
A small cylindrical soft iron piece is kept in a galvanometer so that
A. A radial uniform magnetic fields is produced
B. A uniform magnetic fields is produced
C. There is a steady deflection of the coil
D. All of these
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: A moving coil galvanometer is simply a very sensitive ammeter, which is something we must first understand. It recognises extremely tiny currents in circuits. Now that we are aware of the components and materials used in moving coil galvanometers, we must relate that knowledge to the type of magnetic field those devices generate.
Complete step by step solution:
Based on the idea that a coil carrying current suffers a torque when it is put in a magnetic field, a moving coil galvanometer operates. It basically consists of a PQRS coil wound around a non-conducting, rectangular or cylindrical, ivory or bamboo frame. This coil is connected by phosphor bronze wire to the pole elements of a strong horseshoe magnet, NS.
A radial field is produced by the poles of the magnet being bent. The lower end of the coil has a phosphor-bronze wire spring attached to it. Two terminals, $T_2$ and $T_1$, are attached to the spring and free ends of phosphor bronze wire, respectively, on the top of the instrument's casing. L has a soft iron core.
An extremely small mirror M is used to secure the suspension wire. Using a lamp and scale setup, the coil's deflection can be recorded. The entire apparatus is contained in a non-metallic container.
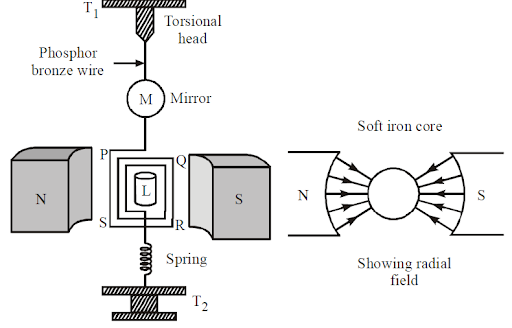
A moving coil galvanometer has a soft iron core. If we utilize a soft iron core, the magnetic lines of force are drawn to it, increasing the magnetic field's strength. Galvanometer sensitivity thus rises. Additionally, the magnetic field is made radial by using a soft iron core (i.e the plane of the coil will be always parallel to the direction of the magnetic field).
Hence, option D is the correct answer.
Note: A moving coil galvanometer uses a soft iron core that is naturally ferromagnetic. This makes sure that the magnetic field lines generated in the core are increased, which in turn increases the moving coil galvanometer's sensitivity. The torque felt by the needle would be much reduced and the sensitivity of the moving coil galvanometer would drop if the magnetic field inside the device were kept consistent.
Complete step by step solution:
Based on the idea that a coil carrying current suffers a torque when it is put in a magnetic field, a moving coil galvanometer operates. It basically consists of a PQRS coil wound around a non-conducting, rectangular or cylindrical, ivory or bamboo frame. This coil is connected by phosphor bronze wire to the pole elements of a strong horseshoe magnet, NS.
A radial field is produced by the poles of the magnet being bent. The lower end of the coil has a phosphor-bronze wire spring attached to it. Two terminals, $T_2$ and $T_1$, are attached to the spring and free ends of phosphor bronze wire, respectively, on the top of the instrument's casing. L has a soft iron core.
An extremely small mirror M is used to secure the suspension wire. Using a lamp and scale setup, the coil's deflection can be recorded. The entire apparatus is contained in a non-metallic container.

A moving coil galvanometer has a soft iron core. If we utilize a soft iron core, the magnetic lines of force are drawn to it, increasing the magnetic field's strength. Galvanometer sensitivity thus rises. Additionally, the magnetic field is made radial by using a soft iron core (i.e the plane of the coil will be always parallel to the direction of the magnetic field).
Hence, option D is the correct answer.
Note: A moving coil galvanometer uses a soft iron core that is naturally ferromagnetic. This makes sure that the magnetic field lines generated in the core are increased, which in turn increases the moving coil galvanometer's sensitivity. The torque felt by the needle would be much reduced and the sensitivity of the moving coil galvanometer would drop if the magnetic field inside the device were kept consistent.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry




