Class 8 Science NCERT Exemplar Solutions Chapter 2 Microorganisms : Friend and Foe
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 8 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Microorganisms : Friend and Foe
1. What is the Nitrogen Cycle according to Chapter 2 of Class 8 Science?
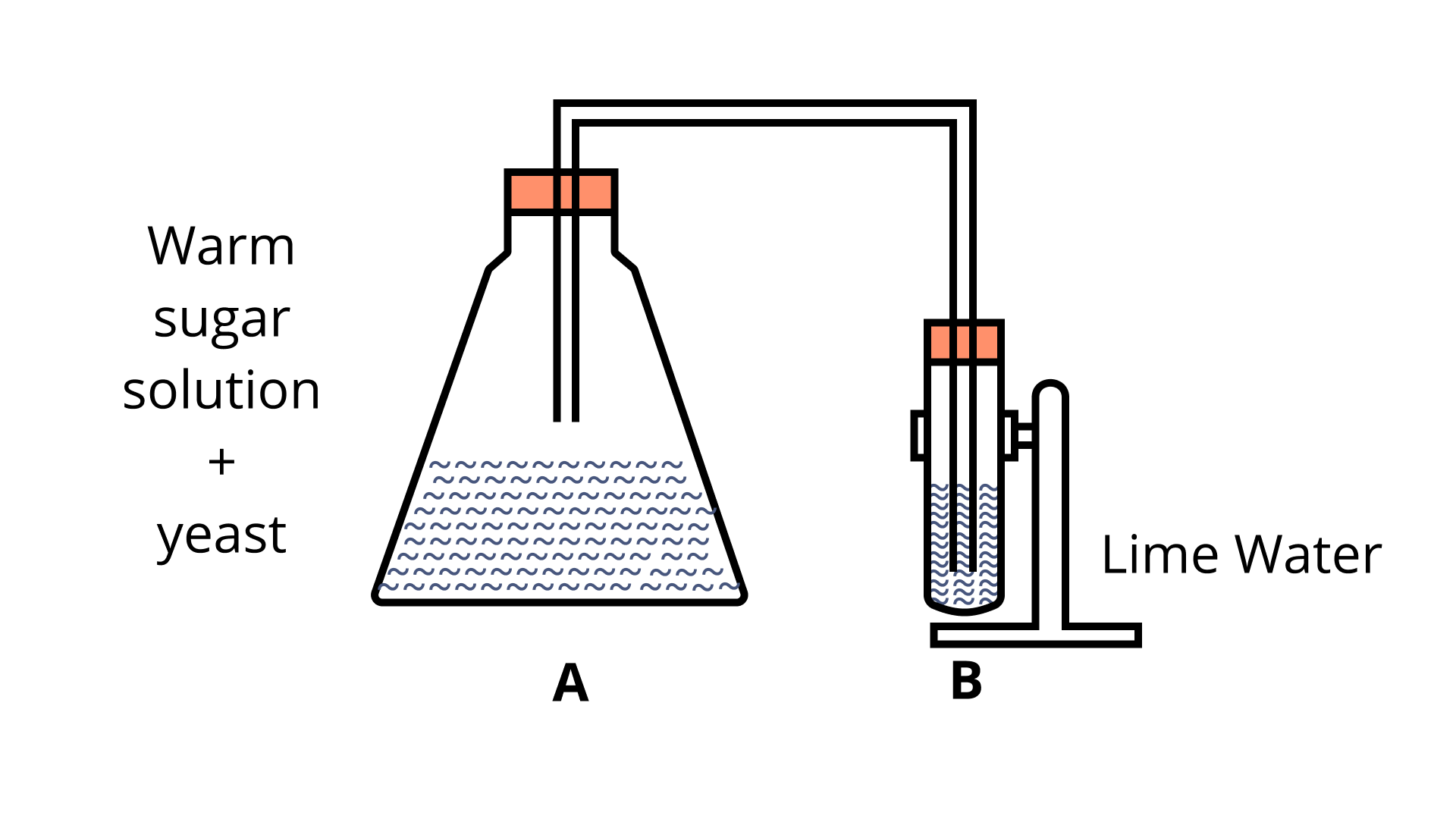
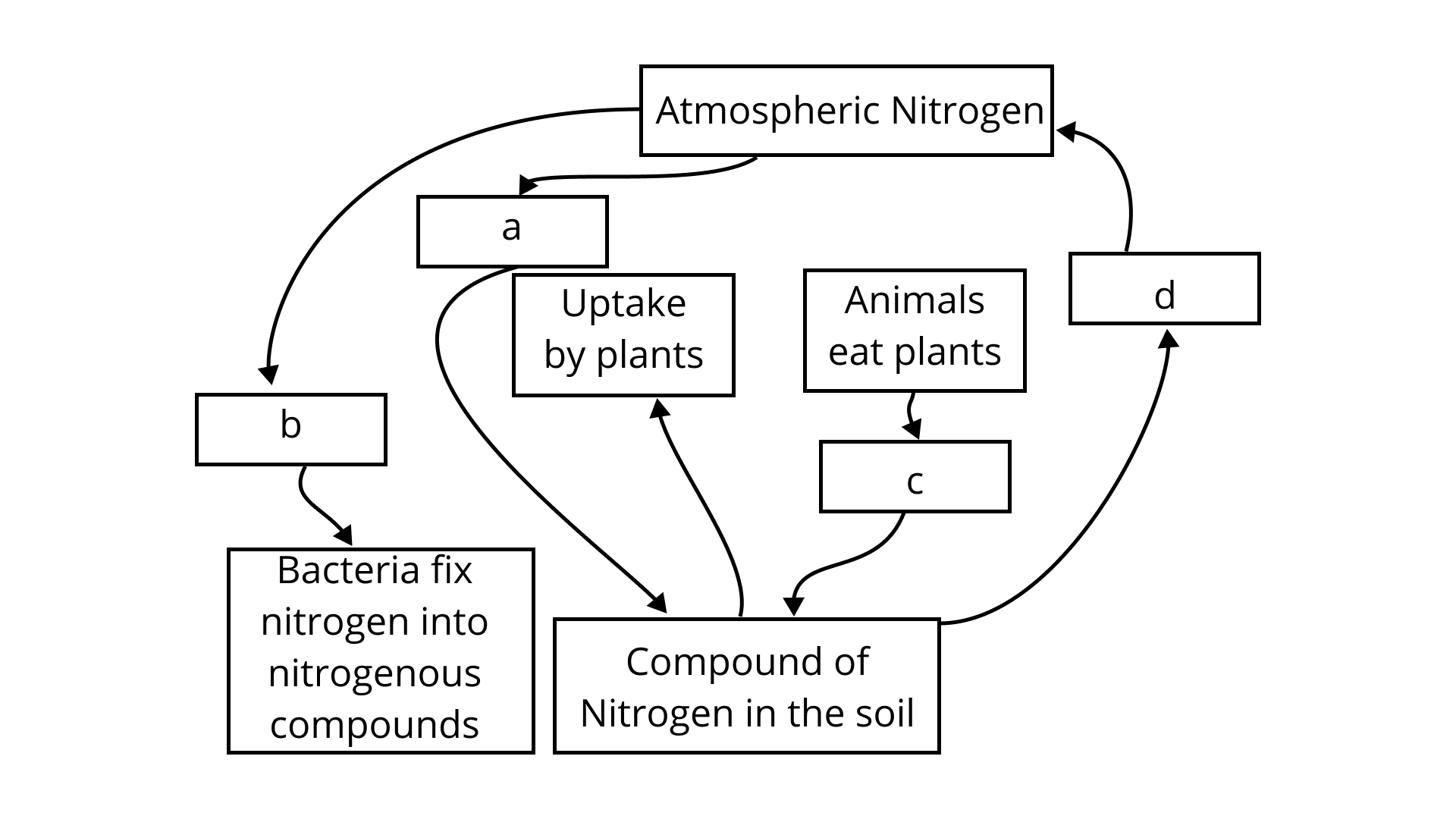
The nitrogen cycle is a biological process that involves nitrogen moving from the atmosphere to the soil, organisms, and ultimately to the atmosphere again. Plants and animals cannot directly utilize nitrogen that is present in the atmosphere. Some microorganisms in the soil must convert this nitrogen to nitrogenous chemicals. The plants consume this transformed form of nitrogen, and the animals that eat them get it. Fungi and bacteria in the soil transform nitrogen from dead plants and animals into gaseous or compound forms that the plants may utilize. As a result, the nitrogen equilibrium in the atmosphere is maintained.
2. How can we prevent food from contamination?
It is critical to use correct food preservation procedures to avoid food contamination. Food may be preserved by decreasing the oxidation of other molecules and blocking the development of germs on it. Cooked food, as well as whole food grains, have distinct storage and preservation requirements. Microbes are attracted to cooked food because they require moisture to reproduce, and whole food is often devoid of moisture. This is why bacteria attack bread that has been left unattended in damp circumstances. Apart from apparent changes, infected food has a foul odor and a different flavor than usual.
3. How do vaccines work in Chapter 2 of NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 8 Science?
