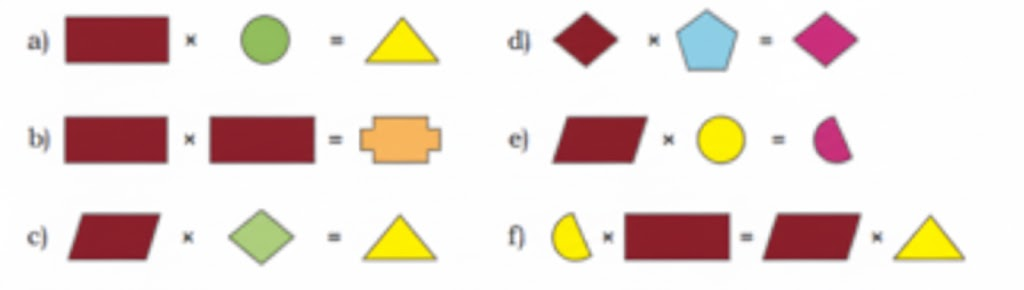
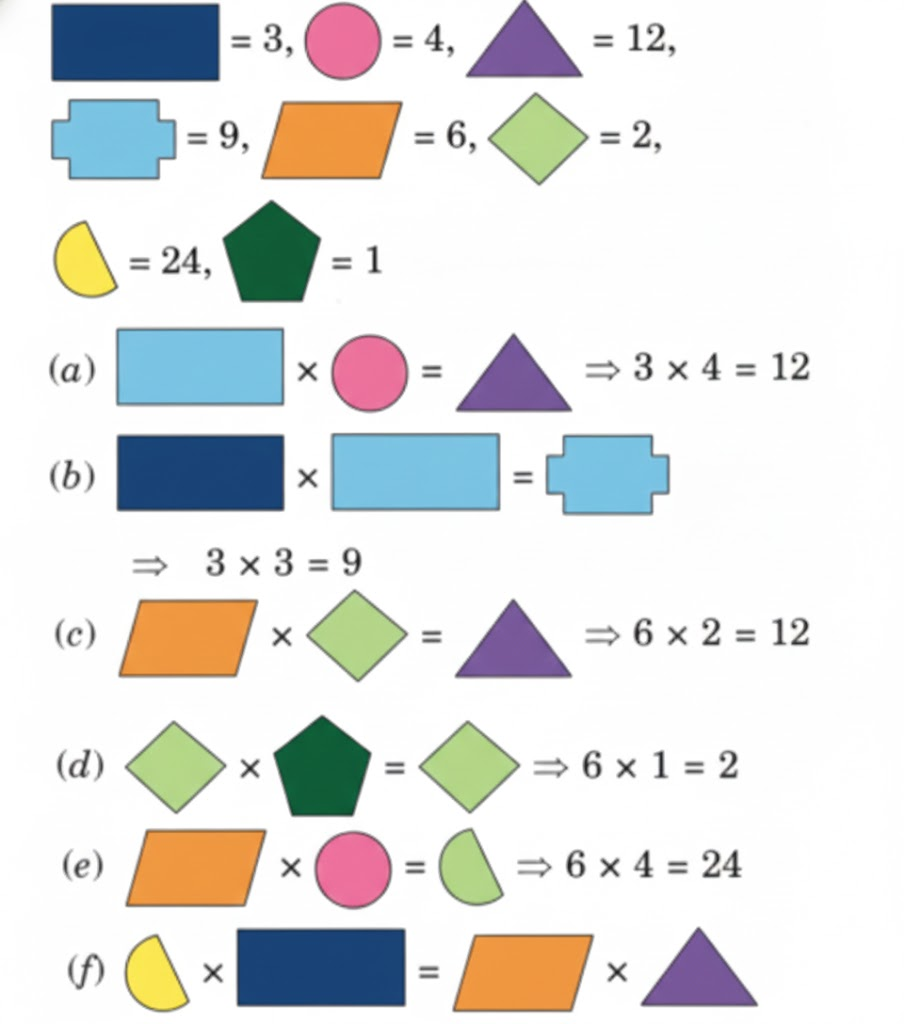
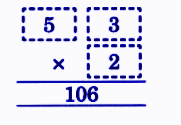
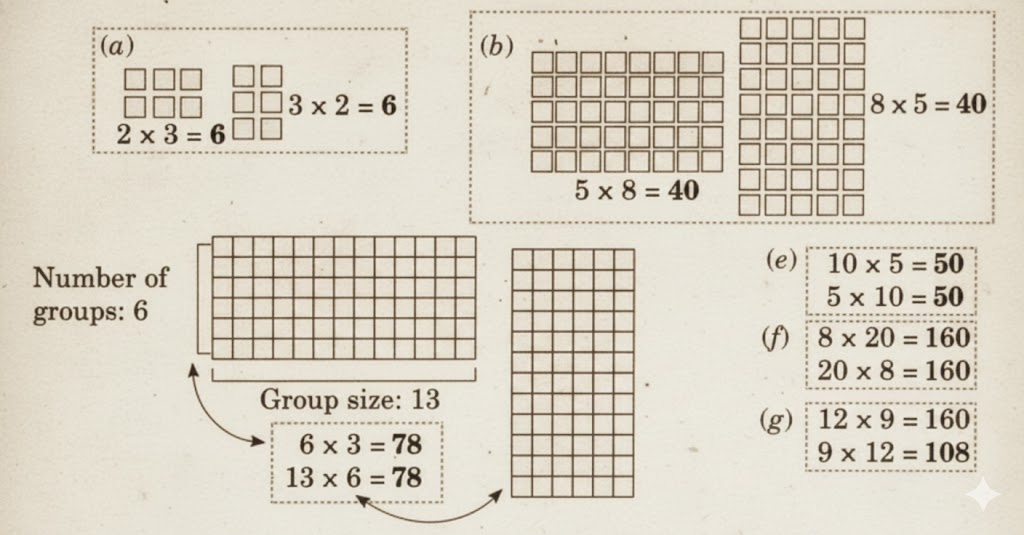
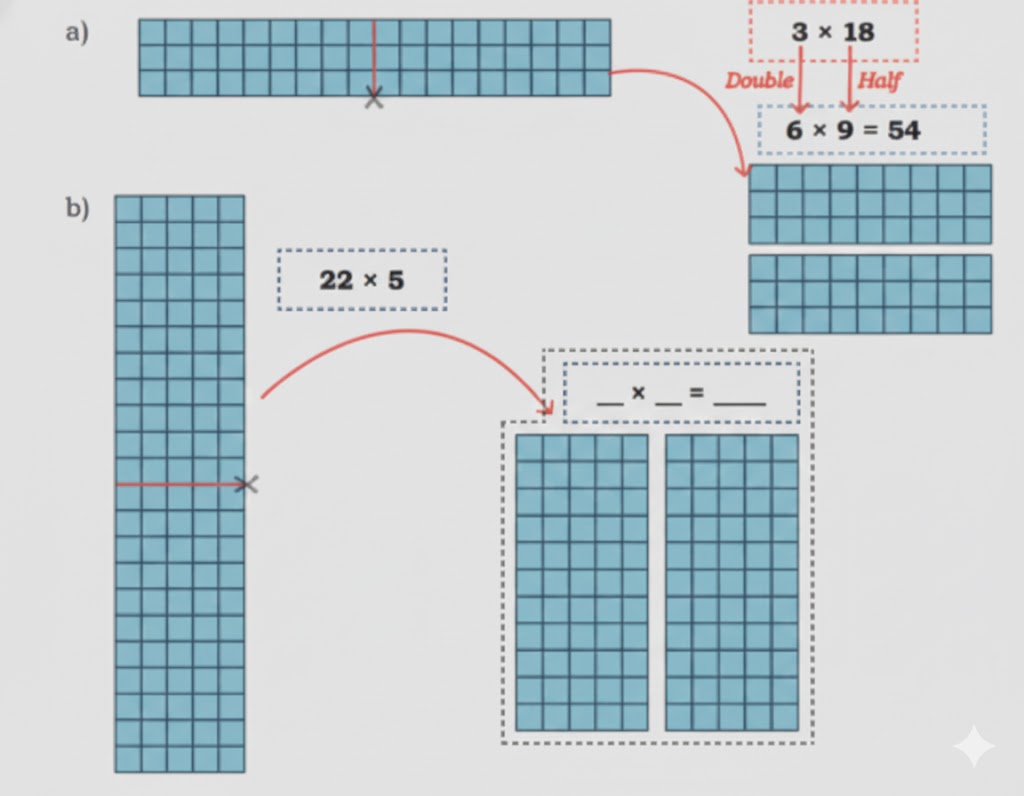
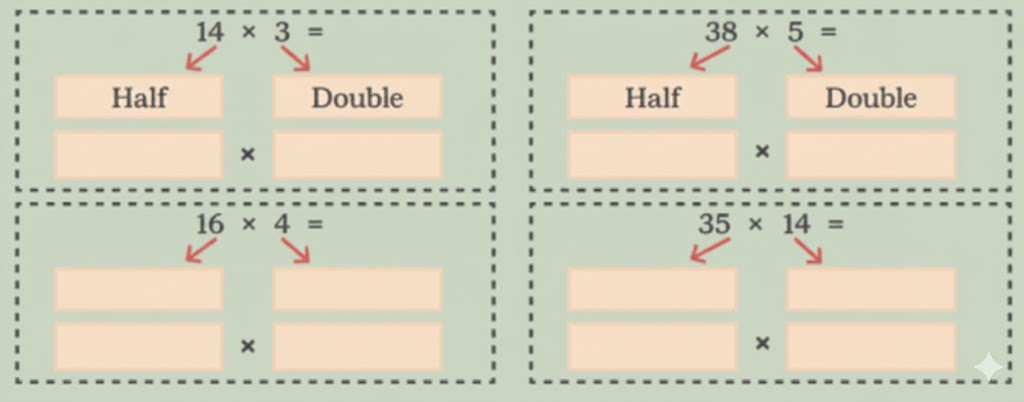
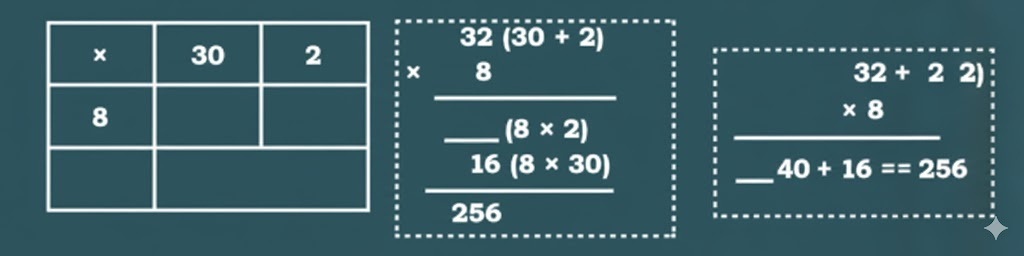
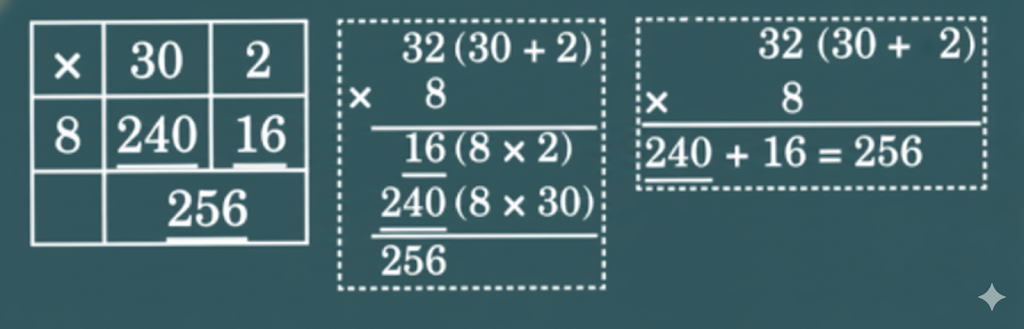
