We can reach the conclusion that chlorophyll is the most important pigment involved in photosynthesis.
Light Reaction:
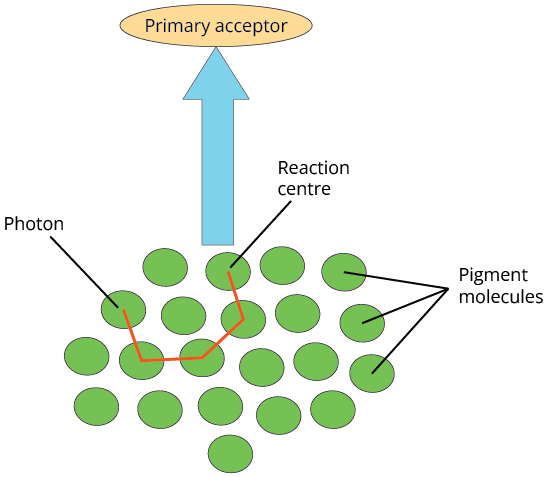
Light-harvesting Complexes
Absorption of light, splitting of water, releasing oxygen, and creating high-energy chemicals such as ATP and NADPH are all part of the process.
Several complexes, namely Light-harvesting complexes (LHC) with pigments in Photosystem-1 (PSI) and Photosystem-2 (PSII), are named in the order of their discovery.
Each photosystem, with the exception of chlorophyll a, contains all of the pigments and constitutes an LHS known as antennae.
The reaction centre is formed by a single molecule of chlorophyll-a.
PSI has a maximum absorption at 700 nm, thus is also known as P700 whereas PSII has a maximum absorption at 680 nm, which is known as P680.
Electron Transport System:
LHC of PSII receives light at 680 nanometers, which excites electrons, causing them to jump out of their orbit and be received by an electron acceptor, which then moves them to the electron transport system.
Electrons are not used up and are transferred to PSI pigments. Because of the absorption of light at 700 nanometers, these electrons pass to an energy molecule NADP+, leading to the formation of NADPH and H+.
The Z scheme is the name given to this electron transport system.
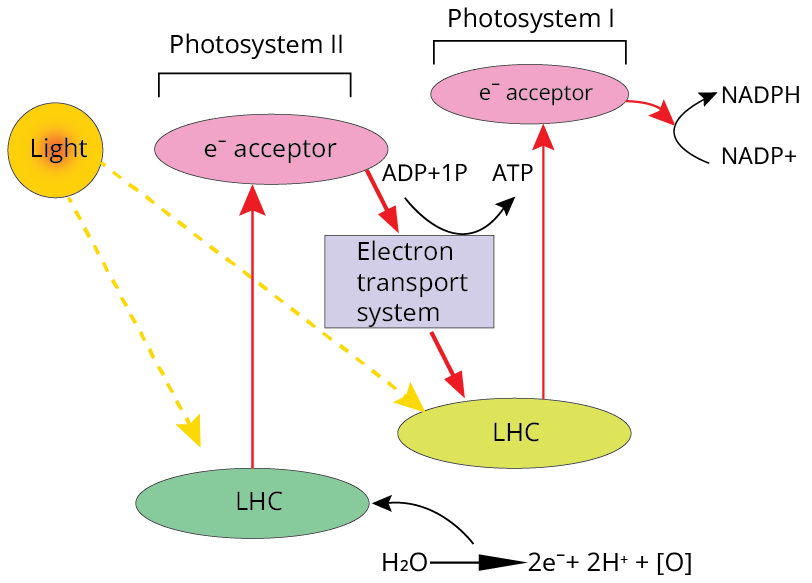
The Z-scheme of Electron Transport System
Splitting of a Water Molecule:
The splitting of H2O replaces the electrons which were transferred from Photosystem-2. This produces oxygen, a byproduct of photosynthesis.
2 H2O ⟶ 4 H+ + O2 + 4 e-
PSII is associated with this splitting of H2O. It provides the electrons required to replace those eliminated from PSI.
