
Who discovered central dogma?
Answer
536.1k+ views
Hint: Molecular biology's central dogma describes the movement of genetic material, from DNA to RNA, to create a protein, a functional product. It was discovered by the scientists who discovered the double helical structure of DNA.
Complete answer:
The 'Central Dogma' is the method of translating the instructions in DNA into a functional product. It was first suggested by the discoverer of the structure of DNA, Francis Crick in the year 1958. Replication, transcription, and translation follow the process. Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British biologist who played a major role in describing the double helical structure of the DNA molecule. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in the year 1962. He also describes the structure and functions of nucleic acids and has summarised the idea of central dogma.
The central dogma suggests that the information needed to produce all our proteins is found in DNA, and that RNA is a messenger carrying this data to the ribosomes. The ribosomes are responsible for the coding of information and translate into the functional product. The mechanism by which the instructions for DNA are translated into a functional product is called gene expression.
The dogma classes these into 3 gatherings of 3: three general exchanges (accepted to happen regularly in many cells), three exceptional exchanges (known to happen, yet just under explicit conditions if there should be an occurrence of some infections or during a lab), and three obscure exchanges (accepted never to happen). The overall exchanges portray the traditional flow of biological data: DNA is frequently duplicated to DNA (DNA replication), DNA data are regularly replicated into mRNA (transcription), and proteins can be combined utilizing the information in mRNA as a format (translation).
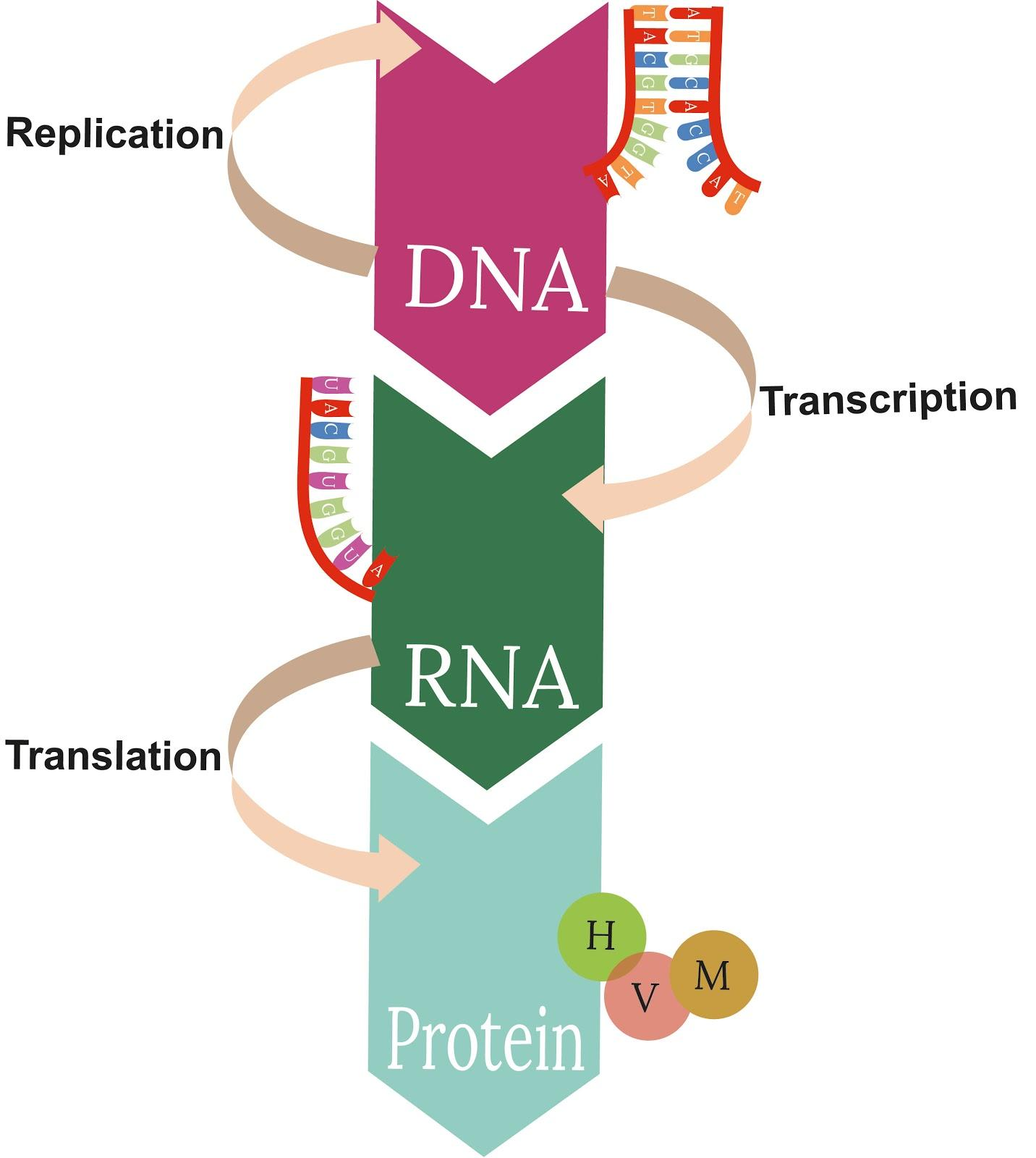
Central Dogma
Note:
Instructions are encoded in DNA for producing proteins with the right sequence of amino acids. This states that it cannot get out again once "information" has passed into protein. More specifically, information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid or from nucleic acid to protein can be transferable, but it cannot be transferred from protein to nucleic acid or from protein to protein.
Complete answer:
The 'Central Dogma' is the method of translating the instructions in DNA into a functional product. It was first suggested by the discoverer of the structure of DNA, Francis Crick in the year 1958. Replication, transcription, and translation follow the process. Francis Harry Compton Crick was a British biologist who played a major role in describing the double helical structure of the DNA molecule. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in the year 1962. He also describes the structure and functions of nucleic acids and has summarised the idea of central dogma.
The central dogma suggests that the information needed to produce all our proteins is found in DNA, and that RNA is a messenger carrying this data to the ribosomes. The ribosomes are responsible for the coding of information and translate into the functional product. The mechanism by which the instructions for DNA are translated into a functional product is called gene expression.
The dogma classes these into 3 gatherings of 3: three general exchanges (accepted to happen regularly in many cells), three exceptional exchanges (known to happen, yet just under explicit conditions if there should be an occurrence of some infections or during a lab), and three obscure exchanges (accepted never to happen). The overall exchanges portray the traditional flow of biological data: DNA is frequently duplicated to DNA (DNA replication), DNA data are regularly replicated into mRNA (transcription), and proteins can be combined utilizing the information in mRNA as a format (translation).

Central Dogma
Note:
Instructions are encoded in DNA for producing proteins with the right sequence of amino acids. This states that it cannot get out again once "information" has passed into protein. More specifically, information from nucleic acid to nucleic acid or from nucleic acid to protein can be transferable, but it cannot be transferred from protein to nucleic acid or from protein to protein.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




