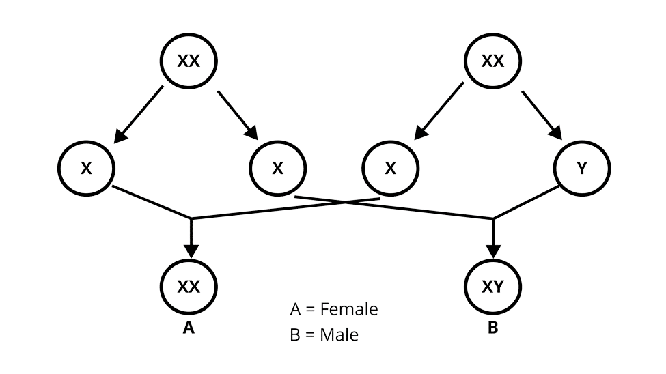
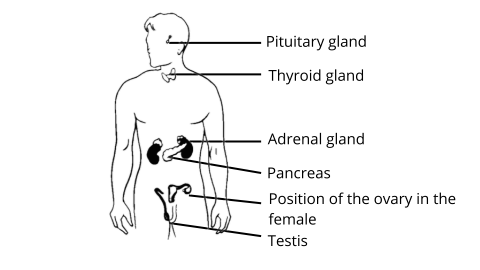
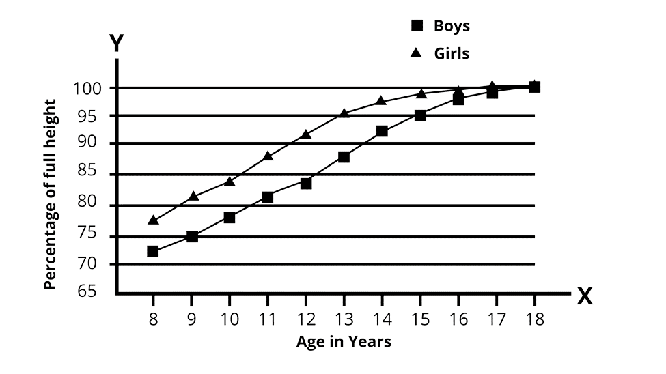
Class 8 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence
1. What are some of the important topics mentioned in the NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence?
Some of the important topics that are mentioned in the NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence can be provided as follows:
1. Introduction to Adolescence and Puberty:
The period of life in which the body tends to undergo a number of changes that are visible and lead to reproductive maturity is termed as adolescence.
It is strictly advised to avoid the usage of drugs.
The beginning of adolescence is the onset of puberty in humans.
It starts at around 11 years of age and goes up to 18 years of age.
2. Secondary sexual characters developed:
Developmenet of breasts in girls and developement of facial hair in boys are some of the secondary sexual changes observed.
In females, menstruation occurs during this phase and goes up to 45 to 0 years of age.
Other hormones are also secreted by several glands, such as thyroxine insulin, growth hormones, adrenaline, etc.
3. Changes observed at Puberty:
Body shape changes in girls as the waist area gets wider, and in boys, the shoulders get broadened.
Voice change is observed in both boys and girls, where boys have a growth of Adam's apple and girls have a high pitched voice.
2. Why use the NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence by Vedantu in order to solve the questions?
The following features make it convenient to use the NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence via Vedantu for solving the questions:
The experts at Vedantu have solved all the questions that are mentioned in the NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence, hence providing a detailed answer format.
The solutions that are provided in the NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence are simple and easy to understand.
There is comprehensive assistance provided for each of the questions that are mentioned in the NCERT Exemplar Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 10 Reaching the Age of Adolescence, hence providing an interactive way of learning.
3. Is the content of Vedantu's notes the same as in the NCERT textbooks?
Yes, the content of the notes is identical to those of the NCERT textbooks. The notes are written in the style of a simplified and easy-to-understand textbook. Experts develop Vedantu notes after conducting considerable study. These notes will assist students in grasping all of the chapter's complicated and basic themes. If students don't have time to study the complete textbook during examinations, they can use these notes to revise faster and save time. The Vedantu app may also be used to access the notes.