Cyclic and Non-cyclic Photophosphorylation:
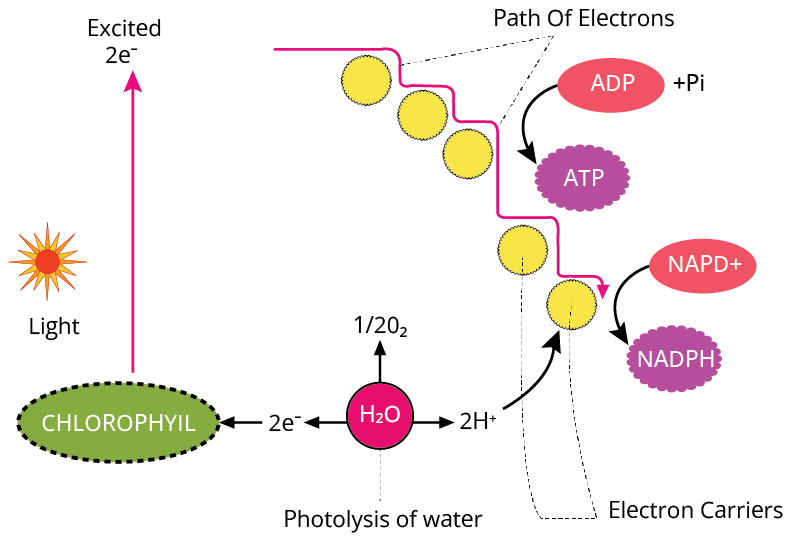
Cyclic Phosphorylation
Photophosphorylation is the process by which ATP is synthesised from ADP and Pi in the existence of light.
Non-cyclic photophosphorylation occurs when PSII and then PSI act in series, resulting in the synthesis of both ATP and NADPH.
Cyclic photophosphorylation occurs when only PSI is active, the electron is distributed within PSI and phosphorylation occurs as a result of the cyclic flow of electrons. It occurs in the stroma lamellae. It lacks the NADP reductase enzyme, so ATP is synthesised but not NADPH and H+.
It also takes place when only light with a wavelength greater than 680 nanometers is available.
Chemiosmosis Hypothesis:
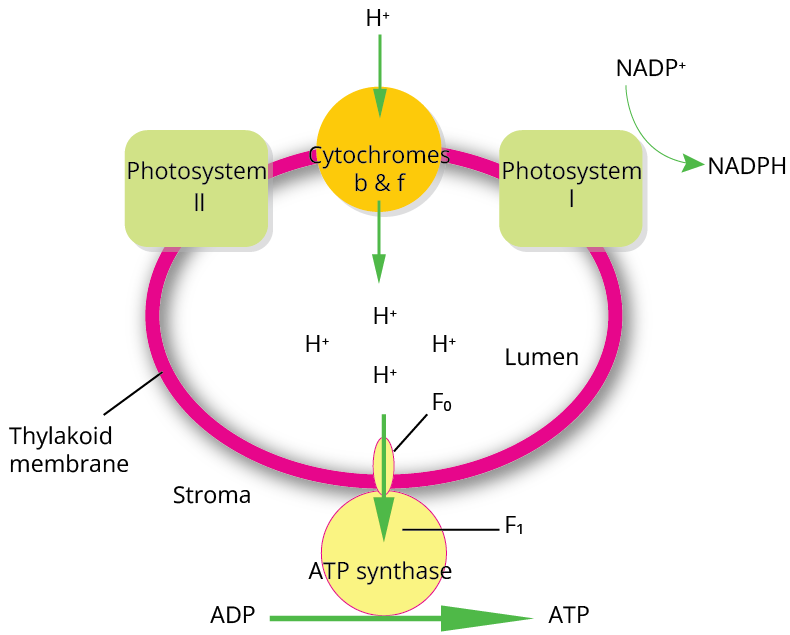
Chemiosmosis Hypothesis
The ATP synthase enzyme is composed of two parts: F0 and F1.
F0, which is presented into the thylakoid layer and creates a transmembrane channel that enables protons to easily diffuse across the layer.
F1 is the other half, which is situated on the stroma-facing side of the thylakoid external surface of the membrane.
The gradient's breakdown offers enough energy to cause a conformational shift in the F1 moiety of the ATP synthase, allowing the enzyme to synthesise multiple molecules of ATP.