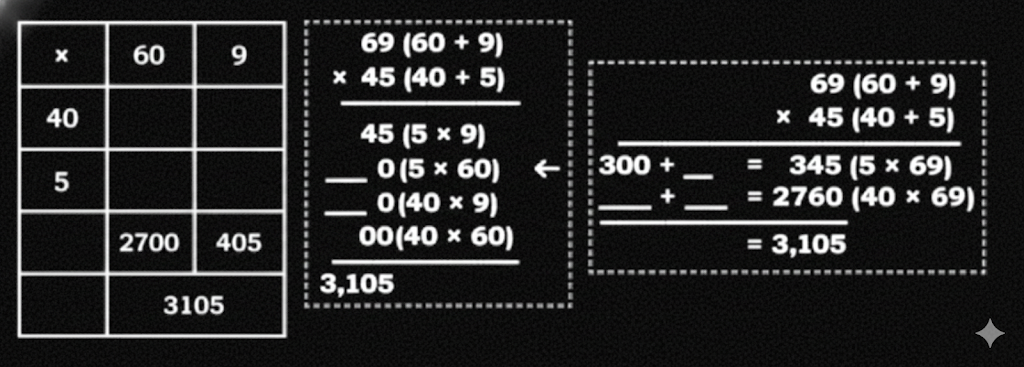
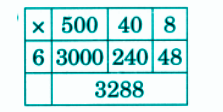
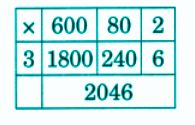
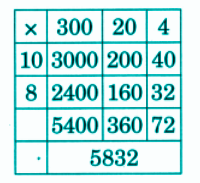
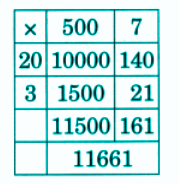
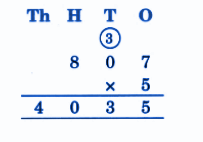
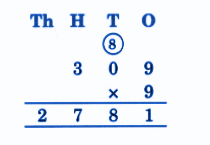
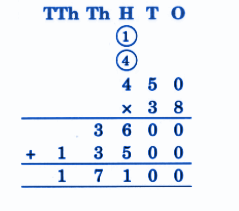
