
Nitrogen exists as a diatomic molecule and phosphorus as \[{P_4}\]. Why?
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Due to repulsion between the bound atoms, the smaller atoms can make numerous bonds, whereas the large molecule cannot. Applying this concept on the given questions helps in reaching the answer.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Both nitrogen and phosphorus belong to the same family of elements. As a result, their valence shell electrical configurations are identical. They have a lot of chemical features in common because of their electrical arrangement. There are some distinctions between nitrogen and phosphorus, such as size, effective nuclear charge, and so on.
The size of the metal grows as we travel down in the group. The size grows as a group electron is added to the next principal quantum number, increasing the distance between the outermost shell electrons and the nucleus. As a result, the effective nuclear charge falls, and the size grows.
As a result, phosphorus is more abundant than nitrogen. The effective nuclear charge of nitrogen is higher than that of phosphorus.
Because of its tiny size and high effective nuclear charge, nitrogen can establish as many bonds as it wishes to complete its octet with another nitrogen atom. The nitrogen atom has five valence electrons; thus, it needs three more to complete its octant and create a triple bond with another nitrogen atom.
The high effective nuclear charge aids in the binding of a large number of electrons in a tiny space between the two nitrogen atoms. Because of its small size, another nitrogen atom can get close enough to stabilize the diatomic nitrogen molecule, allowing it to live as a diatomic molecule.
Because of its huge size and ineffective nuclear charge, phosphorus is unable to create as many bonds as it would want to complete its octant with another phosphorus atom. When phosphorus forms a triple bond with another phosphorus atom, the repulsion between the two phosphorus atoms becomes so strong that the diatomic phosphorus molecule becomes unstable. As a result, it exists as \[{P_4}\] to complete its octet and reduce repulsion.
The structure of nitrogen is as follows:

Image: Structure of Nitrogen
The structure of \[{P_4}\] is as follows:
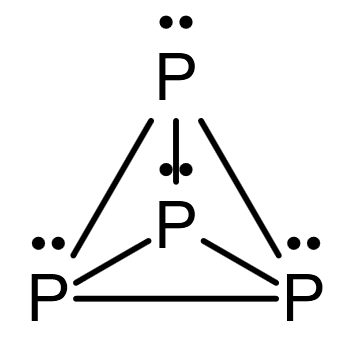
Image: structure of \[{P_4}\]
Note: The stability of a single bond is lower than that of a triple bond. As a result, the triple-bonded nitrogen atoms are closer together than the four single-bonded phosphorus atoms. The advantage of being in the \[{P_4}\] state is that the phosphorus octet is completed. Single bond atoms remain as far apart as feasible to reduce repulsion.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Both nitrogen and phosphorus belong to the same family of elements. As a result, their valence shell electrical configurations are identical. They have a lot of chemical features in common because of their electrical arrangement. There are some distinctions between nitrogen and phosphorus, such as size, effective nuclear charge, and so on.
The size of the metal grows as we travel down in the group. The size grows as a group electron is added to the next principal quantum number, increasing the distance between the outermost shell electrons and the nucleus. As a result, the effective nuclear charge falls, and the size grows.
As a result, phosphorus is more abundant than nitrogen. The effective nuclear charge of nitrogen is higher than that of phosphorus.
Because of its tiny size and high effective nuclear charge, nitrogen can establish as many bonds as it wishes to complete its octet with another nitrogen atom. The nitrogen atom has five valence electrons; thus, it needs three more to complete its octant and create a triple bond with another nitrogen atom.
The high effective nuclear charge aids in the binding of a large number of electrons in a tiny space between the two nitrogen atoms. Because of its small size, another nitrogen atom can get close enough to stabilize the diatomic nitrogen molecule, allowing it to live as a diatomic molecule.
Because of its huge size and ineffective nuclear charge, phosphorus is unable to create as many bonds as it would want to complete its octant with another phosphorus atom. When phosphorus forms a triple bond with another phosphorus atom, the repulsion between the two phosphorus atoms becomes so strong that the diatomic phosphorus molecule becomes unstable. As a result, it exists as \[{P_4}\] to complete its octet and reduce repulsion.
The structure of nitrogen is as follows:

Image: Structure of Nitrogen
The structure of \[{P_4}\] is as follows:

Image: structure of \[{P_4}\]
Note: The stability of a single bond is lower than that of a triple bond. As a result, the triple-bonded nitrogen atoms are closer together than the four single-bonded phosphorus atoms. The advantage of being in the \[{P_4}\] state is that the phosphorus octet is completed. Single bond atoms remain as far apart as feasible to reduce repulsion.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