Chemiosmosis requires a membrane, a proton pump, a proton angle, and ATP synthase.
To create a gradient or a larger proportion of protons inside the thylakoid lumen, energy is used to pump protons across a membrane.
ATP synthase contains a channel that allows protons to be released back across the membrane, releasing enough energy to activate the ATP synthase chemical, which catalyses the formation of ATP.
Along with the NADPH produced by electron development.
Where Do ATP and NADPH Play a Role in Photosynthesis?
These are used in a dark reaction known as the biosynthetic phase of photosynthesis, where food is synthesised.
There are two pathways for the Dark reaction:
C3 pathway or Calvin cycle
C4 pathway or Hatch-Slack pathway
In the C3 pathway, the first stable product of the carbon fixation is a three-carbon molecule like PGA (Phosphoglyceric acid) whereas, in the C4 pathway, it is a four-carbon molecule like OAA (Oxaloacetate).
C3 Pathway or Calvin Cycle:
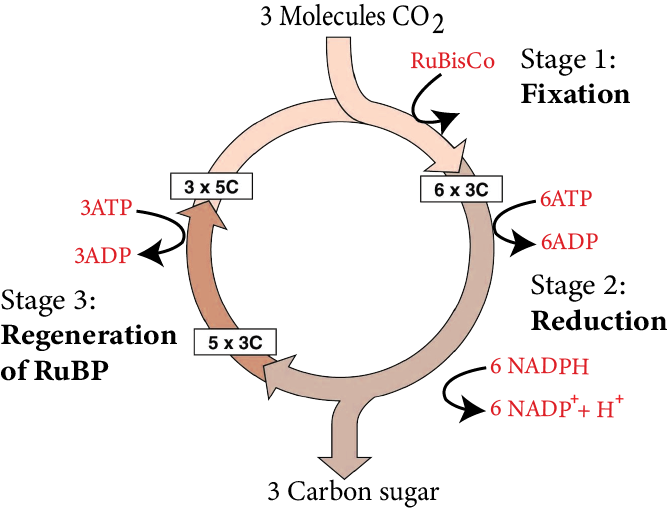
Calvin Cycle
Melvin Calvin found that the first molecule of carbon dioxide fixation was a three-carbon organic acid named 3-phosphoglyceric acid or PGA, hence the Calvin cycle.
The primary CO2 acceptor in this pathway or C3 plants is a 5-C-containing RuBP (ribulose bisphosphate) molecule that integrates with CO2 to generate sucrose.
Steps included in the Calvin Cycle
Carboxylation: In the availability of an enzyme known as RuBP carboxylase-oxygenase (RuBisCO), carbon dioxide is used for decarboxylation of RuBP, resulting in two molecules of 3-PGA. RuBisCO enzyme has an affinity for both carbon dioxide and oxygen.
Reduction: Carbon dioxide reduction requires two molecules of ATP for phosphorylation as well as two molecules of NADPH for reduction. Six carbon dioxide molecules must be fixed, as the cycle repeats six times.
Regeneration: To regenerate the carbon dioxide acceptor molecule RuBP, one ATP must be phosphorylated.