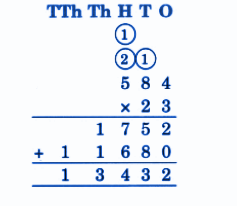
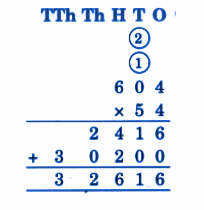
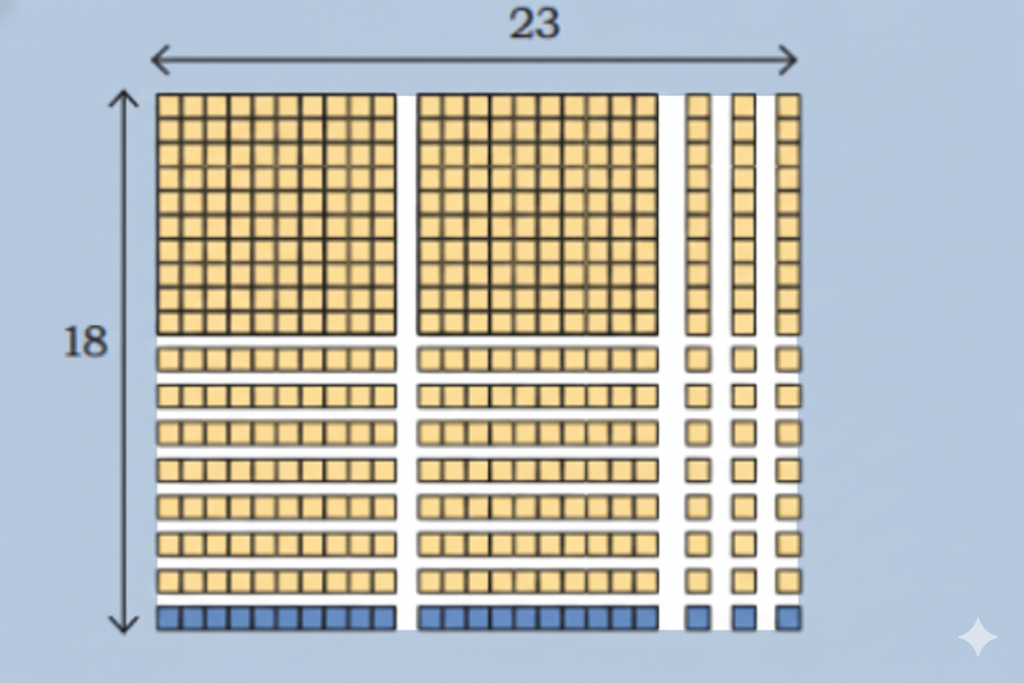
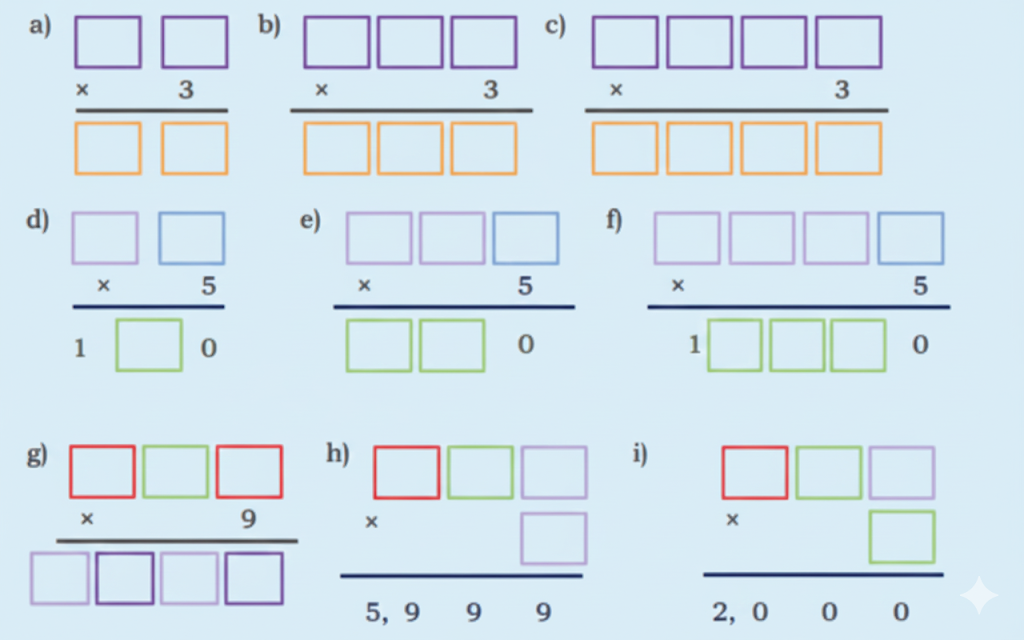
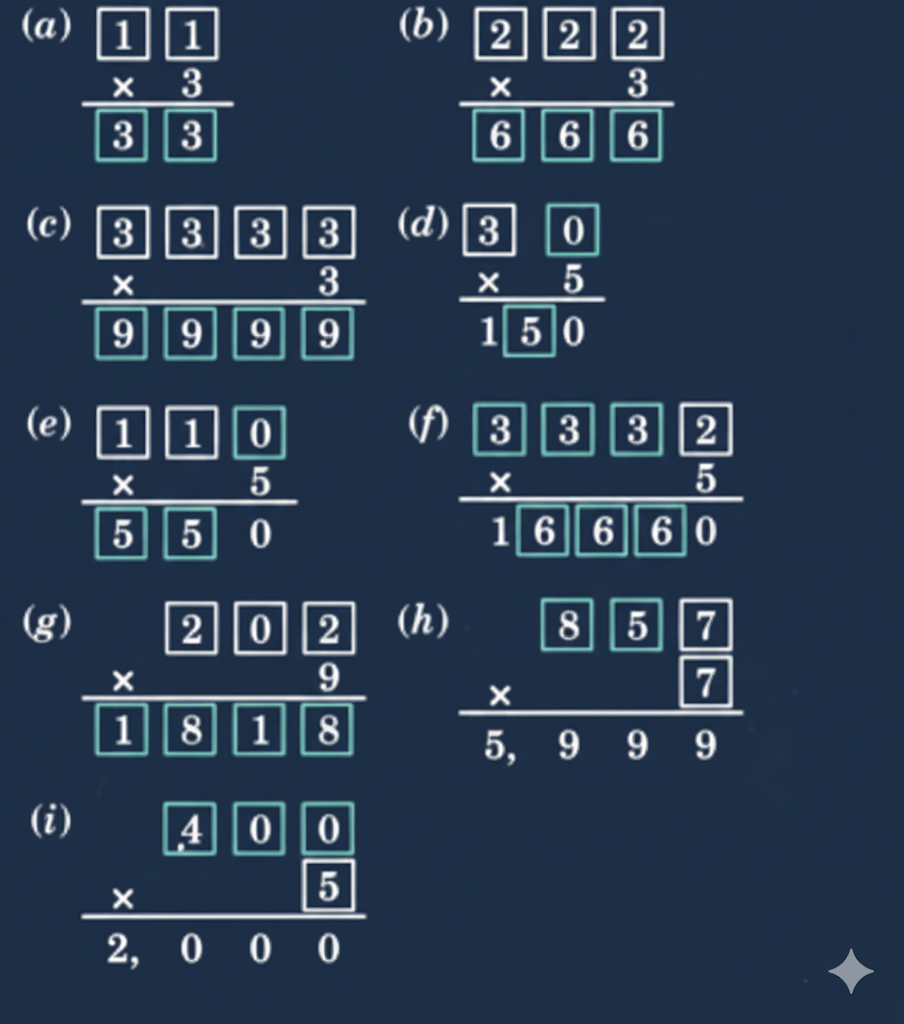
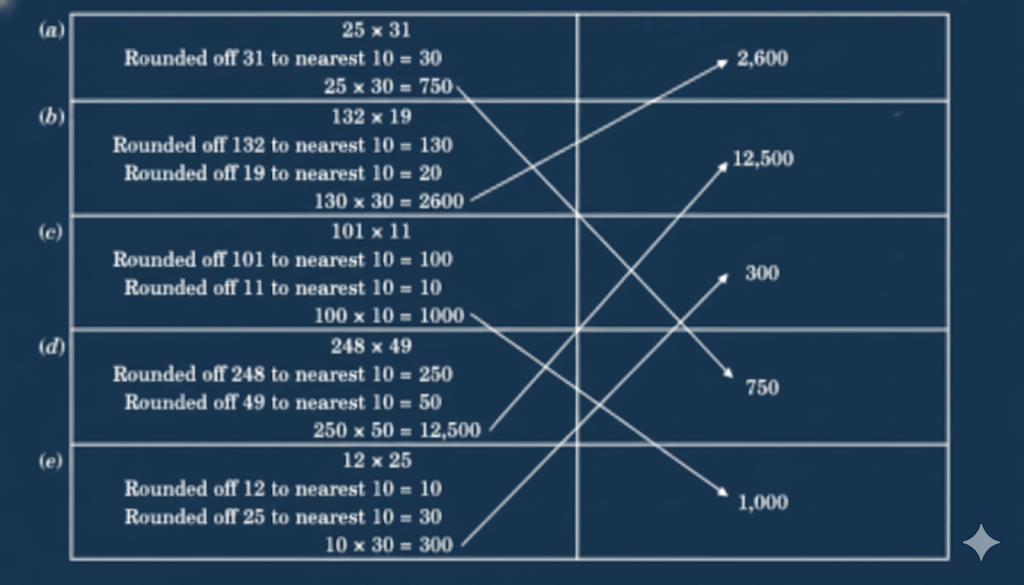
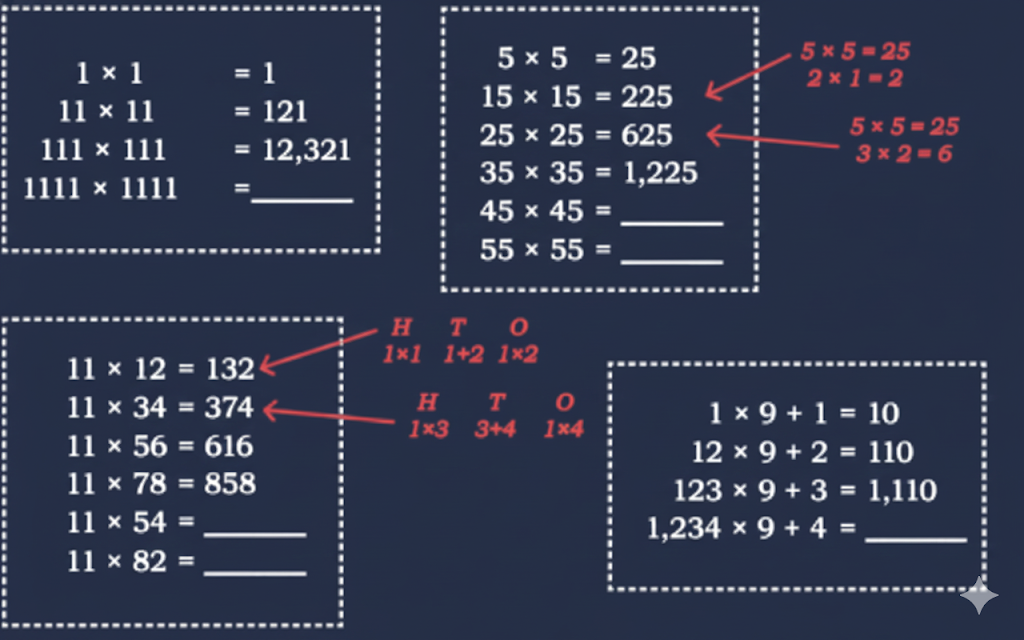
