
In the ground state of cobalt atom (\[Z = 27\]), number of unpaired electrons and the magnetic nature of cobalt are respectively:
(A) $2$, diamagnetic
(B) $2$, paramagnetic
(C) $3$, diamagnetic
(D) $3$, paramagnetic
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Cobalt is a d block element belonging to group $8$of the periodic table. Para magnetism is a property of an element having at least one unpaired electron. If all the electrons are paired then the element is known to be diamagnetic in nature.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
This is the ground state electronic configuration of cobalt when cobalt is carrying no charge.
The \[4s\] and $3d$ subshell can be represented by a pictorial representation of orbitals as follows
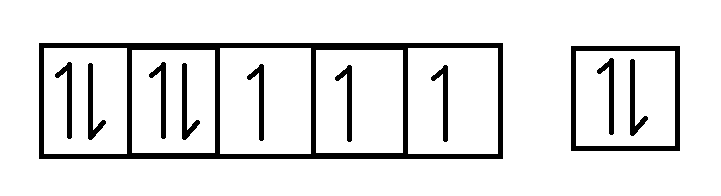
$3d$ \[4s\]
Thus, there are $3$ unpaired electrons in $3d$ subshell whereas all there is one pair of electrons in \[4s\]. hence, it is paramagnetic in nature.
Additional information: The electrons are filled according to two governing principles in chemistry- first the subshell energy is defined by the Aufbau principle and then filling of electrons in the subshell is governed by Hund’s principle.
According to Aufbau principle, the subshell whose energy is less will be filled first and higher energy subshell will be filled after that. The energy order is defined by sum of principle quantum number and azimuthal quantum number.
According to Pauli exclusion principle, electrons are first singly filled in the orbitals and then pairing takes place.
Note: Increase in covalency is due to excitation of electrons. This excitation of electrons can be free as well as forced. $2nd$ period elements do not show excitation because of the absence of low-lying vacant orbitals. Also, expansion of covalency is only possible in $3rd$ period elements when there is charge contraction due to presence of a side atom with greater electronegativity along with low- lying vacant orbitals.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
This is the ground state electronic configuration of cobalt when cobalt is carrying no charge.
The \[4s\] and $3d$ subshell can be represented by a pictorial representation of orbitals as follows

$3d$ \[4s\]
Thus, there are $3$ unpaired electrons in $3d$ subshell whereas all there is one pair of electrons in \[4s\]. hence, it is paramagnetic in nature.
Additional information: The electrons are filled according to two governing principles in chemistry- first the subshell energy is defined by the Aufbau principle and then filling of electrons in the subshell is governed by Hund’s principle.
According to Aufbau principle, the subshell whose energy is less will be filled first and higher energy subshell will be filled after that. The energy order is defined by sum of principle quantum number and azimuthal quantum number.
According to Pauli exclusion principle, electrons are first singly filled in the orbitals and then pairing takes place.
Note: Increase in covalency is due to excitation of electrons. This excitation of electrons can be free as well as forced. $2nd$ period elements do not show excitation because of the absence of low-lying vacant orbitals. Also, expansion of covalency is only possible in $3rd$ period elements when there is charge contraction due to presence of a side atom with greater electronegativity along with low- lying vacant orbitals.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