C4 or Hatch-Slack Pathway:
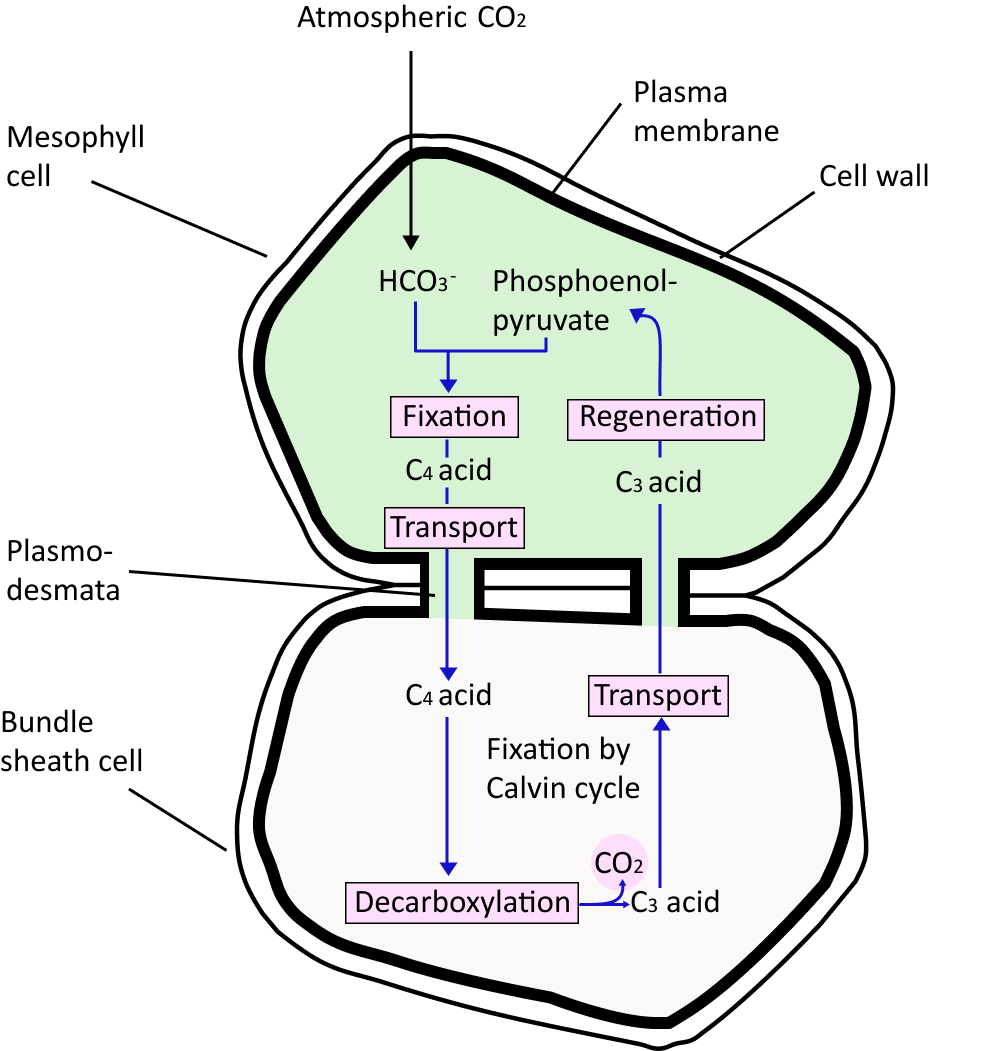
Hatch-Slack Pathway
The mesophyll cells and vascular bundles are the two types of cells found in the C4 plants.
Bundle sheath cells are large cells that surround vascular bundles, and the leaves of these plants have kranz anatomy.
Bundle sheath cells can have multiple layers of chloroplasts and are resistant to gaseous exchange.
The mesophyll cells contain the three-carbon molecule called phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP), which serves as the primary carbon dioxide acceptor.
The enzyme in charge is PEP carboxylase or PEP case, where the RuBisCO enzyme is missing.
C4 acid OAA is formed here, which is then transferred to bundle sheath cells where C4 acids are split to release carbon dioxide and a three-carbon molecule.
It is then shipped to mesophyll, where it constructs PEP once more, completing the cycle.
The carbon dioxide produced in the bundle sheath cells reaches the C3/ Calvin pathway, which is shared by all plants, C3 or C4.
The enzyme RuBisCO is abundant in the bundle sheath cells, but PEPcase is lacking. Carbon dioxide gas concentration rises as bundle sheath cells become impermeable to it.
Photorespiration:
RuBisCO, the most abundant enzyme on the planet, is distinguished by its ability to bind both O2 and CO2.
Some O2 binds with RuBisCO in C3 plants, leading to the formation of phosphoglycerate and phosphoglycolate via a pathway known as photorespiration.
Because there is no production of sugar or ATP/NADPH in this pathway, it is referred to as a wasteful process.
Photorespiration does not occur in C4 plants, so they are more productive.
Factors Influencing Photosynthesis:
The photosynthesis rate is affected by both internal and external factors.
