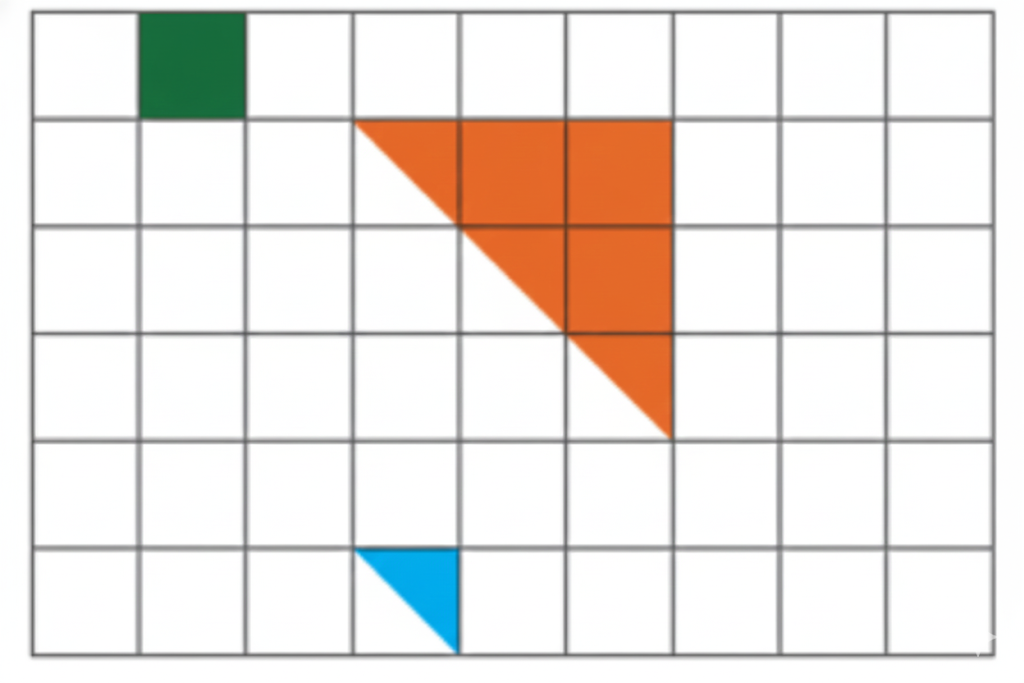
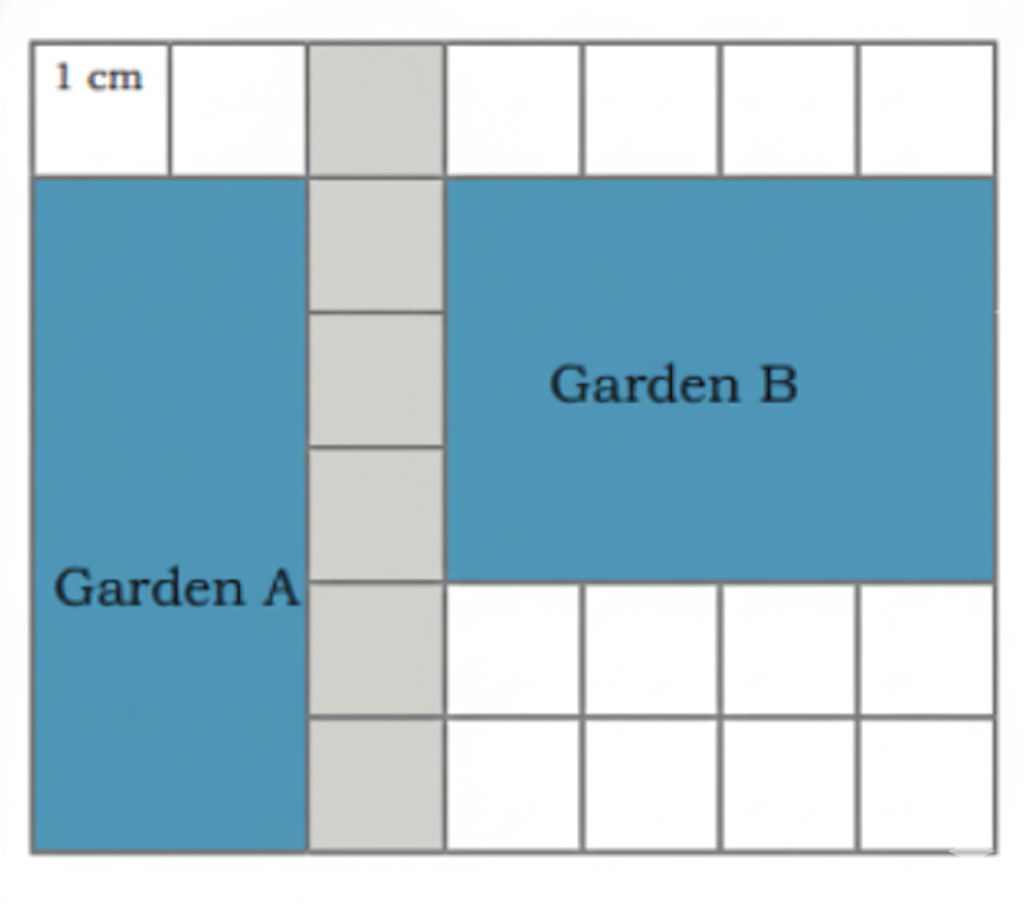
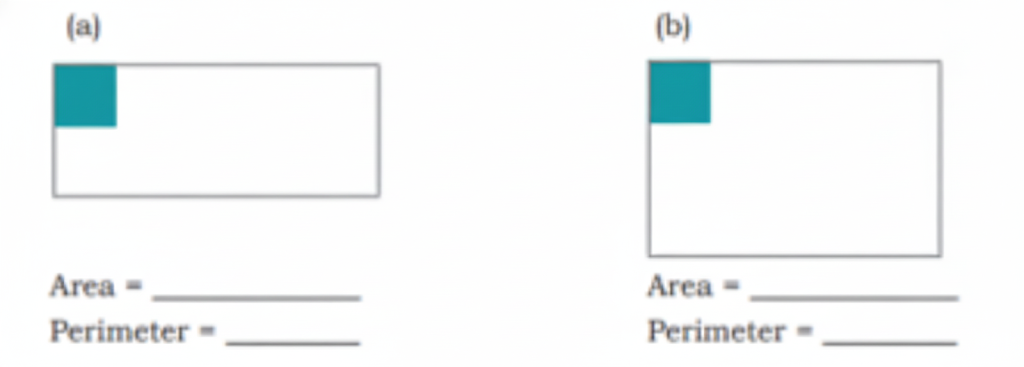
