Physics Notes for Chapter 1 Units And Measurements Class 11 - FREE PDF Download
FAQs on CBSE Notes Class 11 Physics Chapter 1 - Units And Measurements - 2025-26
1. What is a quick summary of the key concepts in the Class 11 chapter on Units and Measurements?
This chapter establishes the foundation of physics by introducing the need for standard units. Key concepts to revise include the International System of Units (SI), distinguishing between fundamental and derived units, understanding the concepts of accuracy and precision, applying dimensional analysis to check equations and derive relationships, and correctly using significant figures and error analysis in calculations.
2. What are the seven fundamental quantities and their SI base units that I must remember?
For a quick recap, you should memorise the seven fundamental quantities as defined by the SI system and their corresponding base units:
- Length - meter (m)
- Mass - kilogram (kg)
- Time - second (s)
- Electric Current - ampere (A)
- Thermodynamic Temperature - kelvin (K)
- Amount of Substance - mole (mol)
- Luminous Intensity - candela (cd)
3. How are physical units categorized for revision?
For revision, you can categorise all physical units into two main types:
- Fundamental Units: These are the base units for the seven fundamental quantities (like meter, kilogram, second) that are independent of each other.
- Derived Units: These are units that are formed by combining one or more fundamental units. For example, the unit for speed (m/s) is derived from the fundamental units of length (meter) and time (second).
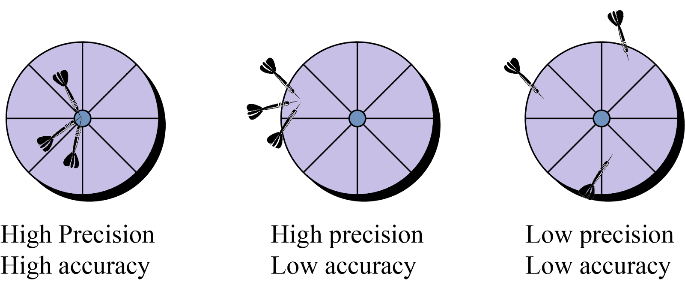
4. What is the core difference between accuracy and precision in measurements?
The key difference to remember is that accuracy refers to how close a measured value is to the true or accepted value. In contrast, precision refers to how close multiple measurements of the same quantity are to each other, regardless of their accuracy. An instrument can be precise without being accurate.
5. How does the principle of homogeneity of dimensions help in checking the correctness of a physical equation?
The principle of homogeneity states that a physically valid equation must have the same dimensions on both sides of the equals sign. This is because we can only add, subtract, or equate quantities that have the same physical nature. For revision, remember this simple check: if the dimensions of the Left Hand Side (LHS) do not match the dimensions of the Right Hand Side (RHS), the equation is dimensionally incorrect and therefore physically wrong.
6. What are the basic rules for determining significant figures that I should recap?
To quickly revise significant figures, focus on these key rules:
- All non-zero digits are significant.
- Zeros between two non-zero digits are significant (e.g., 101 has 3).
- Leading zeros (e.g., 0.05) are not significant.
- Trailing zeros are significant only if there is a decimal point (e.g., 5.00 has 3, but 500 has 1).
7. Why can't dimensional analysis determine the value of dimensionless constants in a formula?
This is a key limitation to remember. Dimensional analysis works by comparing the base dimensions (M, L, T, etc.) on both sides of an equation. Dimensionless constants (like π, 1/2, or k) have no dimensions by definition. Therefore, the method of equating powers of M, L, and T cannot provide any information about their presence or their value. Their values must be determined through experimentation or more advanced theory.
8. How should I summarise the concepts of absolute, relative, and percentage errors for quick revision?
For a quick summary, think of them as a progression:
- Absolute Error is the basic difference between the true value and a measured value. It tells you the magnitude of the error in the same units as the quantity.
- Relative Error provides context by comparing the absolute error to the true value (Relative Error = Absolute Error / True Value). It is a dimensionless ratio.
- Percentage Error is simply the relative error expressed as a percentage (Relative Error × 100). It is the most common way to express experimental uncertainty.
9. Beyond checking equations, what are the other key applications of dimensional analysis?
While checking correctness is a primary use, dimensional analysis has two other powerful applications you should revise:
- Deriving relationships between physical quantities. If you know how one quantity depends on others, you can deduce the form of the equation connecting them (e.g., deriving the formula for the time period of a simple pendulum).
- Converting units from one system to another. By understanding the dimensional formula of a quantity, you can easily find the conversion factor between different unit systems (e.g., converting Newtons to dynes).
10. How do these revision notes for Units and Measurements align with the latest CBSE 2025-26 syllabus?
These revision notes are carefully crafted to cover all the core concepts prescribed in the CBSE syllabus for the 2025-26 academic year. They focus on the essential topics for Class 11 Physics, Chapter 1, including the SI system, significant figures, error analysis, and dimensional analysis, ensuring your revision is comprehensive and aligned with board requirements.