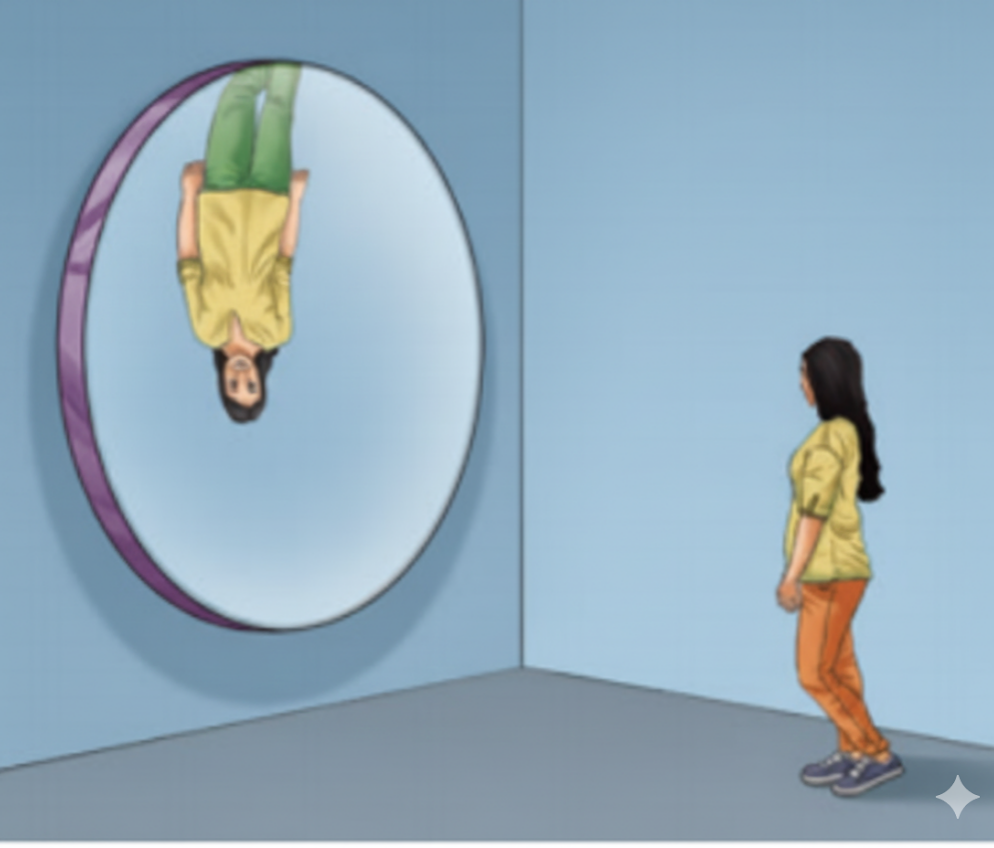
How to Answer Light: Mirrors and Lenses Questions for Full Marks
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 8 Science Chapter 10 Light Mirrors And Lenses - 2025-26
1. What are NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 10: Light: Mirrors and Lenses?
NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 10 provide step-by-step answers, definitions, and diagrams for all textbook exercises related to Light: Mirrors and Lenses. Key features include:
- Chapter 10 question answers covering intext and back exercises
- Important diagrams for mirrors and lenses
- Clear and concise definitions and formulae
- Exam-aligned answers for CBSE Class 8 Science 2025-26
- Free PDF download for offline revision
2. How can I write stepwise NCERT answers for Class 8 Science Chapter 10 to score full marks?
To score full marks in Chapter 10 of Class 8 Science, present your NCERT answers in clear, stepwise points:
- Begin with a direct answer to the question
- Include key definitions and formulae when required
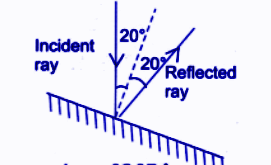
- Draw neat labelled diagrams for mirrors/lenses as needed
- Underline or highlight important terms
- Number steps if the answer has a process
3. Are diagrams or definitions mandatory in answers for Light: Mirrors and Lenses?
Yes, diagrams and definitions are essential in answers for Chapter 10 Light: Mirrors and Lenses. To score well:
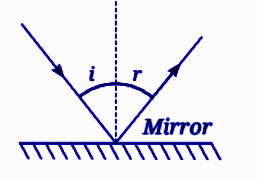
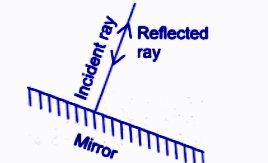
- Always add labelled diagrams of mirrors, lenses, and ray diagrams when asked
- Write precise definitions for key terms like 'concave', 'convex', 'real image', etc.