Whenever these disease-carrying bacteria infiltrate our bodies, antibodies are produced to combat the intruder. If the microorganism enters again, the body remembers how to combat it. When dead or weakened germs are put into a healthy body, the host produces antibodies that fight and kill the invading bacteria. Antibodies stay in the body indefinitely, protecting humans from disease-causing microorganisms. Students may also use Vedantu to get NCERT Exemplar Solutions to understand better the crucial concepts in the CBSE Class 8 syllabus. Free resources available on Vedantu for students to access for free. These include chapter wise solutions, syllabus and everything else you may require to ace your exams!
4. What are Microbes?
Microbes, often known as microorganisms, are microscopic creatures that cannot be seen with the naked eye. Some microbes may be observed using a magnifying glass, while others need the use of a microscope. Anton Van Leeuwenhoek was the first to notice microorganisms. Diseases caused by viruses, bacteria, and protozoa. Microbes can thrive in various conditions, including freezing temperatures, hot springs, deserts, and marshy plains. Some survive on their own, while others dwell inside the bodies of other species as parasites.
5. What are the four types of microorganisms?
Microorganisms are divided into four categories:
Single-celled creatures with a rigid cell wall are known as bacteria. Only a microscope capable of magnifying pictures by 100 to 1000 times can view them.'
Fungi are non-green plants that cannot produce sustenance. They either exist as parasites (feeding on host organisms, such as Puccinia, which causes wheat leaf rust), or they grow on organic debris (such as bread mould)
Algae are elemental plant-like creatures that are typically found in water. They have a cell wall and chlorophyll and can photosynthesize; some examples can be either single-celled or multicellular. Diatoms, Chlamydomonas, and seaweed are some of the most prevalent examples.
Protozoa are creatures with only one cell. Some of them are self-sufficient, while others are parasites. Many parasitic protozoans infect plants, domestic animals, and humans, causing illness.