Science Notes for Chapter 14 Natural Resources Class 9 - FREE PDF Download
CBSE Notes Class 9 Science Chapter 14 - Natural Resources - 2025-26
FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 9 Science Chapter 14 - Natural Resources - 2025-26
1. What is a quick summary of the key concepts in CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 14, Natural Resources?
This chapter provides a summary of Earth's essential resources required for life. The key concepts for revision include the three main spheres of Earth (lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere), the composition and role of air and water, and the formation of soil. It also covers the major biogeochemical cycles (Water, Nitrogen, Carbon, Oxygen), the Greenhouse Effect, and the importance and depletion of the Ozone layer.
2. What are the three main natural resources that this chapter focuses on for revision?
For a quick revision of this chapter, focus on the three primary natural resources essential for life on Earth:
- Air (Atmosphere): A mixture of gases like nitrogen, oxygen, and carbon dioxide that regulates temperature and is vital for respiration and photosynthesis.
- Water (Hydrosphere): Covers a majority of the Earth's surface and is essential for all physiological processes in living organisms.
- Soil (Lithosphere): The outer crust of the Earth, which provides nutrients and anchorage for plants and supports terrestrial life.
3. How does the atmosphere act as a blanket to regulate Earth's temperature?
The atmosphere acts as a protective blanket because air is a poor conductor of heat. During the day, it prevents a sudden and extreme rise in temperature by filtering sunlight. At night, it slows down the escape of heat from the Earth's surface into outer space, preventing the temperature from dropping drastically. This moderation of temperature is crucial for sustaining life.
4. What is the core concept behind the water cycle for a quick revision?
The core concept of the water cycle is the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. The key processes to remember for revision are evaporation (water turns into vapour), condensation (vapour forms clouds), and precipitation (water falls back as rain or snow). Transpiration from plants also contributes significantly to atmospheric water vapour, linking forests directly to the water cycle.
5. What are the key points to remember about soil formation?
For revision purposes, remember that soil formation is a very slow process influenced by several factors. The key points are:
- Weathering of Rocks: The sun, water, wind, and living organisms break down large parent rocks into smaller particles over thousands of years.
- Role of Living Organisms: Lichens, mosses, and microbes break down rock surfaces and their decaying organic matter (humus) enriches the soil, making it fertile.
6. Why are biogeochemical cycles a crucial topic for revision in this chapter?
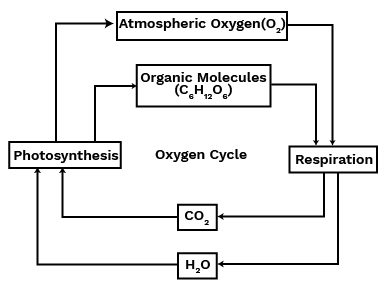
Biogeochemical cycles are a crucial revision topic because they explain the dynamic transfer of matter and energy between the biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) components of an ecosystem. Understanding these cycles helps connect individual concepts like respiration (carbon cycle), protein synthesis (nitrogen cycle), and photosynthesis (oxygen and carbon cycles) into a complete, interconnected system that sustains all life on the planet.
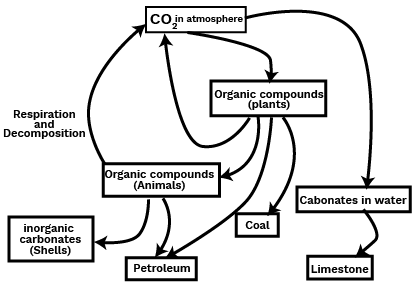
7. How does the carbon cycle connect the concepts of the greenhouse effect and fossil fuels?
The carbon cycle shows how carbon moves through the environment. Respiration and burning of fossil fuels release carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere. While CO2 is essential, an excess amount traps heat, causing the greenhouse effect and global warming. This demonstrates how disrupting one part of the carbon cycle (burning stored carbon in fossil fuels) directly impacts the atmosphere's temperature-regulating function.
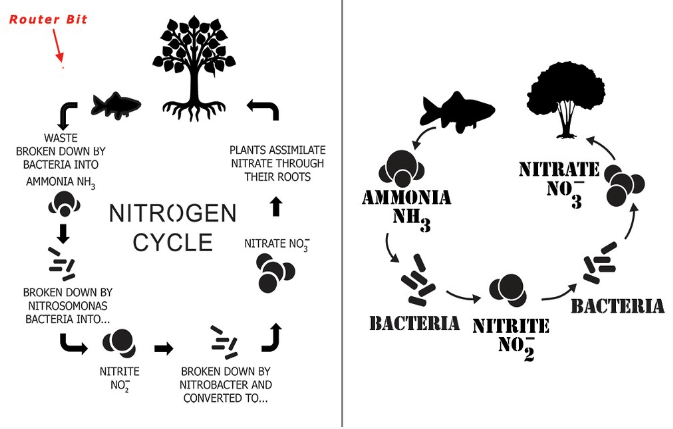
8. What is the fundamental difference between the nitrogen and carbon cycles that is important for revision?
The fundamental difference is that while most organisms can use atmospheric carbon dioxide directly for processes like photosynthesis, they cannot use atmospheric nitrogen directly. Nitrogen gas (N2) must first be converted into usable forms like nitrates and nitrites through a process called nitrogen fixation, primarily carried out by specific bacteria. This extra step makes the nitrogen cycle unique and vital for producing proteins and nucleic acids.




















 Watch Video
Watch Video