NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 13: Light - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 16 Light - 2025-26
1. Mention which one of them will have a diffused reflection when exposed to strikes.
Polished table
Cardboard Surface
Mirror
Marble flooring
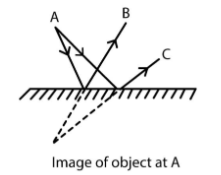
Reflection occurs only in the places that have plane surfaces and polished or even surfaces. Therefore, the mirror, marble flooring, and polished table will have reflections.
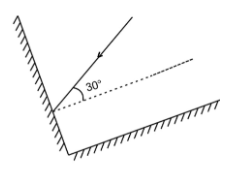
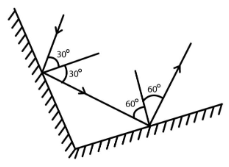
2. What are the Laws of Reflection?
The laws of reflection are stated below:
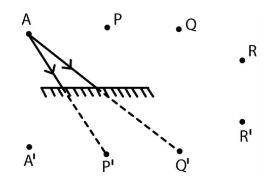
The incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal ray all will lie in the same place.
The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
3. What are the topics covered under NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 13?
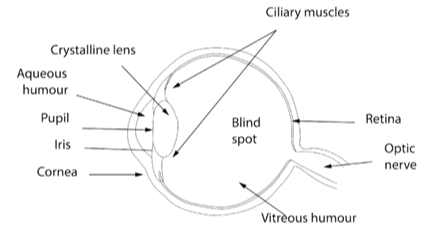
Under Chapter 13 of Class 8 Science, several topics have been covered. These are all based on a basic understanding of Light. Questions like what makes things visible are discussed. On a more technical note, the laws of reflection are discussed along with regular and diffused reflection. The concept of multiple images is explained in simple terms. A basic layout of the structure of the eye is also given. To know more, visit the page NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science.
4. What is the Braille system as discussed in the chapter?
The Braille system is defined as a helpful resource for visually challenged people that allows them to read and write. The system as it is presently used was adopted in the year 1932. There is unique Braille code that is different for common languages, for mathematics and for scientific notation. Many Indian languages can also be read by blind people by using the Braille system.
5. What is white light Class 8 in short answer?
White light is a combination of all the colours of the visible spectrum. When white light passes through a prism, it splits into its component colours, creating a spectrum of colours ranging from red to violet. This phenomenon is called dispersion.
6. How is reflected light useful?
Objects either radiate light of their own or they reflect it. Most objects simply reflect light. Nearly everything we see around us is visible solely due to reflected light. Even celestial bodies like the moon simply reflect the light of the sun, which is a luminous body that creates its own light source. For further clarity on this concept or to download NCERT solutions for free, visit the page NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science on the Vedantu website or download the Vedantu app.
7. What are the benefits of using the NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 13?
Using Vedantu's NCERT Class 8 Science Chapter 13 Solutions helps acquaint students with the kind of questions that are important from the examination point of view. It also helps them identify weak points and topics that they might need to work more on. Practicing these questions regularly can yield great results and help students ace their school examinations. Visit the above page to access these solutions.
8. What is a mirror in Class 8 Light?
A mirror is a smooth and highly reflective surface that can reflect light rays. Mirrors are commonly made of glass coated with a thin layer of metal, such as silver or aluminium, which reflects light efficiently. They are used to produce images by reflecting light rays, enabling us to see ourselves or objects placed in front of them. Mirrors can be flat or curved, playing a crucial role in various optical devices, such as telescopes, microscopes, and cameras.