
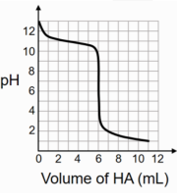
A 0.1 M weak base (B) solution is titrated with 0.1 M of a strong acid (HA). The image below depicts the change in pH of the solution as a function of the amount of HA added. What is the \[p{k_b}\] of the base? The neutralisation reaction is given by \[B + HA - \]\[B{H^ + } + {A^ - }\].
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In general, titration is a type of quantitative analysis that involves measuring the volume of a chemical species' solution in a suitable solvent in order to estimate its quantity. The Law of Equivalence underpins this strategy. As a result, titration can be defined as the process of calculating the volume of reagents by bringing a specific reaction to a close. The titrant is the solution used in titration that has an accurate concentration and the titrated substance is the substance whose volume needs to be determined.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The given chemical reaction is \[B + HA \to B{H^ + } + {A^ - }\]
At Equivalence Point:
Total vol. = 12 ml
Concentration of salt = \[\dfrac{{0.6}}{{12}}\]
pH = 6 = \[\sqrt {\dfrac{{{k_w}}}{{{k_b}}}} \times c = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 14}} \times 0.6}}{{{k_b} \times 12}}} \]
{ pH = 0.6, \[[{H^ + }] = {10^{ - 6}}\]}
\[ \Rightarrow \]pH = 0.6 = \[\sqrt {\dfrac{{{k_w}}}{{{k_b}}} \times \dfrac{{0.1 \times 6}}{{12}}} \]
\[{10^{ - 12}} = \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 14}} \times {{10}^{ - 1}}}}{{{k_b}}} \times \dfrac{1}{2}\]
$ \Rightarrow {k_b} = 5 \times {10^{ - 4}} \\$
$ \Rightarrow p{k_b} = - \log {k_b} = - \log (5 \times {10^{ - 4}}) = - \log 5 + 4\log 10 \\$
$ \Rightarrow p{k_b} = 4 - 0.7 \\$
$ \Rightarrow p{k_b} = 3.3 \\ $
Note: \[p{k_b}\] is the symbol which is used to estimate the alkalinity of the molecule. It is used to determine the base's strength. The lesser the \[p{k_b}\] value, the more potential the base will be having to dilute an acid. It is equivalent to the negative of logarithm of the base dissociation constant i.e. \[{k_b}\].
\[p{k_b} = - \log {k_b}\]; \[{k_b}\] or base dissociation constant is the symbol used to estimate a base’s strength. It indicates the amount of dissociation of a base in an aqueous solution. \[{k_b}\] is used to distinguish a strong base from a weaker one. More the value of \[{k_b}\] more would be its dissociation.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
The given chemical reaction is \[B + HA \to B{H^ + } + {A^ - }\]
| Conditions | B (0.1 M) | HA (0.1 M) | pH |
| At V = 0 ml | 0 ml | 13 | |
| At V = 3 ml | 3 ml → 50% neutralisation | 11 | |
| At V = 6 ml | 6 ml → Equivalence Point | 3 to 9 |
At Equivalence Point:
| B | HA | BH+ | A- |
| $0.1 \times 6$ = 0.6 mmol | $0.1 \times 6$ = 0.6 mmol | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0.6 mmol |
Total vol. = 12 ml
Concentration of salt = \[\dfrac{{0.6}}{{12}}\]
pH = 6 = \[\sqrt {\dfrac{{{k_w}}}{{{k_b}}}} \times c = \sqrt {\dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 14}} \times 0.6}}{{{k_b} \times 12}}} \]
{ pH = 0.6, \[[{H^ + }] = {10^{ - 6}}\]}
\[ \Rightarrow \]pH = 0.6 = \[\sqrt {\dfrac{{{k_w}}}{{{k_b}}} \times \dfrac{{0.1 \times 6}}{{12}}} \]
\[{10^{ - 12}} = \dfrac{{{{10}^{ - 14}} \times {{10}^{ - 1}}}}{{{k_b}}} \times \dfrac{1}{2}\]
$ \Rightarrow {k_b} = 5 \times {10^{ - 4}} \\$
$ \Rightarrow p{k_b} = - \log {k_b} = - \log (5 \times {10^{ - 4}}) = - \log 5 + 4\log 10 \\$
$ \Rightarrow p{k_b} = 4 - 0.7 \\$
$ \Rightarrow p{k_b} = 3.3 \\ $
Note: \[p{k_b}\] is the symbol which is used to estimate the alkalinity of the molecule. It is used to determine the base's strength. The lesser the \[p{k_b}\] value, the more potential the base will be having to dilute an acid. It is equivalent to the negative of logarithm of the base dissociation constant i.e. \[{k_b}\].
\[p{k_b} = - \log {k_b}\]; \[{k_b}\] or base dissociation constant is the symbol used to estimate a base’s strength. It indicates the amount of dissociation of a base in an aqueous solution. \[{k_b}\] is used to distinguish a strong base from a weaker one. More the value of \[{k_b}\] more would be its dissociation.
Recently Updated Pages
Hess Law of Constant Heat Summation: Definition, Formula & Applications

Disproportionation Reaction: Definition, Example & JEE Guide

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Hydrocarbons Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 9 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Thermodynamics Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 5 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Equilibrium Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 6 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Organic Chemistry Some Basic Principles And Techniques Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 8 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Chemistry Chapter 7 Redox Reactions (2025-26)




