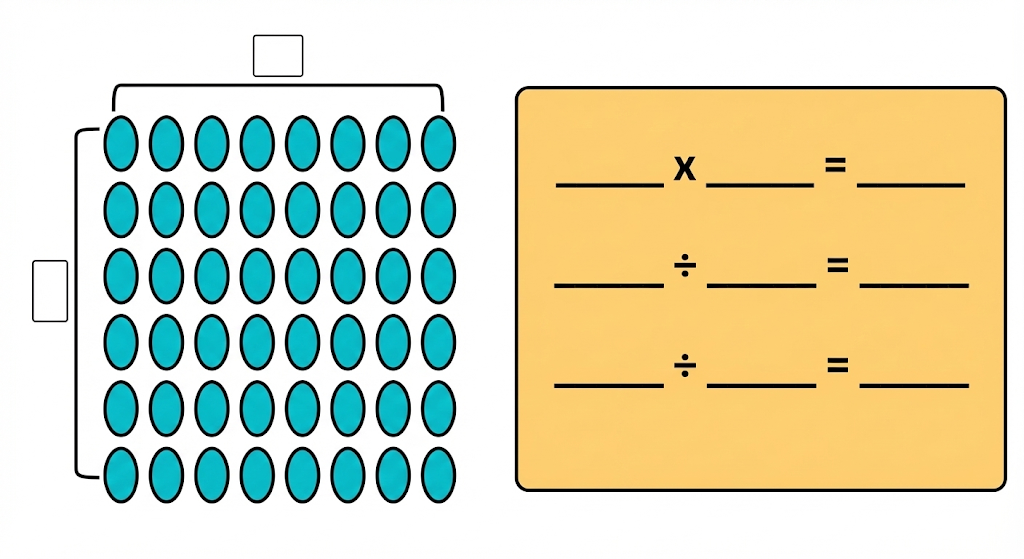
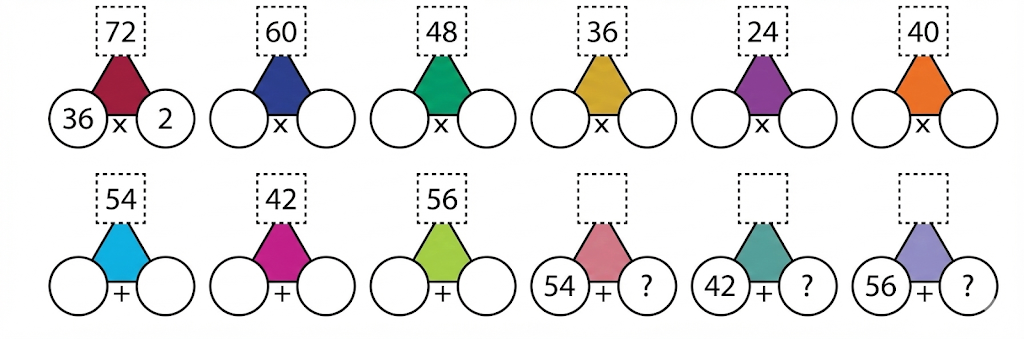
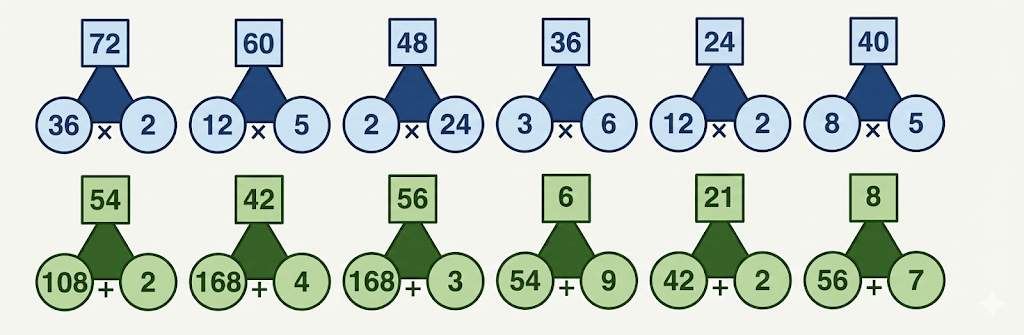
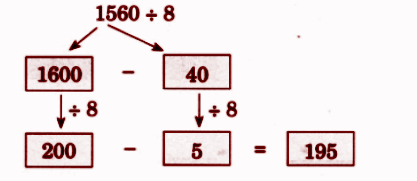
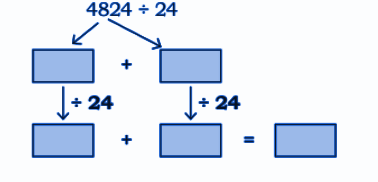
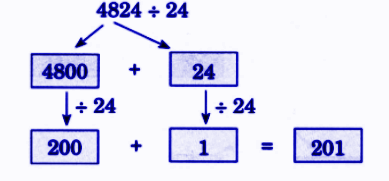
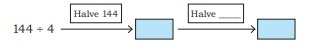
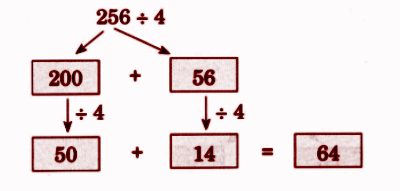
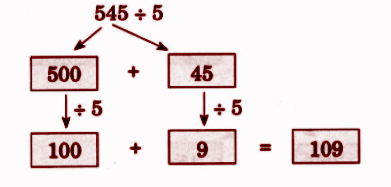
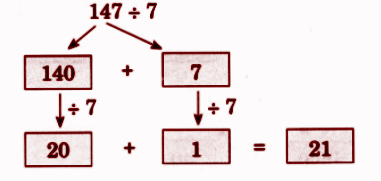