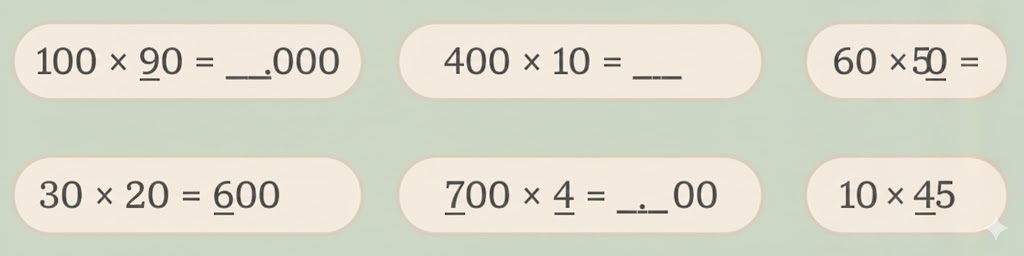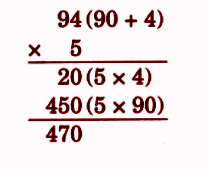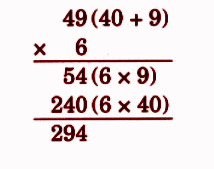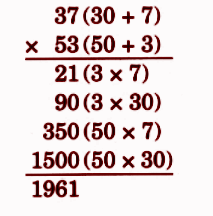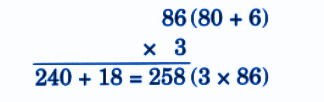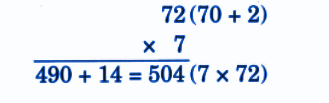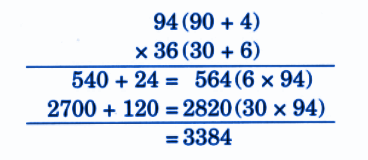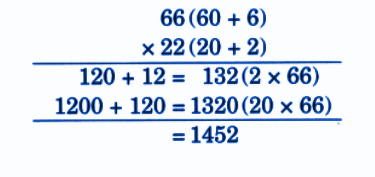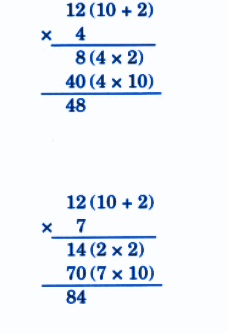