Internal factors such as the number, size, age, alignment of leaves, chloroplasts, and so on, as well as external factors such as CO2 concentration, temperature, water, and so on.
When many factors affect any biological process, Blackman's (1905) Law of Limiting Factors comes into play, which states that if a chemical process is affected by more than one factor, the rate will be determined by the factor that is nearest to its minimal value, which is known as the Limiting factor.
If the amount is changed, the figure identifies the exact method.
Light
Light is being used as 10% of the incident sunlight.
It is directly proportional to CO2 fixation at low intensities. Other factors become confining as the intensity increases.
Excessive light causes the breakdown of chlorophyll, resulting in a decrease in photosynthesis.
Concentration of Carbon Dioxide
As carbon dioxide concentrations in the atmosphere are very low, ranging from 0.03 to 0.04 percent, an increase in concentration of up to 0.05 percent can cause an increase in photosynthesis rate.
Temperature
Because the dark reactions are enzymatic, they are temperature controlled. C4 plants react to higher temperatures and have higher photosynthesis rates, whereas C3 plants have a lower temperature optimum.
Water
Water stress leads to closing of stomata, reducing carbon dioxide accessibility, and causes leaves to wilt, thus reducing the surface area.
Key Points to Remember:
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants produce their own food.
Carbon dioxide from the environment is obtained by leaves via stomata and used to make carbohydrates, primarily glucose and starch, during this process.
Photosynthesis occurs only in the green parts of plants, primarily the leaves.
The mesophyll cells in the leaves contain a large number of chloroplasts, which are capable of CO2 fixation.
The light reaction happens within the chloroplasts, while the chemosynthetic process occurs in the stroma.
The light reaction and the reactions of carbon fixing are the two stages of photosynthesis.
Light energy is absorbed by the pigments in the antenna and channelled to special chlorophyll molecules known as reaction centre chlorophylls during the light reaction.
PSI and PSII are the two photosystems. PSI's reaction centre is a 700 nm trapping chlorophyll, a P700 molecule, whereas PSII reaction centre is a P680 that consumes red light at 680 nm.
After absorbing energy, electrons are emitted and relocated through PSII and PSI to NAD, where they combine to form NADH.
During this process, a proton gradient is formed across the thylakoid membrane.
The loss of the protons gradient caused by movement through the portion of the ATPase enzyme emits sufficient energy for ATP synthesis.
PSII is correlated with water molecule splitting, which leads to the release of O2, protons, and electron transfer to PSII.
CO2 is introduced by the enzyme RuBisCO to a 5-carbon compound RuBP, which is then converted into two molecules of 3-carbon PGA.
The Calvin cycle then converts this to sugar, and the RuBP is recharged.
ATP and NADPH produced during the light reaction are used in this process. RuBisCO also catalyses photorespiration, an inefficient oxygenation reaction in C3 plants.
Some tropical plants exhibit a type of photosynthesis known as the C4 pathway.
The first stable product of $C{O_2}$ fixation in the mesophyll in these plants is a 4-carbon compound.
The Calvin pathway is used in bundle sheath cells to synthesise carbohydrates.