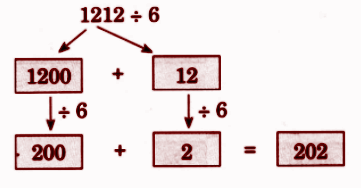
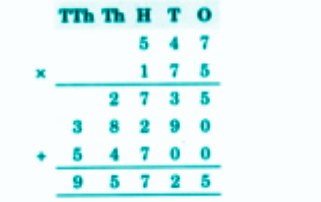
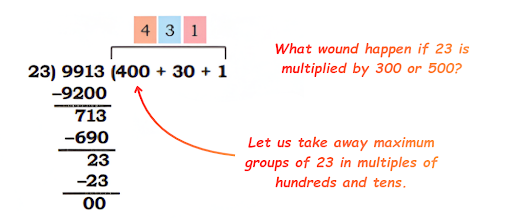
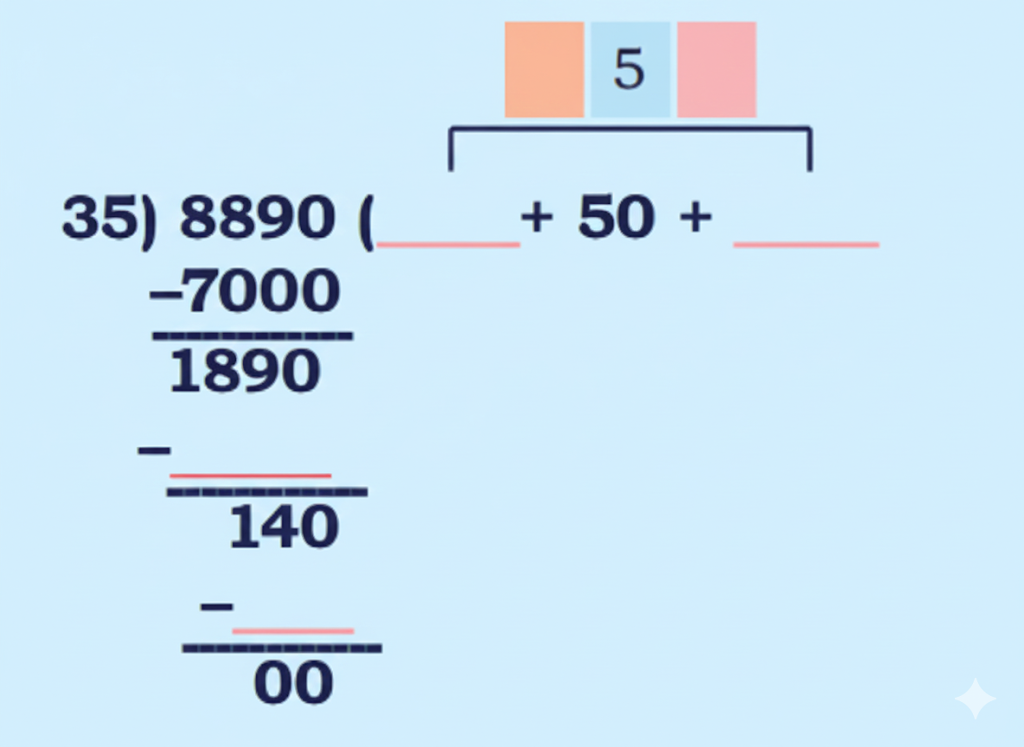
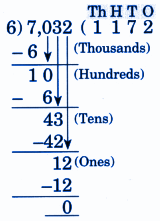
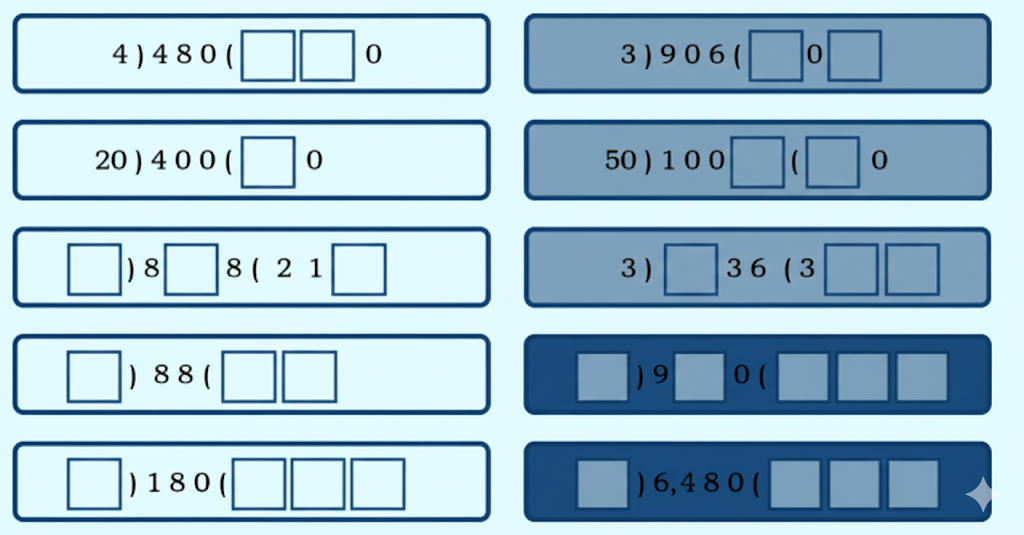
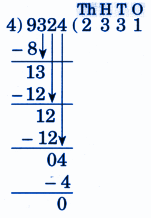
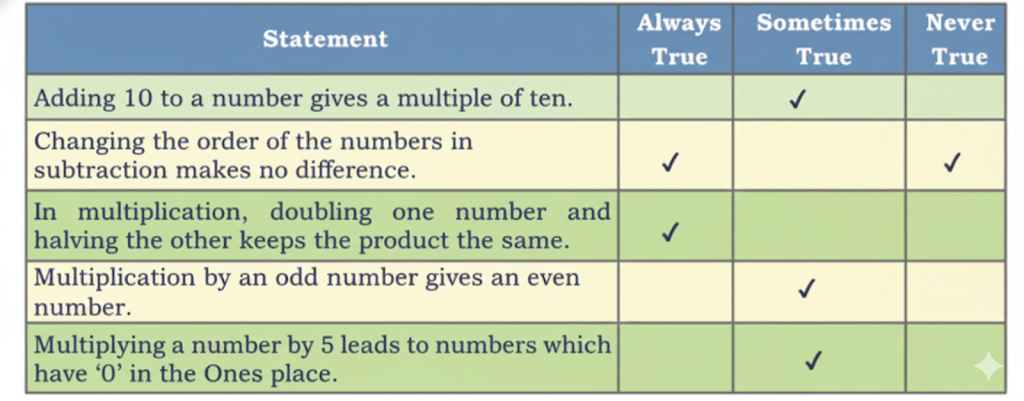
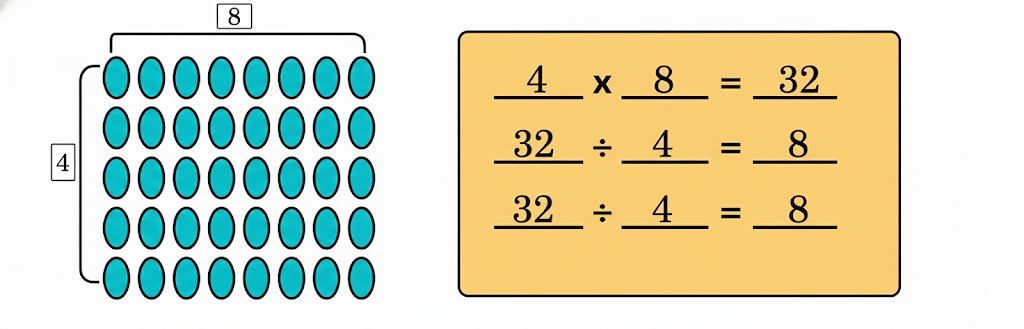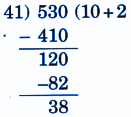