
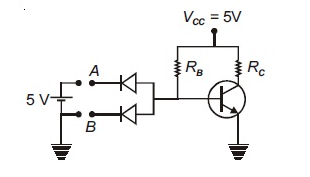
Figure shows practical realization of logic gates. Identify the logic gate
(A) NAND
(B) NOR
(C) XOR
(D) XNOR
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: We can assume the possible cases for point A and B, observe the output of the transistor for each case then match it with the truth table of the gates of NAND, NOR, XOR and XNOR options to get the answer.
Complete step by step answer:
As shown in the figure, point A and B can be at 0 (level 0) or 5V (level 1) with the help of battery.
There are four possible cases- when both A and B are earthed, when A is connected and B is earthed, when B is connected and A is earthed, when both A and B are connected to the battery.
Let us take a possibility - when A is connected to the positive terminal of the battery and B is earthed (A=1 and B=0) then the upper diode is reversed biased and the lower one is forward biased. Due to voltage difference the base current will flow. Hence current will flow in the collector region of the transistor and we will get an output as 1.
When both A and B are connected then diodes are off hence at the end of base resistance the potential will be zero. Hence, the transistor will be saturated, and the output will be 0.
If we check for the remaining two possibilities, we see that the truth table obtained is that of NAND gate.
Hence, the correct option is A. NAND
Note:
On observing carefully, we can see that NAND is nothing but the complement of AND gate. NAND is also known as a universal gate along with NOR as both these logic gates can be used to produce different gates.
Complete step by step answer:
As shown in the figure, point A and B can be at 0 (level 0) or 5V (level 1) with the help of battery.
There are four possible cases- when both A and B are earthed, when A is connected and B is earthed, when B is connected and A is earthed, when both A and B are connected to the battery.
Let us take a possibility - when A is connected to the positive terminal of the battery and B is earthed (A=1 and B=0) then the upper diode is reversed biased and the lower one is forward biased. Due to voltage difference the base current will flow. Hence current will flow in the collector region of the transistor and we will get an output as 1.
When both A and B are connected then diodes are off hence at the end of base resistance the potential will be zero. Hence, the transistor will be saturated, and the output will be 0.
If we check for the remaining two possibilities, we see that the truth table obtained is that of NAND gate.
Hence, the correct option is A. NAND
Note:
On observing carefully, we can see that NAND is nothing but the complement of AND gate. NAND is also known as a universal gate along with NOR as both these logic gates can be used to produce different gates.
Recently Updated Pages
Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