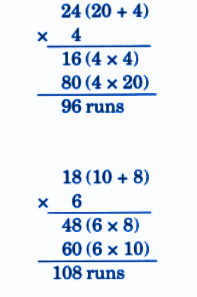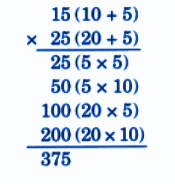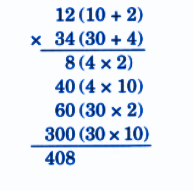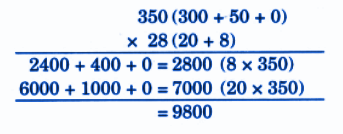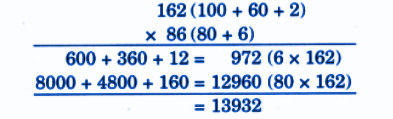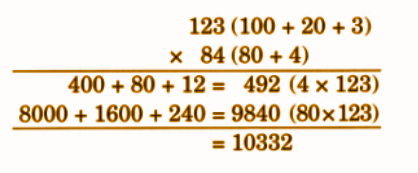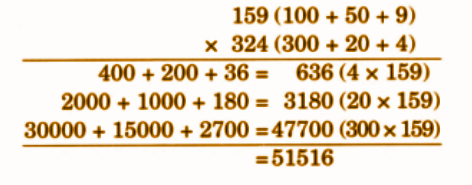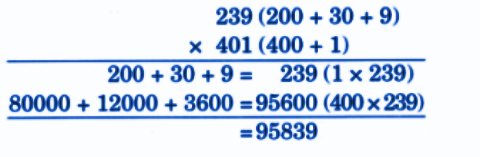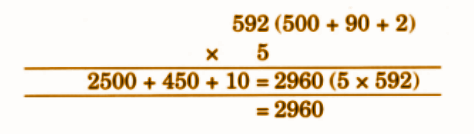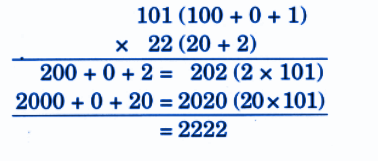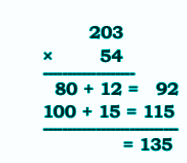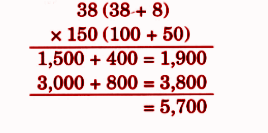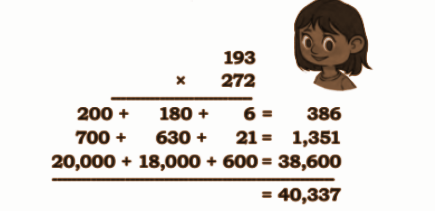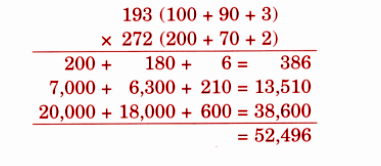Stepwise NCERT Answers for Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 with Exam Tips