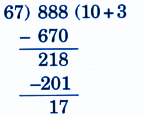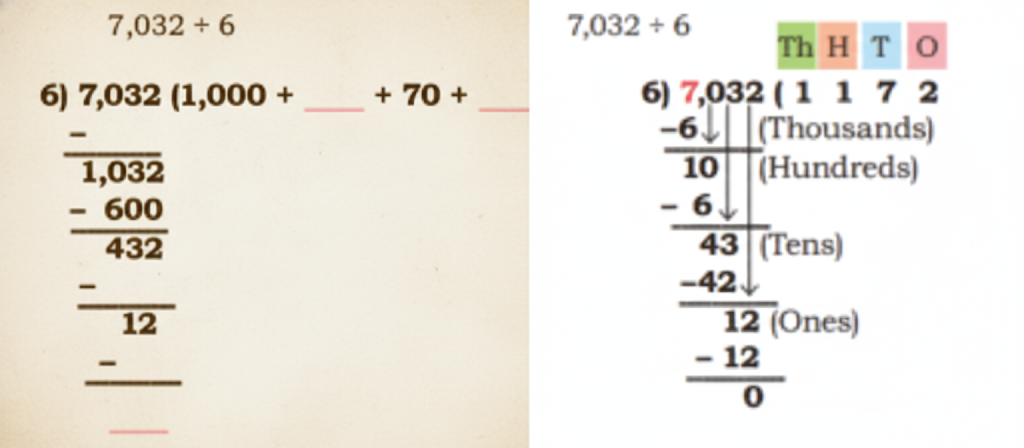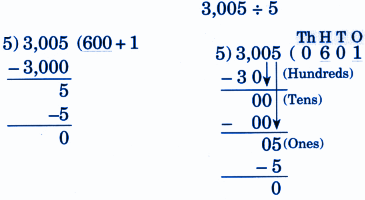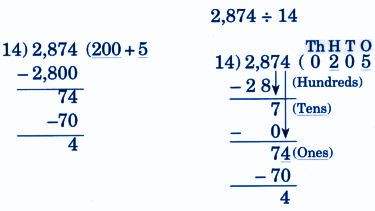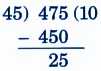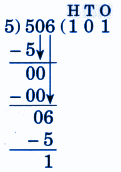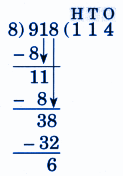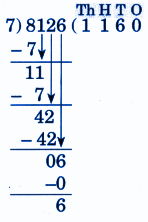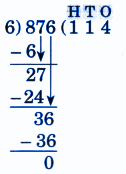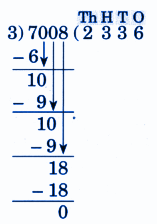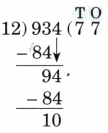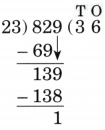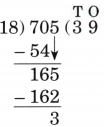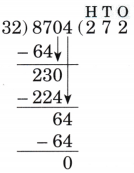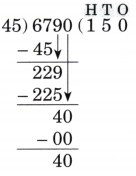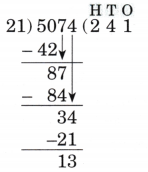Step-by-Step NCERT Answers for Class 5 Maths Chapter 9 with Exam Tips
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 5 Maths Chapter 9 Coconut Farm - 2025-26
