
Consider the following statements: For non-empty sets. A, B and C
1. \[A - \left( {B - C} \right) = \left( {A - B} \right) \cup C\]
2. \[A - (B \cup C) = \left( {A - B} \right) - C\]
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
A) 1 Only
B) 2 Only
C) Both 1 and 2
D) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In this question, we have to find which of the given condition is correct. In order to find this concept of Venn diagram is used. Apply concept of Venn diagram on given options to get the correct option.
Formula used: In this question we are going to use the Venn diagram. This diagram give the relation between various set and their subset.
Complete step by step solution: Draw a Venn-diagram taking three intersecting sets A, B and C under a universal set U. After intersection eight regions will be developed.
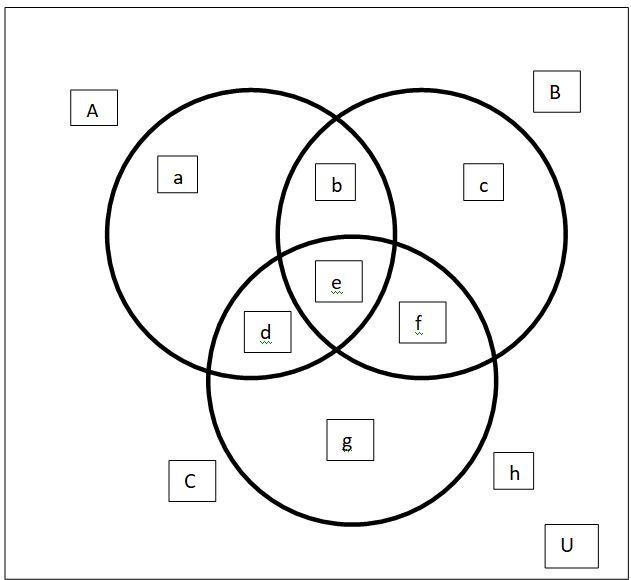
Now we have \[A - \left( {B - C} \right) = \left( {A - B} \right) \cup C\], \[A - (B \cup C) = \left( {A - B} \right) - C\]
First statement: \[A - \left( {B - C} \right) = \left( {A - B} \right) \cup C\]
LHS contain only a while RHS contain a,d,c
Therefore First statement is wrong
Second Statement: \[A - (B \cup C) = \left( {A - B} \right) - C\]
LHS contain only a and RHS also contain a
Therefore statement second is correct.
Thus, Option (B) is correct.
Note: Here we must remember the algebra used in Venn diagram.
Some important properties of Sets are given below:
A. Idempotent Law is given as
(i) Union of two same sets \[A{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}A{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}A\]
(ii) Intersection of two same sets \[A{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}A{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}A\]
B. Associative Law is given as
(i) \[\left( {A{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}B} \right){\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}C{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}A{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}\left( {B{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}C} \right)\]
(ii) \[\left( {A{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}B} \right){\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}C{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}A{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}\left( {B{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}C} \right)\]
C. Commutative Law is given as
(i) \[A{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}B{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}B{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}A\]
(ii) \[A{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}B{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}B{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}A\]
D. Distributive law is given as
(i) \[A{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}\left( {B{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}C} \right){\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}\left( {A{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}B} \right){\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}\left( {A{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}C} \right)\]
(ii) \[A{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}\left( {B{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}C} \right){\rm{ }} = \left( {A{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}B} \right){\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}\left( {A{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}C} \right)\]
Where A, B, C are set or subset of any universal set
E. De Morgan’s law is given as
(i) \[{\left( {A{\rm{ }} \cup B} \right)^c} = {A^c} \cap {\rm{ }}{B^c}\]
(ii) \[{\left( {A{\rm{ }} \cap B} \right)^c} = {A^c} \cup {\rm{ }}{B^c}\]
Where, \[{A^c},{B^c}\] is complement of set A and B respectively
Formula used: In this question we are going to use the Venn diagram. This diagram give the relation between various set and their subset.
Complete step by step solution: Draw a Venn-diagram taking three intersecting sets A, B and C under a universal set U. After intersection eight regions will be developed.

Now we have \[A - \left( {B - C} \right) = \left( {A - B} \right) \cup C\], \[A - (B \cup C) = \left( {A - B} \right) - C\]
First statement: \[A - \left( {B - C} \right) = \left( {A - B} \right) \cup C\]
LHS contain only a while RHS contain a,d,c
Therefore First statement is wrong
Second Statement: \[A - (B \cup C) = \left( {A - B} \right) - C\]
LHS contain only a and RHS also contain a
Therefore statement second is correct.
Thus, Option (B) is correct.
Note: Here we must remember the algebra used in Venn diagram.
Some important properties of Sets are given below:
A. Idempotent Law is given as
(i) Union of two same sets \[A{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}A{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}A\]
(ii) Intersection of two same sets \[A{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}A{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}A\]
B. Associative Law is given as
(i) \[\left( {A{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}B} \right){\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}C{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}A{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}\left( {B{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}C} \right)\]
(ii) \[\left( {A{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}B} \right){\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}C{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}A{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}\left( {B{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}C} \right)\]
C. Commutative Law is given as
(i) \[A{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}B{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}B{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}A\]
(ii) \[A{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}B{\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}B{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}A\]
D. Distributive law is given as
(i) \[A{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}\left( {B{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}C} \right){\rm{ }} = {\rm{ }}\left( {A{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}B} \right){\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}\left( {A{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}C} \right)\]
(ii) \[A{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}\left( {B{\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}C} \right){\rm{ }} = \left( {A{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}B} \right){\rm{ }} \cup {\rm{ }}\left( {A{\rm{ }} \cap {\rm{ }}C} \right)\]
Where A, B, C are set or subset of any universal set
E. De Morgan’s law is given as
(i) \[{\left( {A{\rm{ }} \cup B} \right)^c} = {A^c} \cap {\rm{ }}{B^c}\]
(ii) \[{\left( {A{\rm{ }} \cap B} \right)^c} = {A^c} \cup {\rm{ }}{B^c}\]
Where, \[{A^c},{B^c}\] is complement of set A and B respectively
Recently Updated Pages
Geometry of Complex Numbers Explained

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 12 Limits and Derivatives (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 11 Maths Chapter 10 Conic Sections (2025-26)

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