NEET Biology Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Flashcards
Scientist / Concept | Contribution / Description |
Joseph Priestley | Discovered oxygen |
Conducted Bell jar experiment showing air restoration by plants | |
Jan Ingenhousz | Highlighted importance of sunlight and green parts in photosynthesis |
Julius von Sachs | Demonstrated production of glucose by plants and its storage as starch |
T.W Engelmann | Identified action spectrum of photosynthesis |
Showed maximum absorption in blue and red light | |
Experimented with green alga Cladophora | |
Cornelius van Niel | Proved oxygen evolution from water splitting, not from CO2 |
Conducted experiments on purple and green sulfur bacteria | |
Light Reaction | Occurs in chloroplast membrane system (grana thylakoids and stroma lamellae) |
Light energy trapped, water photolysis, oxygen and ATP/NADPH produced | |
Dark Reaction | Occurs in stroma matrix |
Biosynthetic phase of sugar synthesis | |
Utilizes ATP and NADPH from light reaction | |
Light Harvesting Complex (LHC) | Hundreds of pigments forming antennae |
Increase efficiency by absorbing different light wavelengths | |
PSI (Photosystem I) | Reaction center: Chlorophyll ‘a’ P700 |
Primary electron acceptor: Fe-S protein | |
PSII (Photosystem II) | Reaction center: Chlorophyll ‘a’ P680 |
Primary electron acceptor: pheophytin | |
Noncyclic Photophosphorylation | Z-scheme, occurs in grana thylakoid |
PSII followed by PSI in series | |
Phosphorylation of ADP to ATP, reduction of NADP to NADPH + H+, O2 release | |
Cyclic Photophosphorylation | Occurs only in PSI |
In stroma lamellae, lacks PSII and NADP reductase | |
Phosphorylation of ADP to ATP | |
Chemiosmotic Hypothesis | Proposed by Peter Mitchell |
ATP synthesis coupled with proton gradient development | |
Across the membrane | |
Oxidative Phosphorylation | Occurs in mitochondria |
Photophosphorylation | Occurs in chloroplast |
Thylakoid lumen: low pH, high H+ due to water splitting | |
NADP reductase in stroma utilizes protons and electrons | |
To reduce NADP+ | |
ATP Synthase: CF0 (transmembrane proton channel), CF1 (ATP synthesis) | |
C3 Pathway | Described by Melvin Calvin |
First CO2 fixation product: 3PGA (3-phosphoglyceric acid) | |
Occurs in all photosynthetic plants (C3, C4, CAM) | |
Calvin Cycle Reactions | Carboxylation of RuBP to 3PGA |
Reduction of 3PGA to triose phosphate using ATP and NADPH | |
Regeneration of RuBP | |
RuBP (Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate) | CO2 acceptor in C3 cycle |
Catalyzed by enzyme RuBisCO | |
Involves carboxylation and oxygenation reactions (photorespiration) | |
C3 Cycle Utilization | Six rounds produce a glucose molecule using |
6 CO2, 18 ATP, and 12 NADPH | |
C4 Pathway | Described by Hatch Slack Pathway |
First CO2 fixation product: OAA (oxaloacetate) | |
Primary CO2 acceptor: PEP (phosphoenolpyruvate) | |
Occurs in plants with Kranz anatomy (e.g., maize, sorghum) | |
C4 Cycle Reactions | Mesophyll cells: CO2 fixation by carboxylation of PEP to form OAA |
Bundle sheath cells: Decarboxylation of OAA to release CO2 for Calvin cycle | |
Photorespiration | RuBP oxidation yields PGA and Phosphoglycolate, releasing CO2 |
Competes with Calvin cycle in C3 plants, wastes energy | |
Law of Limiting Factors | Formulated by Blackman |
Temperature affects photosynthesis | |
C3 and temperate plants have low optimum temperature | |
C4 and tropical plants have high optimum temperature | |
CO2 level affects photosynthesis positively at high light intensity | |
C4 plants have a lower saturation level than C3 |
Importance of NEET Class 11 Photosynthesis in Higher Plants
Photosynthesis can be coined as the most important biochemical reaction occurring in the leaves of plants that provide the prime source of energy to different ecosystems. It ensures the survival of a food chain. Plants are the producers of food and the consumers depend on them.
In this chapter, the biochemical process of photosynthesis taking place in different steps will be explained. All the steps have been explained with proper chemical equations. The scientific derivation of all these steps will guide students to understand the mechanism of the entire process in detail.
This chapter will also explain the background of discovering the mechanism of this reaction. The pictorial representation of this process will explain how and where such chemical reactions take place in the leaves. The Photosynthesis in Higher Plants notes for NEET will help you understand the scientific principles of this botanical biochemical reaction perfectly.
This chapter holds immense importance in the NEET Biology syllabus as it explains one of the most important life reactions occurring in nature. It explains how majestically a plant can trap solar energy and convert simple molecules like carbon dioxide and water into glucose, the main respiratory substrate used by animals to survive.