1. What is included in the NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Chapter 9 Coconut Farm?
NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Chapter 9 Coconut Farm provide stepwise answers, clear diagrams, key definitions, and important exam strategies. These solutions include:
- Intext and back exercise solutions following the CBSE syllabus
- Stepwise explanations for every question
- Important definitions and formulae to help with quick revision
- Tips for drawing and labelling diagrams
- CBSE marking scheme insights for scoring high marks
- Downloadable PDF for offline study
2. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 9 Coconut Farm help me score more marks in CBSE exams?
NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 9 Coconut Farm are teacher-reviewed, follow the CBSE 2025–26 marking scheme, and use stepwise answers to boost scores. They help by:
- Showing how to write step-by-step solutions for each question
- Including important keywords, diagrams, and definitions required for exams
- Offering answer structure and length guidance as per CBSE marking
- Highlighting common mistakes and how to avoid them
3. Which questions from Chapter 9 Coconut Farm are likely to be asked in school exams?
Key questions from Chapter 9 Coconut Farm often appear in CBSE school exams:
- Stepwise problem solving related to the coconut farm context
- Word problems that test understanding of farm mathematics
- Definitions and short answers from the chapter
- Diagram-based questions requiring clear labelling
- Exercise and exemplar questions at the end of the chapter
4. Are diagrams or definitions mandatory in NCERT answers for Class 5 Maths Chapter 9?
Diagrams and definitions are important in Class 5 Maths Chapter 9 answers to score full marks:
- Well-labelled diagrams can fetch easy marks in CBSE exams
- Clear definitions improve answer quality and exam grades
- Follow NCERT conventions for neatness and accuracy
5. How can I write stepwise NCERT answers to score full marks in Class 5 Maths Chapter 9?
To score full marks in Class 5 Maths Chapter 9, always write step-by-step solutions:
- Start with a clear statement of the problem
- Show all calculation steps with working
- Use proper units and label diagrams neatly
- End with final answer in a box
6. Where can I download the free PDF of NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Chapter 9 Coconut Farm?
You can download the free PDF of NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Chapter 9 Coconut Farm from trusted educational websites like Vedantu. The PDF includes:
- Chapterwise stepwise solutions
- Revision notes and diagrams
- Ready for offline study and quick revision
7. How should I structure long answers for CBSE marking in Class 5 Maths?
For CBSE exams, structure long answers using the following steps:
- Begin with a clear introduction or statement of the problem
- Break down the solution into logical steps
- Use diagrams and labelled sketches if required
- Write definitions or explanations where necessary
- Underline key points or box the final answer
8. What are the most important definitions and formulae in Class 5 Maths Chapter 9 Coconut Farm?
The most important definitions and formulae in Chapter 9 Coconut Farm include:
- Area and perimeter of rectangular fields
- Number patterns used in farming contexts
- Basic units of measurement (metre, square metre, etc.)
- Simple word problem methods relevant to farm scenarios
9. Are NCERT Solutions enough for Class 5 Maths exams?
NCERT Solutions are sufficient for Class 5 Maths exams if you practice all intext, back exercises, and understand each step. For best results:
- Revise each solution regularly
- Solve exemplar and sample questions for extra practice
- Use marking-scheme insights included in the solutions
10. How to learn diagrams or maps for Class 5 Maths Chapter 9 quickly?
To master diagrams and maps in Chapter 9 Coconut Farm:
- Practice drawing each type of diagram multiple times
- Use a checklist for labels and units
- Follow CBSE tips for neatness – use pencil and ruler, box labels
- Study the solved examples in NCERT Solutions