
Why do we use a multiplier with a voltmeter?
Answer
232.5k+ views
Hint: The device used to measure the electric potential difference between two locations in an electric circuit is called a voltmeter. It has parallel connections. It typically has a high resistance such that it uses very little circuit current. A galvanometer and series resistor can be used to make analogue voltmeters, which move a pointer across a scale in proportion to the voltage detected. Microvolts or less can be measured using metres that use amplifiers.
Complete answer:
By attaching a multiplier, the voltage that indicates the voltmeter's range may be raised. A resistor is all that the multiplier is. To raise the voltmeter's resistance, the multiplier and voltmeter are linked in series.
In that they convert AC voltages to DC voltages for use in a variety of electrical and electronic circuit applications, such as microwave ovens, powerful electric field coils for cathode-ray tubes, electrostatic and high voltage test equipment, etc., where it is necessary to have a very high DC voltage generated from a relatively low AC supply, voltage multipliers are similar in many ways to rectifiers.
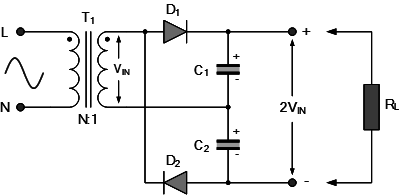
A rectifier circuit's DC output voltage (Vdc) is typically constrained by the sinusoidal input voltage's peak value. However, by combining rectifier diodes and capacitors, we may double this input peak voltage to produce a DC output that is an odd or even multiple of the AC input voltage peak voltage. A simple voltage multiplier circuit is shown below.
Note: Voltmeters come in a broad variety of designs, some powered independently (by a battery, for example), and some powered directly by the source of the voltage being measured. Generators and other stationary equipment are monitored by instruments that are permanently positioned in a panel. Standard test tools are used in electrical and electronic work and are often portable equipment with a multimeter that can also measure current and resistance. Any measurement that can be converted to a voltage, such as pressure, temperature, flow, or level in a chemical processing facility, can be shown on a properly calibrated metre.
Complete answer:
By attaching a multiplier, the voltage that indicates the voltmeter's range may be raised. A resistor is all that the multiplier is. To raise the voltmeter's resistance, the multiplier and voltmeter are linked in series.
In that they convert AC voltages to DC voltages for use in a variety of electrical and electronic circuit applications, such as microwave ovens, powerful electric field coils for cathode-ray tubes, electrostatic and high voltage test equipment, etc., where it is necessary to have a very high DC voltage generated from a relatively low AC supply, voltage multipliers are similar in many ways to rectifiers.
A rectifier circuit's DC output voltage (Vdc) is typically constrained by the sinusoidal input voltage's peak value. However, by combining rectifier diodes and capacitors, we may double this input peak voltage to produce a DC output that is an odd or even multiple of the AC input voltage peak voltage. A simple voltage multiplier circuit is shown below.

Note: Voltmeters come in a broad variety of designs, some powered independently (by a battery, for example), and some powered directly by the source of the voltage being measured. Generators and other stationary equipment are monitored by instruments that are permanently positioned in a panel. Standard test tools are used in electrical and electronic work and are often portable equipment with a multimeter that can also measure current and resistance. Any measurement that can be converted to a voltage, such as pressure, temperature, flow, or level in a chemical processing facility, can be shown on a properly calibrated metre.
Recently Updated Pages
Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals Important Concepts and Tips for JEE

How to find Oxidation Number - Important Concepts for JEE

How Electromagnetic Waves Are Formed Explained Simply

Household Electricity: Basics, Usage & Safety Explained

Hinge Force Explained: Formula, Examples & Applications

Half Life of Zero Order Reaction for JEE

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