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 The Dairy Farm - 2025-26
1. What are NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 The Dairy Farm?
NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 The Dairy Farm provide detailed stepwise answers to all textbook questions, following the latest CBSE 2025–26 syllabus. These solutions help students:
- Understand chapter concepts with clear explanations and stepwise methods
- Prepare for school exams with exam-style answers
- Clarify doubts in both intext and back exercise questions
- Download free PDFs for handy offline revision
2. How can I score full marks using NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Chapter 6?
To score full marks with NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 The Dairy Farm, follow these tips:
- Write stepwise answers as shown in the solutions
- Use correct formulas and definitions where required
- Draw neat diagrams if asked and label them properly
- Follow the CBSE marking scheme for long answers—introduction, steps, final answer
- Revise key concepts and practice previous year questions
3. Which questions from Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 are important for exams?
Questions that require calculation, use of diagrams, and key definitions from Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 The Dairy Farm are frequently asked in school exams. Important question types include:
- Step-based mathematical problems on dairy data
- Short and long answer questions needing explanations or diagrams
- Map or schematic representation of a dairy farm (if included in your book)
- Key terms and short notes from the chapter
4. Are diagrams and definitions mandatory in Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 answers?
Including neat diagrams and accurate definitions in your Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 answers can help you get full marks. Diagrams are usually required when questions specifically mention them; definitions give clarity to your answers, especially for important concepts.
5. How should I structure long answers in The Dairy Farm chapter for better marks?
For higher marks in long answers for The Dairy Farm chapter, structure your answer as follows:
- Start with an introduction sentence explaining the main idea
- Write each step clearly and in order
- Include relevant definitions and diagrams if asked