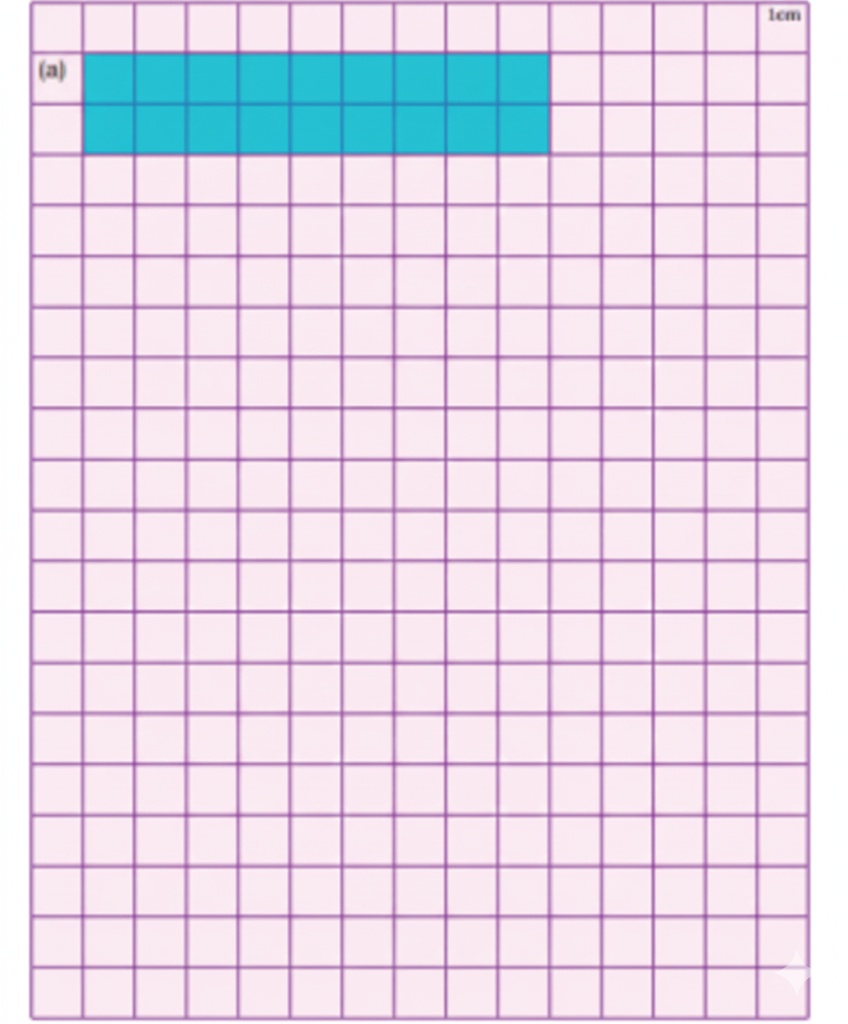
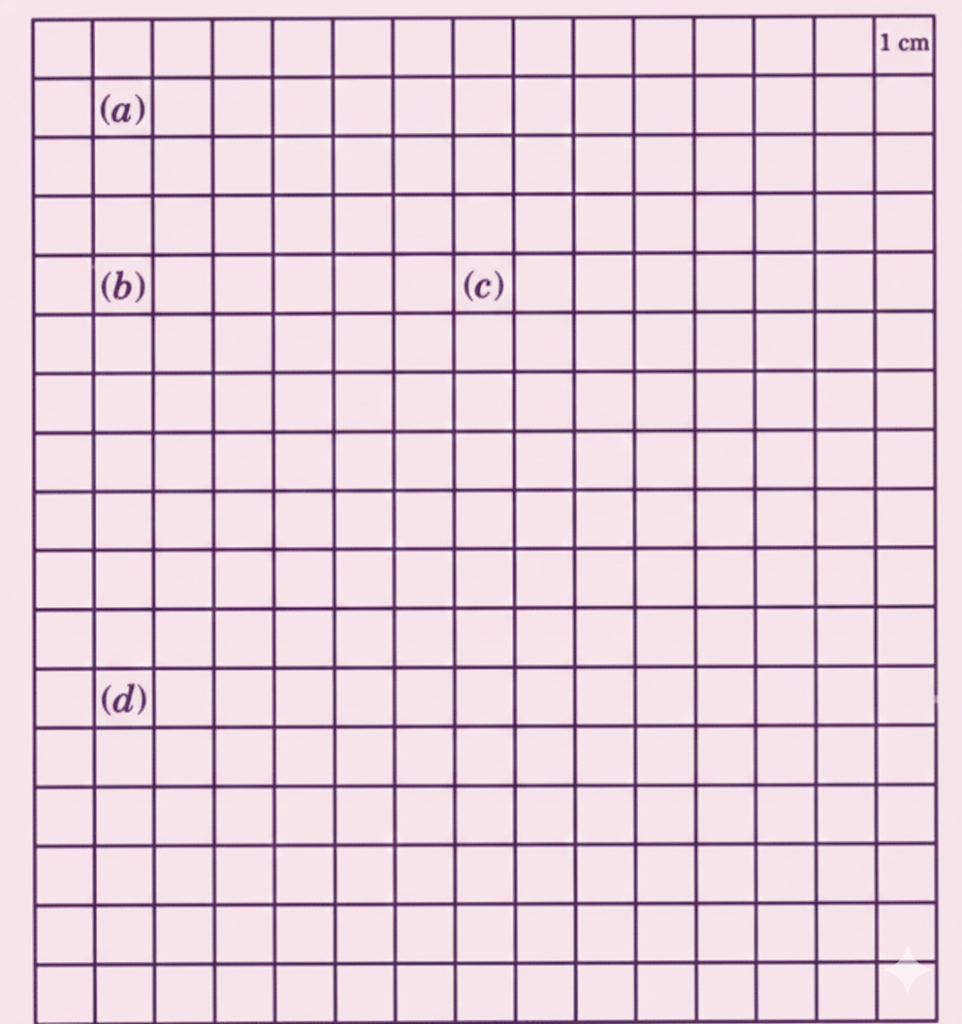
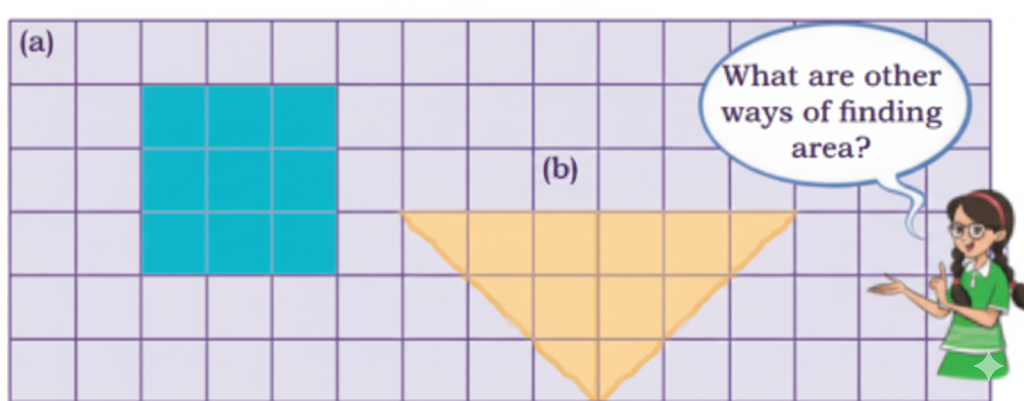
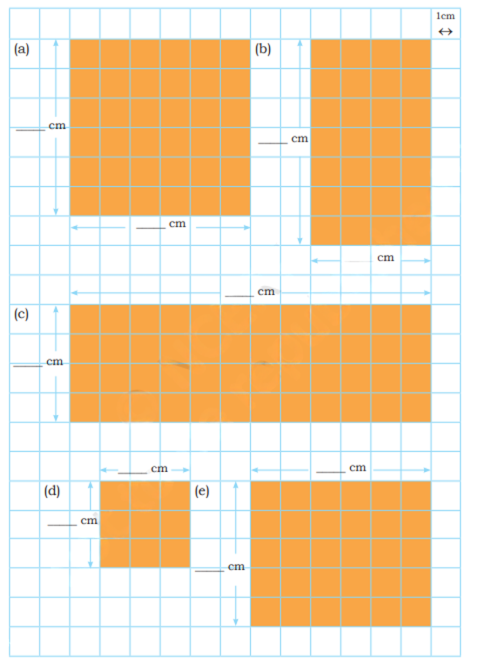
How to Write Stepwise Answers and Score Full Marks in Grandmother’s Quilt?
