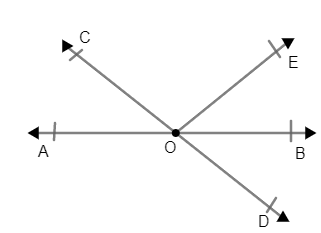
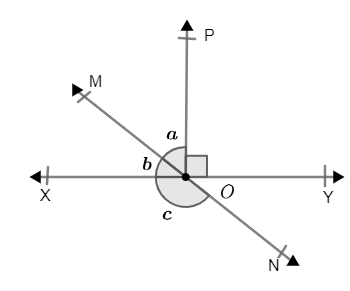
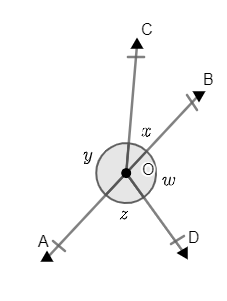
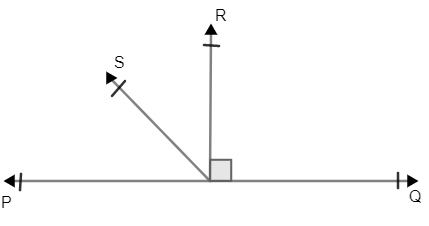
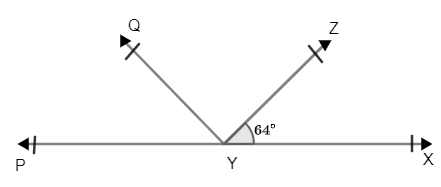
Solved answers for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines and Angles Exercise 6.1: FREE PDF download
NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines And Angles Exercise 6.1 - 2025-26
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Lines And Angles Exercise 6.1 - 2025-26
1. Are answers for Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 available exercise-wise?
2. Do Exercise 6.1 Class 9 Maths solutions match the NCERT answer format?
2. Do Exercise 6.1 Class 9 Maths solutions match the NCERT answer format?
Yes, Exercise 6.1 Class 9 Maths solutions on Vedantu match the NCERT-prescribed answer format used in school exams.
3. Is Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 fully covered in NCERT solutions?
Yes, Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 is fully covered on Vedantu, and no NCERT question is skipped.
4. Can students check Exercise 6.1 Class 9 Maths answers online?
Yes, students can check Exercise 6.1 Class 9 Maths answers online on Vedantu without downloading the textbook.
5. Are Class 9 Maths Lines and Angles Exercise 6.1 solutions useful before tests?
Yes, Class 9 Maths Lines and Angles Exercise 6.1 solutions on Vedantu are useful before tests because they follow exam-oriented presentation.
6. Do the Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 solutions use simple language?
Yes, the Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 solutions on Vedantu use simple and student-friendly language.
7. Are Exercise 6.1 Class 9 Maths solutions suitable for written practice?
Yes, Exercise 6.1 Class 9 Maths solutions on Vedantu are suitable for written practice in notebooks.
8. Can Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 solutions be used by private candidates?
Yes, private candidates following the NCERT syllabus can use Class 9 Maths Chapter 6 Exercise 6.1 solutions available on Vedantu.
9. Do NCERT Solutions for Exercise 6.1 Class 9 Maths follow the textbook question order?
Yes, NCERT Solutions for Exercise 6.1 Class 9 Maths on Vedantu follow the same question order as the NCERT book.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video