Benefits of Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Notes for NEET
These revision notes will offer the easiest explanation of this complex biochemical reaction occurring in the leaves of plants. Every step will be explained using a proper and concise explanation. The reactions will also have definite equations so that you can understand the reactants, products, and catalysts/enzymes used in every step.
The concise format of the notes will also enable you to focus on the fundamental principles and concepts related to this reaction. Rest assured that referring to these notes before an exam will reduce your preparation time considerably. After you have completed studying this chapter, Photosynthesis in Higher Plants notes will be the ideal study material to revise.
The easier format will also enable you to recall the concepts faster and accurately. It means you will not have to waste time in remembering the concepts while answering fundamental questions asked in NEET. You will be able to score better in this competitive exam.
Download Free Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Notes PDF
It is now easy to get the free version of these notes in PDF format. Download the notes today and refer to them at your convenience. You will now be able to resolve your queries without any hassle using Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Class 11 notes NEET at home. Clarify your doubts and understand all the concepts related to photosynthesis, pigments, reactions, etc. better.
NEET Biology Revision Notes - Chapter Pages
NEET Biology Chapter-wise Revision Notes | |
Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Notes | |
Other Important Links for NEET Biology Notes
Other Important Links for NEET Biology Revision Notes |
NEET Biology Important Chapter - Photosynthesis in Higher Plants |
Conclusion
Understanding photosynthesis in higher plants is crucial for NEET Biology. Focus on grasping the process of converting light energy into chemical energy, primarily occurring in chloroplasts. Key components include the light-dependent and light-independent reactions, where water and carbon dioxide are converted into oxygen and glucose. Pay close attention to factors affecting photosynthesis like light intensity, temperature, and carbon dioxide concentration. Memorize key molecules involved such as chlorophyll, ATP, and NADPH. Additionally, understand the significance of photosynthesis in sustaining life on Earth and its interconnectedness with other biological processes. Regular revision and practice questions will solidify comprehension.
FAQs on NEET Biology Photosynthesis in Higher Plants Class 11 Notes
1. Which pigment traps solar energy in plants?
Chlorophyll A, B, C, and D are the green pigments that trap the solar energy in the sunrays.
2. Which gas is required for photosynthesis to synthesise glucose?
Plants need carbon dioxide to synthesise glucose in their leaves.
3. Which gas is the by-product of photosynthesis?
Oxygen is the by-product of photosynthesis. It is produced due to the breakdown of water molecules during the chemical reactions of photosynthesis.
4. What are photosynthetic pigments?
The biochemical substances that can trap solar energy emitting from the sun and convert it into energy to use for promoting various biochemical reactions are called photosynthetic pigments.
5. What is the important note of photosynthesis in higher plants?
Higher plants perform photosynthesis in specialized organelles called chloroplasts. These chloroplasts contain chlorophyll pigments that trap sunlight to fuel the process. This light-driven conversion of carbon dioxide and water into organic molecules (primarily glucose) is the foundation of most life on Earth, as plants provide the base of the food chain for most ecosystems.
6. What are the important points of photosynthesis in plants?
Light Dependent Reactions (Light Phase): Capture light energy and convert it into ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADPH (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate).
Light Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle): Use the energy from ATP and NADPH to fix carbon dioxide into organic molecules (sugars).
Location: Occurs primarily in the mesophyll cells of leaves.
Gas Exchange: Takes in carbon dioxide (CO2) and releases oxygen (O2).
7. Which plant has a high rate of photosynthesis?
Plants with C4 photosynthetic pathways, like corn and sugarcane, generally have higher rates of photosynthesis compared to plants with C3 pathways like most trees. C4 plants have a more efficient way to capture CO2, which can be limiting in hot and dry environments.
8. Where are ATP and NADPH used?
ATP: Provides energy for the Calvin Cycle to fix carbon dioxide into organic molecules.
NADPH: Supplies electrons and hydrogen ions for the Calvin Cycle to convert CO2 into sugars.
9. Can photosynthesis occur without sunlight?
No, sunlight is essential for photosynthesis. Light energy provides the power to drive the light-dependent reactions that generate ATP and NADPH, which are necessary for the Calvin Cycle to fix carbon dioxide.
