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 5 Maths Chapter 11 Grandmother's Quilt - 2025-26
1. What is the main concept in Grandmother’s Quilt?
The main concept of NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 11 Grandmother’s Quilt is to understand mathematical patterns, shapes, and reasoning through creative and visual activities like quilt-making.
- Focuses on patterns and spatial reasoning
- Encourages visualization and creative thinking
- Teaches pattern identification and repetition through everyday examples
2. How to score full marks in Chapter 11 of Class 5 Maths?
To score full marks in Class 5 Maths Chapter 11, present your answers stepwise, use correct terms, and add neat diagrams where asked.
- Write clear, stepwise solutions using all keywords
- Draw and label diagrams accurately (if required)
- Revise definitions, formulae, and key patterns before the exam
- Check answers for neatness and completeness
- Practice with NCERT Solutions and attempt extra questions for confidence
3. Are diagrams needed in answers for Grandmother’s Quilt?
Yes, including diagrams in your answers is important, especially when describing or explaining patterns.
- Neat and labelled diagrams fetch extra marks
- Some questions specifically ask for pattern drawings, quilt designs, or shapes
- Always use a ruler and pencil for clear presentation
4. How do I present long answers to match CBSE marking?
Present long answers for CBSE Class 5 Maths Chapter 11 using a structured format:
- Start with a short introduction or definition of the concept
- List steps or observations using bullet points or numbers
- Add examples or diagrams if needed
- Underline or bold key terms and answers
- Summarize with a concluding statement
5. Where can I download the NCERT Solutions PDF for Class 5 Maths Chapter 11?
You can easily download the NCERT Solutions PDF for Class 5 Maths Chapter 11 Grandmother’s Quilt from trusted educational websites offering free study materials.
- Search for "Class 5 Maths Chapter 11 NCERT Solutions PDF free download"
- Look for platforms with up-to-date (2025–26) content
- Check if the PDF includes exercise-wise, stepwise answers and diagrams
- Save for offline study and revision
6. What are the most important topics from Chapter 11 Grandmother’s Quilt?
The most important topics in Class 5 Maths Mela Chapter 11 include:
- Identifying and creating patterns
- Arranging and counting shapes in quilts
- Visualizing spatial arrangements
- Reasoning and completing pattern-based questions
- Drawing and labeling pattern diagrams correctly
7. How does practising stepwise NCERT Solutions help in Class 5 Maths exams?
Practising stepwise NCERT Solutions for Chapter 11 helps you:
- Understand concepts deeply and logically
- Learn the correct exam format for each question
- Avoid missing steps that can cost marks
- Boost confidence for difficult or creative reasoning questions
- Score higher by matching the CBSE marking scheme
8. What are the common mistakes to avoid in Class 5 Maths Chapter 11 answers?
To avoid losing marks, watch out for these common mistakes:
- Omitting steps or logic in your solutions
- Missing diagrams or drawing untidy patterns
- Forgetting to label shapes and explain reasoning
- Not following the exam structure (introduction, steps, conclusion)
- Leaving answers incomplete or not revising basic pattern rules
9. Is NCERT Solutions enough for Class 5 Maths exams?
NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths cover all the important topics and exercise questions as per the CBSE syllabus.
- They are sufficient for scoring well if thoroughly practiced
- Also revise with exemplar questions and sample papers for more practice
- Review diagrams, definitions, and marking schemes as given in NCERT
10. How can I revise Chapter 11 quickly before the test?
For fast revision of Chapter 11 Grandmother’s Quilt:
- Read key definitions and formulae first
- Review solved examples and stepwise answers from NCERT
- Practice drawing at least 2–3 pattern diagrams
- Attempt previous year and sample questions
- Go through a summary or quick revision notes