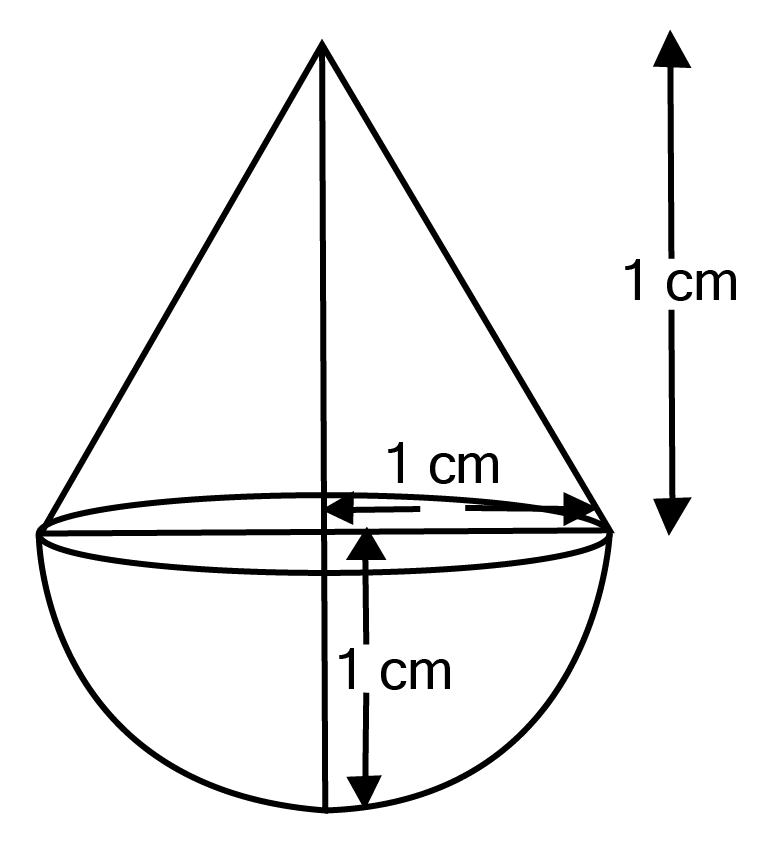
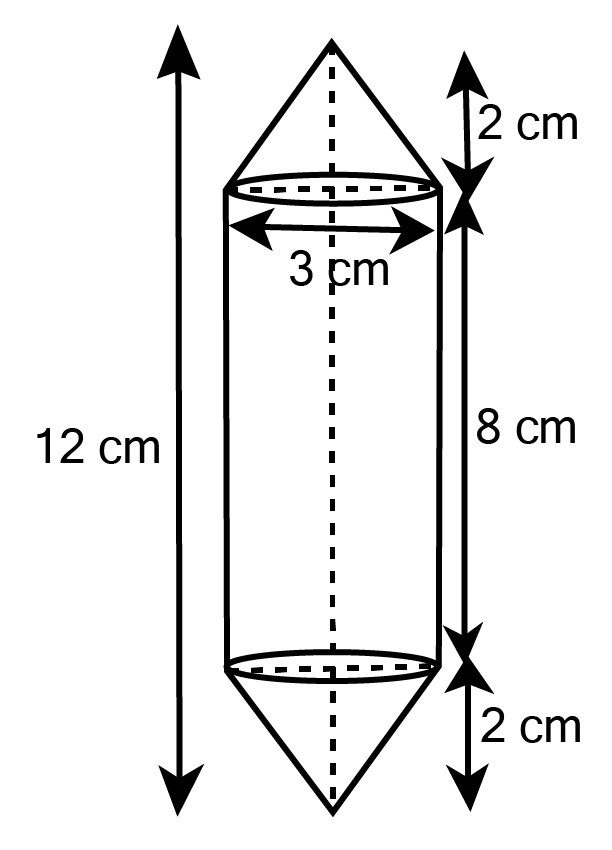
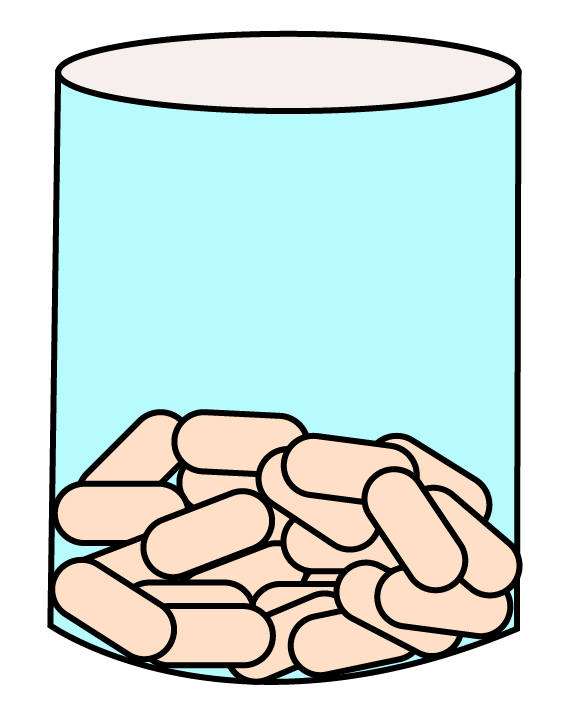
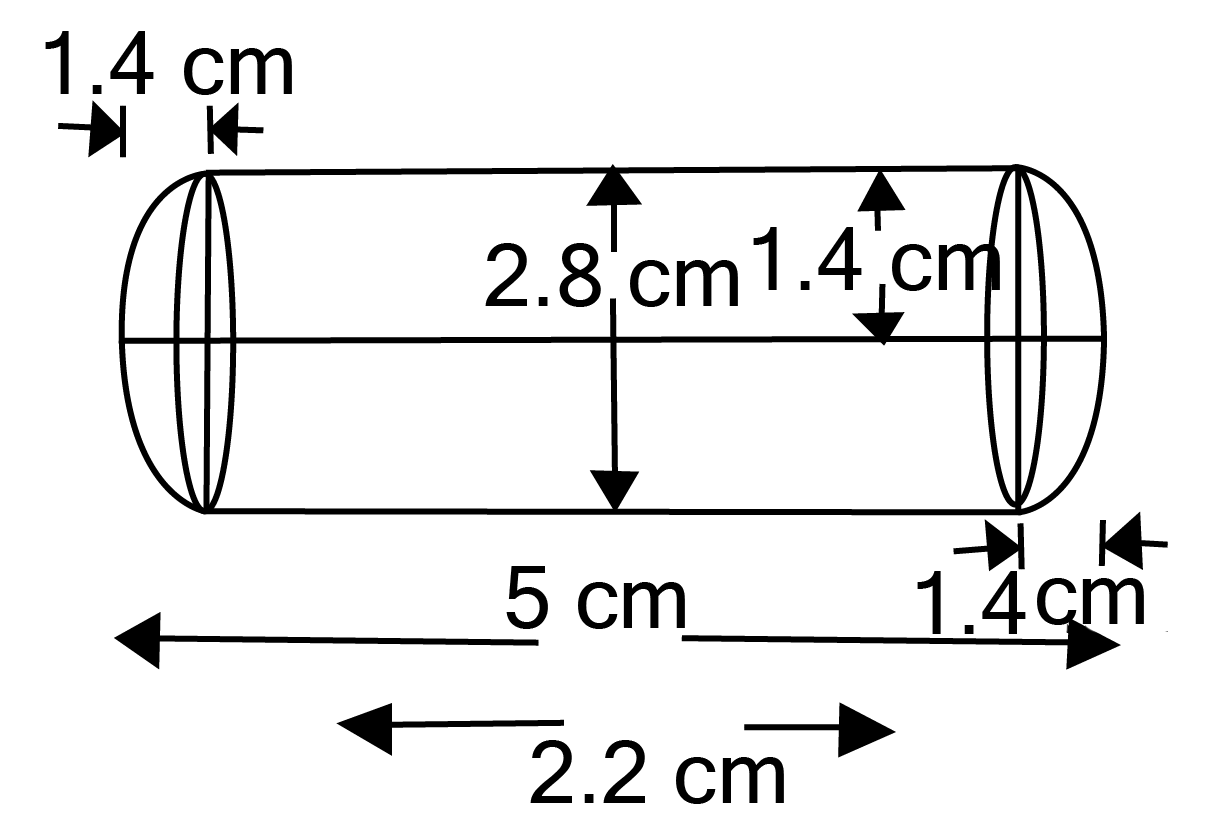
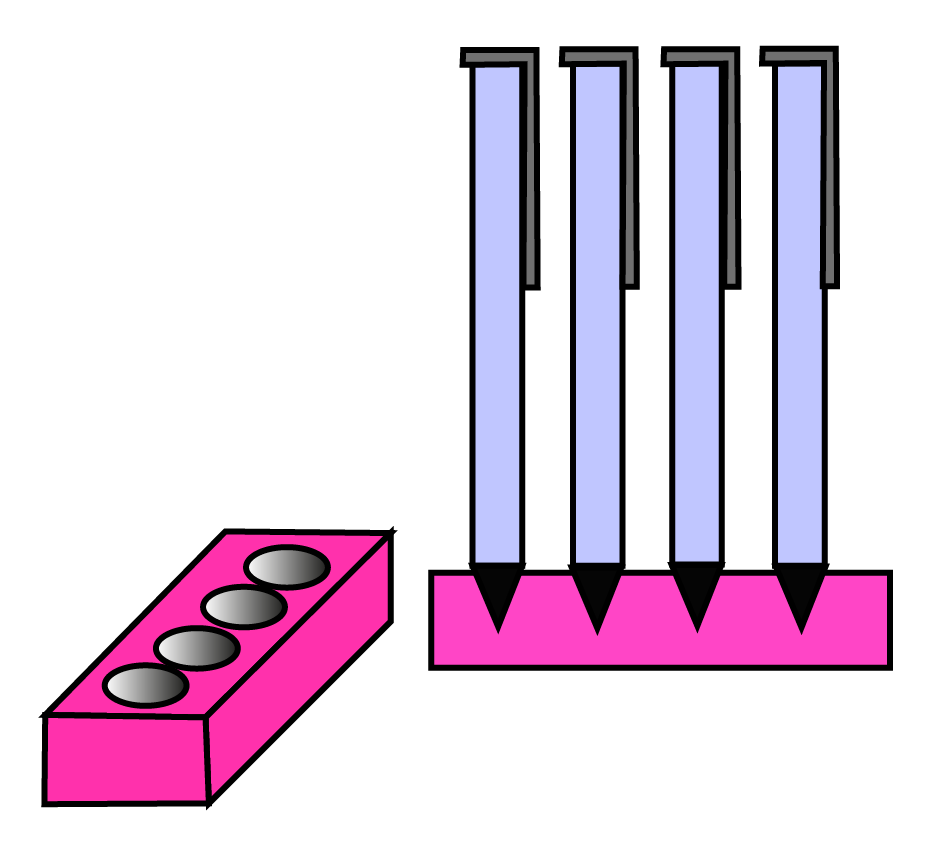
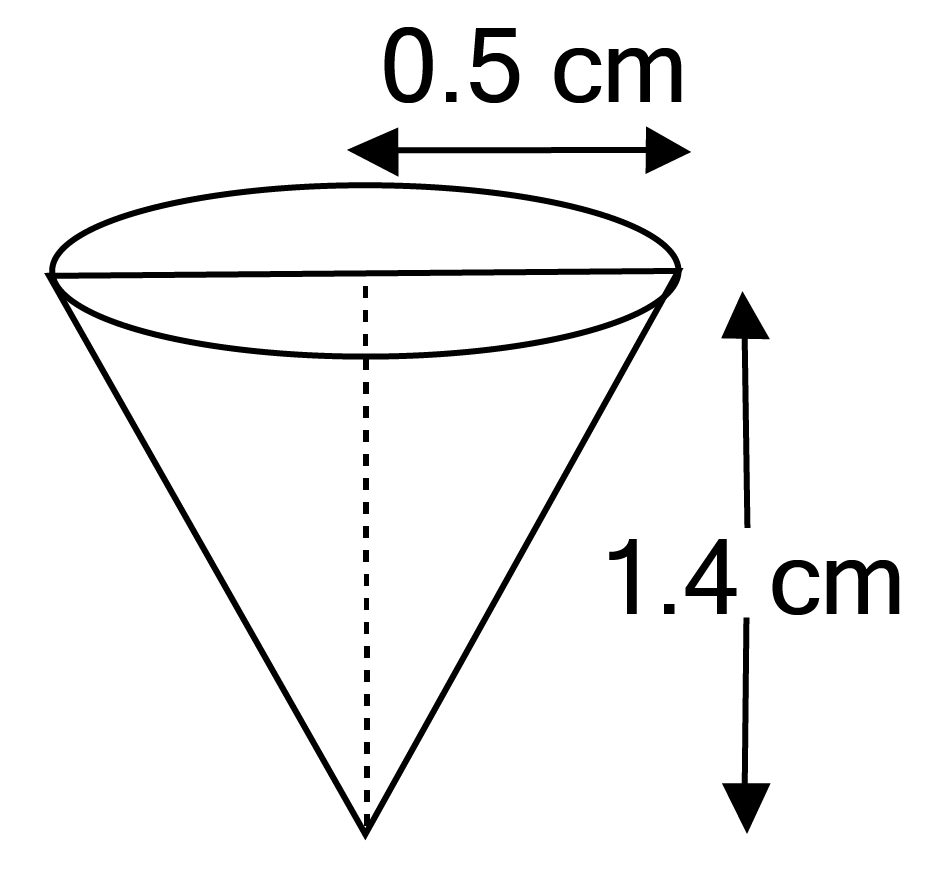
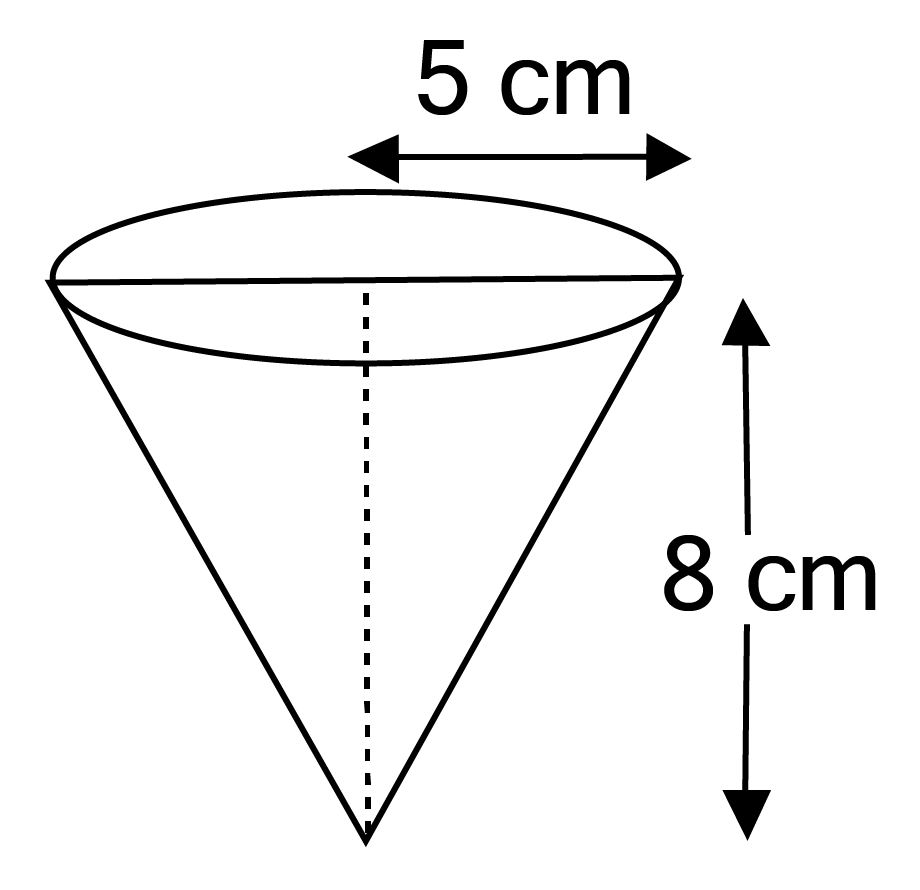
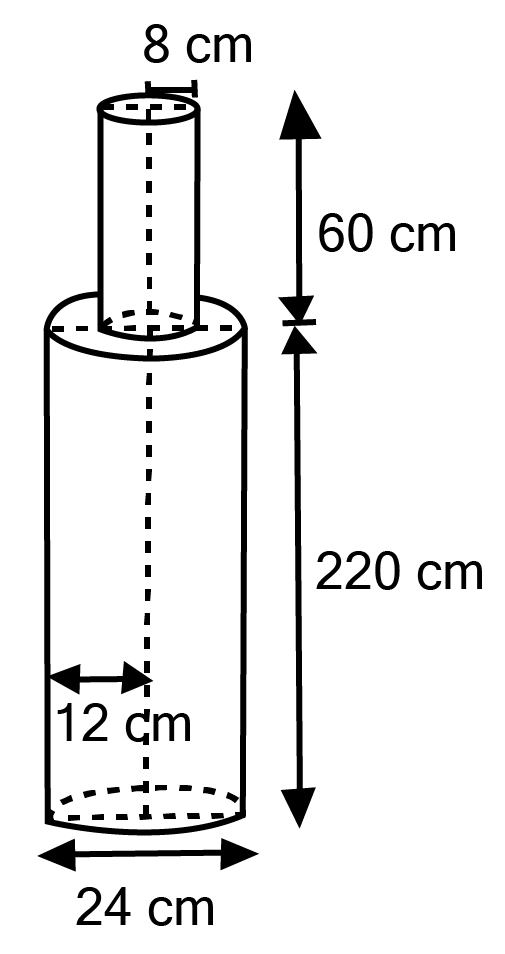
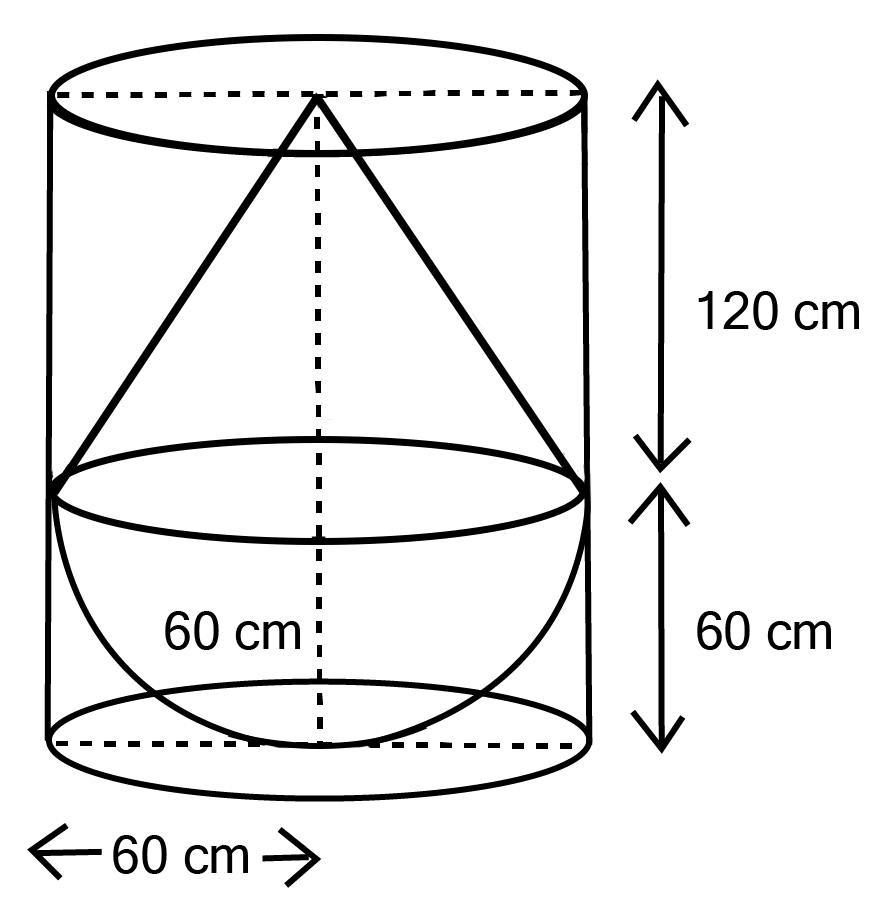
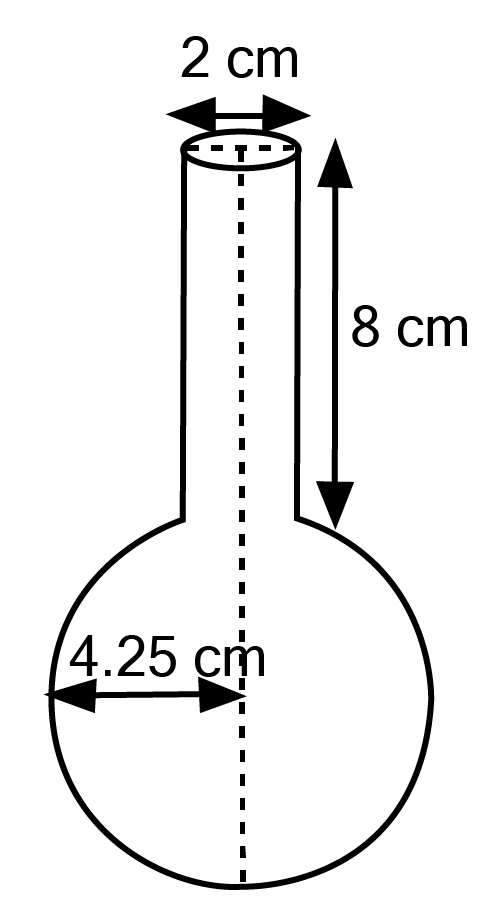
Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 Solutions for Surface Areas and Volumes: FREE PDF
NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Areas And Volumes Exercise 12.2 - 2025-26
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Areas And Volumes Exercise 12.2 - 2025-26
1. Why should I practice NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes Exercise 12.2?
Practicing NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 helps build confidence in solving surface areas and volumes problems accurately and improves problem-solving speed.
2. Where can I find NCERT Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes Exercise 12.2 question answers?
You can find the NCERT Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 question answers on Vedantu with detailed solutions following the latest NCERT board pattern.
3. Do NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes Exercise 12.2 cover all questions?
Yes, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 cover every exercise question, including numerical problems based on surface areas and volumes.
4. How do NCERT Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 solutions help in exams?
NCERT Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 solutions help students understand the correct method for solving surface area and volume questions that commonly appear in board exams.
5. Are the NCERT question answers for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 easy to understand?
Yes, NCERT question answers for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 are explained in a simple and student-friendly manner to make surface areas and volumes concepts easy.
6. Can I use NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes Exercise 12.2 for revision?
Absolutely, NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 are perfect for revision and help strengthen concepts before tests and board exams.
7. Are there formulas included in the NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 answers?
Yes, the NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 include all relevant formulas for surface areas and volumes and show how to apply them in each question.
8. Do board exam questions relate directly to Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2?
Yes, many board exam questions are directly based on or similar to problems from Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2, so practising NCERT Solutions is essential.
9. Can I download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes Exercise 12.2?
Yes, you can download the NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Exercise 12.2 PDF from Vedantu for offline study and revision.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video