Science Notes for Chapter 2 Microorganisms: Friend and Foe Class 8 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 8 Science Chapter 2 - Microorganisms: Friend and Foe - 2025-26
1. How can I quickly revise the main types of microorganisms mentioned in Chapter 2?
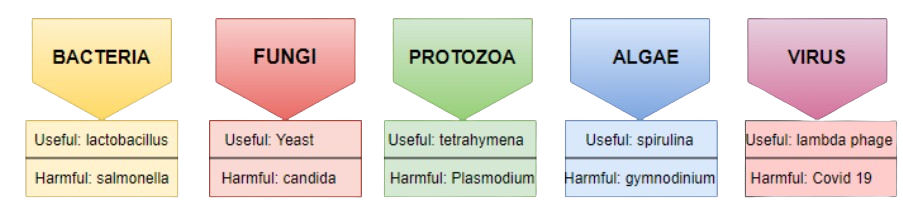
For a quick recap, remember the five major groups: Bacteria (single-celled organisms), Fungi (like yeast and mould), Protozoa (like Amoeba and Paramecium), Algae (like Chlamydomonas and Spirogyra), and Viruses. Viruses are unique as they are on the borderline of living and non-living.
2. What are the most important friendly uses of microorganisms to remember for exams?
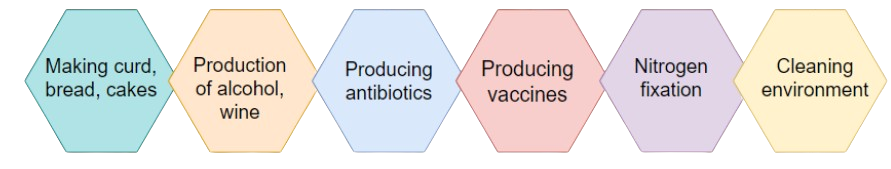
When revising, focus on these key points:
- Making food: Bacteria like Lactobacillus help make curd. Yeast is used for baking bread and cakes.
- Commercial use: Microorganisms are used for large-scale production of alcohol, wine, and acetic acid.
- Medicinal use: Antibiotics like penicillin are produced from fungi and bacteria to fight diseases. Vaccines also use weakened microbes to build immunity.
- Environmental cleaning: Decomposers break down dead organic waste, cleaning the environment.
- Increasing soil fertility: Some bacteria and blue-green algae fix atmospheric nitrogen to enrich the soil.
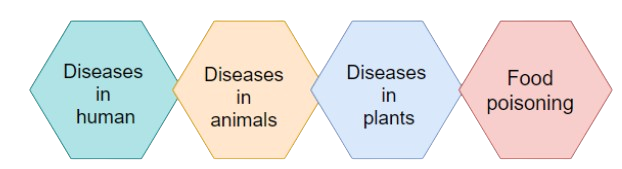
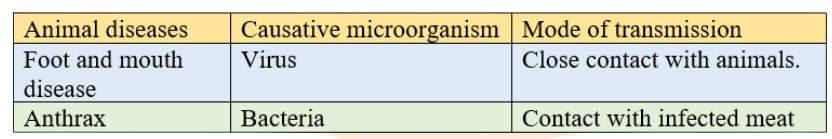
3. What are the key harmful effects of microorganisms covered in this chapter?
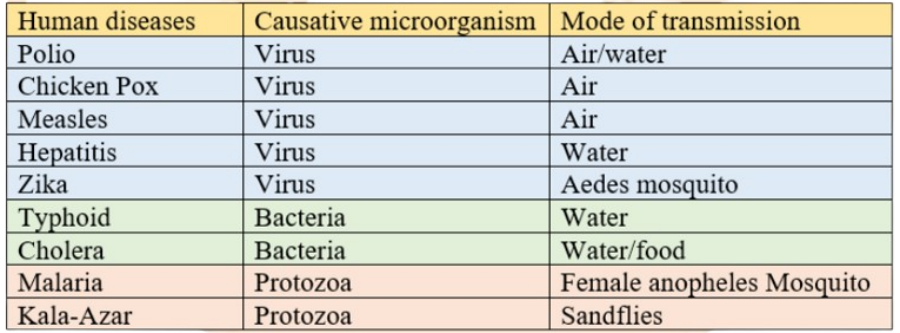
The main harmful effects to summarize are from pathogens, which are disease-causing microbes. They can cause diseases in humans (like cholera, typhoid, malaria), animals, and plants (like citrus canker). Some microorganisms also cause food poisoning by spoiling food.
4. Why are viruses so different from other microorganisms like bacteria?
This is a key concept for revision. Viruses are different because they only show characteristics of living things when they are inside the cells of a host organism (like a plant, animal, or bacterium). Outside a host cell, they are non-living and cannot reproduce. Bacteria, on the other hand, are true cells that can live and reproduce on their own in the right environment.
5. For a quick summary, how do common food preservation methods work against microbes?
Food preservation methods create conditions that stop or slow down microbial growth. For revision, remember:
- Chemical Methods: Adding salt, sugar, or preservatives like sodium benzoate prevents microbial growth.
- Heat Treatment (Pasteurisation): Heating milk to about 70°C for 15-30 seconds and then suddenly chilling it kills most bacteria.
- Cooling: Refrigeration slows down the growth of microbes.
- Drying: Removing water from food items stops microbes from growing.
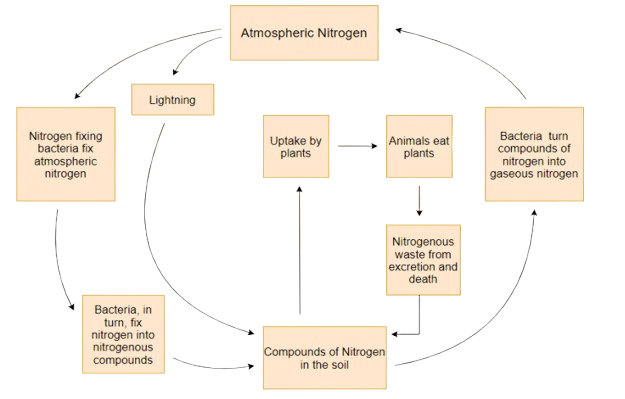
6. How does the nitrogen cycle connect microorganisms to plants and animals?
The nitrogen cycle is a perfect example of how microbes act as friends. In simple terms, plants cannot use the nitrogen gas from the air. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria and blue-green algae convert this unusable gas into usable nitrogen compounds in the soil. Plants absorb these compounds to grow, and then animals get nitrogen by eating the plants. It's a vital link in the chain of life, all thanks to microbes.
7. What is the main idea behind calling microorganisms both a 'Friend and Foe'?
This is the central theme of the chapter. They are 'friends' because many are essential for life, helping in food production, making medicines, and cleaning the environment. They are 'foes' because some cause dangerous diseases in humans, animals, and plants, and spoil our food. Understanding this dual role is key to revising the chapter effectively.
8. What is the difference between an antibiotic and a vaccine for revision?
It's important not to confuse them. An antibiotic is a medicine (like penicillin) that kills or stops the growth of disease-causing bacteria *after* you are sick. A vaccine contains weakened or dead microbes that are introduced into the body to train your immune system to fight a specific disease *before* you get it, thus preventing future infection.