- Use correct conventions (arrows, labels) in the diagrams for full marks
4. Which topics and questions are most important from Class 8 Science Chapter 10 for CBSE exams?
The most important topics from Chapter 10 Light: Mirrors and Lenses include:
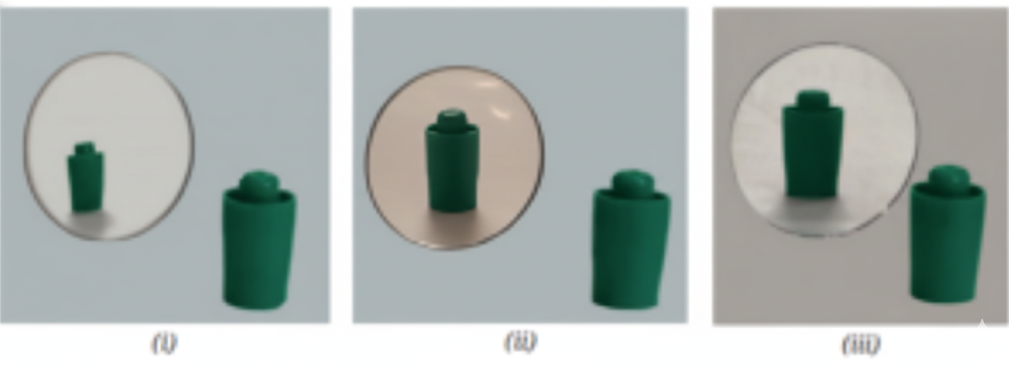
- Types of mirrors and lenses
- Ray diagrams for formation of images
- Uses of concave and convex mirrors/lenses
- Definitions (real & virtual image, principal axis, focal length)
- Differentiating between real and virtual images
5. How do I prepare and label diagrams for Class 8 Science Light Mirrors and Lenses?
To draw and label diagrams correctly in Chapter 10:
- Use sharp pencils and a ruler for straight lines
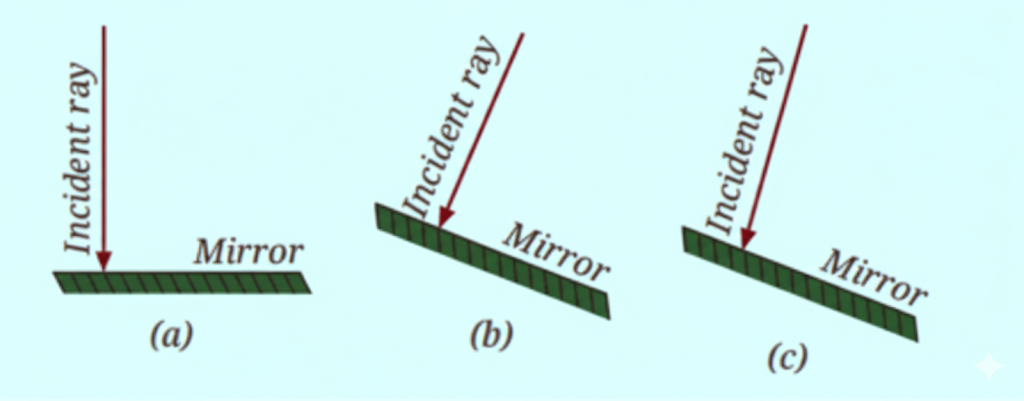
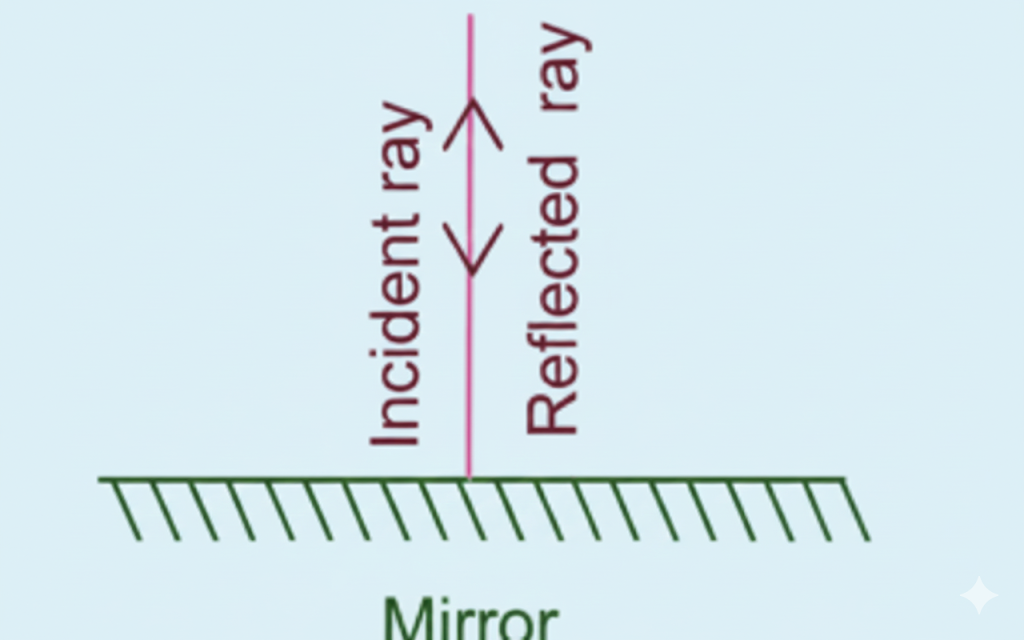
- Draw principal axis, mirror/lens, focal points (F, 2F)
- Label incident ray, reflected/refracted ray, object, and image clearly
- Keep the diagram neat and uncluttered
- Practice the standard diagrams given in NCERT and worksheets for accurate labelling
6. Where can I download the NCERT Solutions PDF for Class 8 Science Chapter 10?
You can download the NCERT Solutions PDF for Class 8 Science Chapter 10: Light: Mirrors and Lenses free from trusted educational websites. This helps you study offline, revise stepwise answers, and practice diagram questions easily for CBSE 2025-26 exams.
7. What is the best way to revise Class 8 Science Chapter 10: Light Mirrors and Lenses before an exam?