- Conclude with a direct answer or summary sentence
6. Where can I download the Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 solutions PDF for free?
You can download the free NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 PDF from educational platforms offering CBSE-aligned resources. Look for a clear download button, ensuring the PDF covers all exercise-wise questions with stepwise answers for easy offline study.
7. Are NCERT Solutions enough for Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 exam preparation?
NCERT Solutions for Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 are usually sufficient for exam preparation, as they follow the CBSE syllabus and marking scheme. For best results, also practice:
- Class assignments and worksheets
- Previous year and sample papers for extra practice
- Additional problems from NCERT Exemplar if available
8. How can I quickly revise Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 before exams?
Revise Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 quickly by:
- Studying summary notes and key formulae
- Practicing important questions from NCERT Solutions
- Memorizing key definitions and map/diagram labels
- Solving sample and previous year questions for time management
9. What are the key concepts and formulae in Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 The Dairy Farm?
Some key concepts and formulae in Class 5 Maths Chapter 6 The Dairy Farm include:
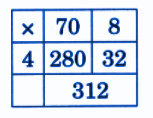
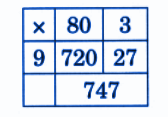
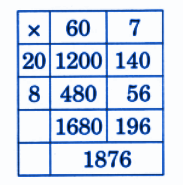
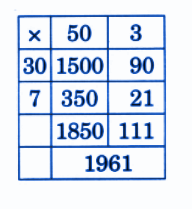
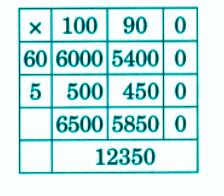
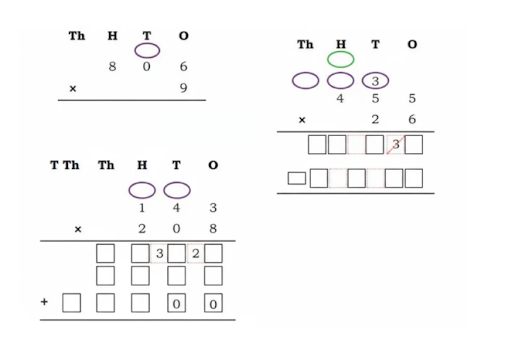
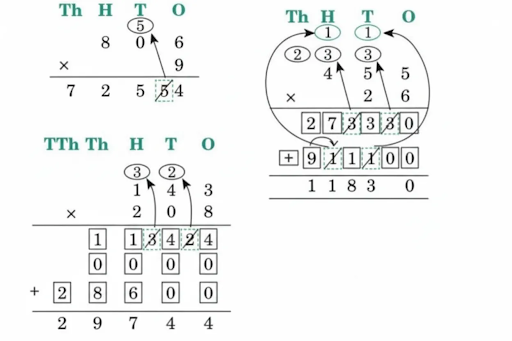
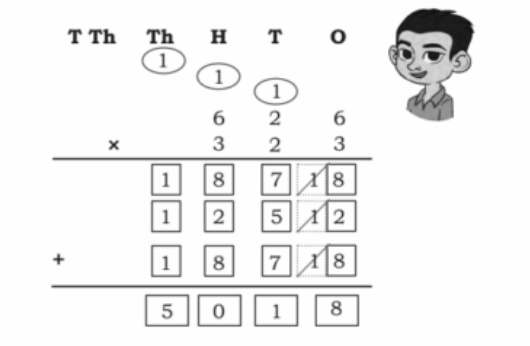
- Calculation of totals such as number of cows and milk yield
- Understanding graphical or tabular data (if in your book)
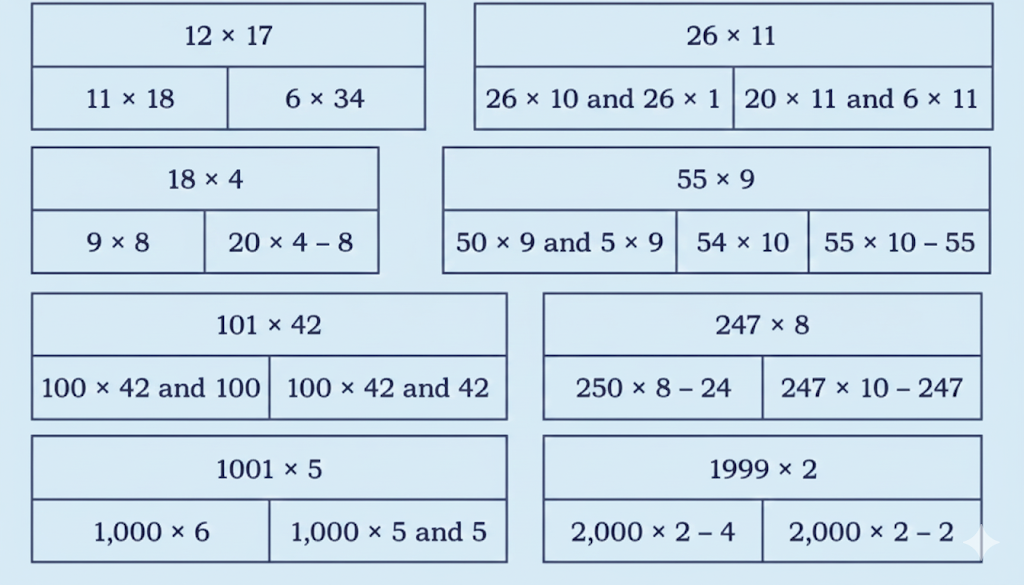
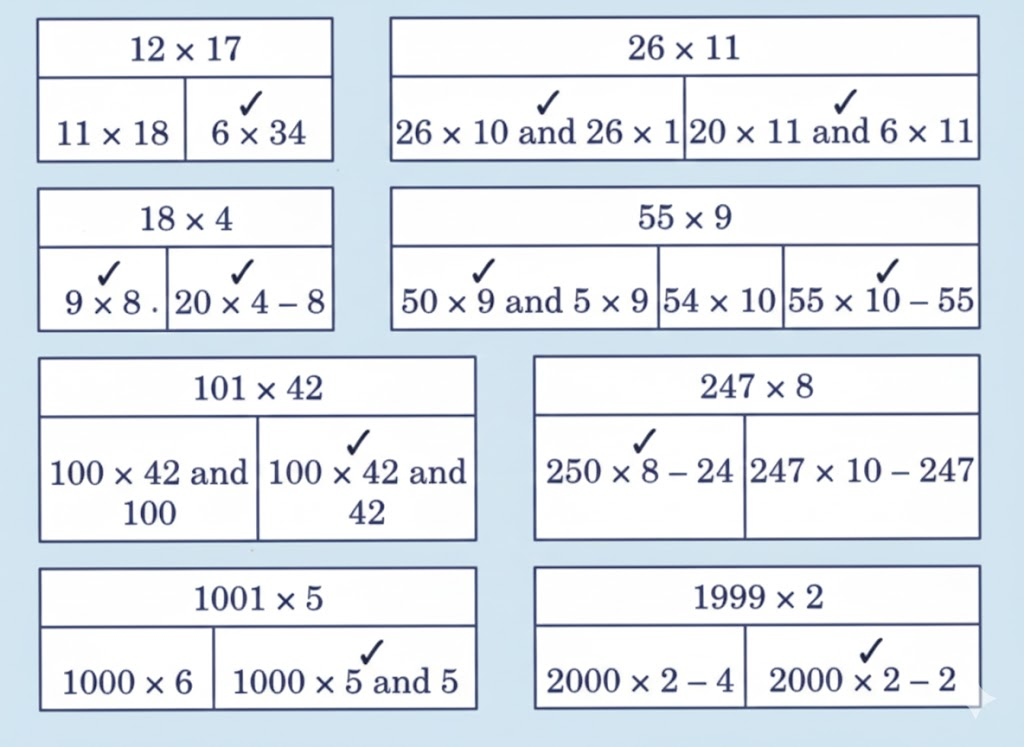
- Basic multiplication, addition, and comparison problems related to dairy farm operations
- Definitions like dairy, farm, produce, and measurements
10. Do examiners award partial marks for correct steps even if the final answer is wrong in Class 5 Maths?
Yes, in CBSE marking scheme for Class 5 Maths, partial marks are awarded for showing correct stepwise working even if the final answer is incorrect. Always write each step clearly to maximize your chances of scoring.