NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chemical Effects of Electric Current- Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 14 Chemical Effects Of Electric Current - 2025-26
1. What does this Chapter Summarise Students About?
In this chapter, students will learn that specific liquids are excellent conductors of electricity while some aren’t. Additionally, most liquids that do conduct electricity are mixtures of acids, bases, and salts. Along with this, you will understand that the path of an electric current through conducting liquid produces chemical effects. Lastly, you’ll learn about electroplating- it is the methodology of depositing a layer of any respective metal on another object through electricity.
2. How is Vedantu’s Class 8 Science NCERT Chapter 11 Solutions Advantageous for Preparing for Your Exams?
Vedantu is a leading website that offers students key insights on how they can prepare for their exams. Now get premium access to Class 8 Science NCERT Chapter 14 free of cost and gain knowledge on electricity and different concepts of electricity. The study material offered by Vedantu will help students create a strong foundation for their academics, thereby helping them learn how they can use knowledge about what they’ve learned so far correctly. Additionally, students will also learn distinguishing skills to get clarity on concepts like electroplating.
3. What are the three chemical effects of electric current?
Chemical effects of electric current include permanent changes that cannot be reversed. Upon passing current through a solution, gases may be evolved at electrodes. Deposits of metal may also be seen along with a change in the colour of the solution. These are the three main chemical effects of electric current. You can refer to Vedantu Class 8 NCERT Chapter 11 Solutions to get more clarity on the topic.
4. What is the chemical effect of electricity? Give some examples of chemical effects?
Chemical effects of electricity are seen when an electric current is passed through a conducting liquid solution. The changes seen are permanent and irreversible. Gas evolution at anodes and cathodes, visual changes like a shift in the colour of the solution and deposition of metal are also seen. These are all examples of the various chemical effects of electricity.
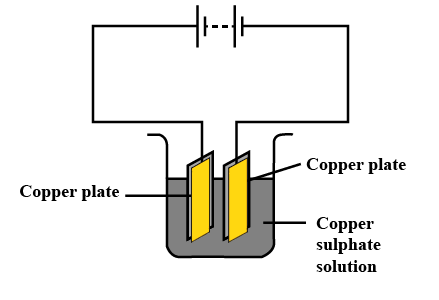
5. What is Electroplating?
Electroplating is one of the real-time applications of the chemical effects of electricity. It is a process in which a layer of a desirable metal is deposited atop another material. The deposited metal generally has some attributes that the original metal lacks and could benefit from. For example, chromium plating is done on many household objects such as bath taps and kitchen gas burners. This is simply because chromium does not corrode and resists scratches.
6. Why is iron coated with zinc?
The process of coating iron with a layer of zinc is termed galvanization. Iron is used for construction purposes because it is a very sturdy and strong metal. However, iron tends to corrode and rusts on exposure to air and moisture due to the formation of hydrated ferric oxide. This is why a coating of zinc is deposited on iron to protect it from corrosion and inhibit the formation of rust.
7. What are good and bad conductors?
Some materials allow for the passage of electricity quite easily while other materials resist its flow. It is recommended to classify materials as good conductors and poor conductors instead of classifying them as insulators and conductors as most materials can conduct under certain conditions. Check out Vedantu's Class 8 Science Chapter 11 Solutions to download NCERT solutions for free of cost from the Vedantu website. You can also download the Vedantu app to access these solutions for free.
8. What are the main topics are covered in NCERT Solutions for Chapter 11 Chemical Effects Of Electric Current Class 8?
Vedantu’s Class 8 Chemical Effects Of Electric Current Questions And Answers cover topics such as electrolysis, electroplating, chemical changes due to electric current, and their applications.
9. How do the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 11 help in understanding the practical applications of chemical effects of electric current?
The NCERT Solutions for Chapter 11 not only explain theoretical concepts but also illustrate practical applications of the chemical effects of electric current, such as electrolysis and electroplating. By providing real-life examples and detailed processes, the solutions help students understand how these concepts are applied in various industries and everyday life. This practical understanding enhances their learning experience and prepares them for higher-level science courses.