The best revision strategy for Chapter 10 includes:
- Reviewing key definitions and important formulae
- Practicing all standard diagrams (mirrors, lenses, images)
- Solving intext and back exercise questions stepwise
- Attempting extra questions and MCQs for better practice
- Using a 1-day or 3-day quick revision plan before exams
8. Do examiners award partial marks for correct steps if the final answer is wrong in CBSE Science exams?
Yes, partial marks are often awarded in CBSE Science exams if you show correct steps or logic, even if the final answer is incorrect. To maximize step marks:
- Write clear intermediate steps and process
- Use correct scientific terms and diagram conventions
- Attempt every part of the question, even if unsure of the last step
9. How should long answers in Class 8 Science Chapter 10 be structured to match the CBSE marking scheme?
For long answers in Chapter 10, follow these guidelines:
- Start with an introduction or definition
- Break the answer into clear sub-points or steps
- Include labelled diagrams where relevant
- Conclude with a summary or application
- Highlight key words and main concepts
10. Are NCERT Solutions alone enough for scoring well in Class 8 Science Chapter 10?
NCERT Solutions provide a strong foundation for scoring well in Chapter 10, but for top marks:
- Practice extra questions and worksheets for Light: Mirrors and Lenses
- Revise exemplar problems and previous year questions
- Review diagrams and short notes regularly