Stepwise Answers, Key Diagrams & Important Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 7
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 7 Science Chapter 7 Adolescence A Stage Of Growth And Change - 2025-26
1. What are the types of heat transfer in nature?
Heat transfer in nature occurs through three main processes: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction happens through direct contact, convection occurs in fluids (liquids and gases), and radiation transfers heat through electromagnetic waves.
2. How is heat transferred through solids?
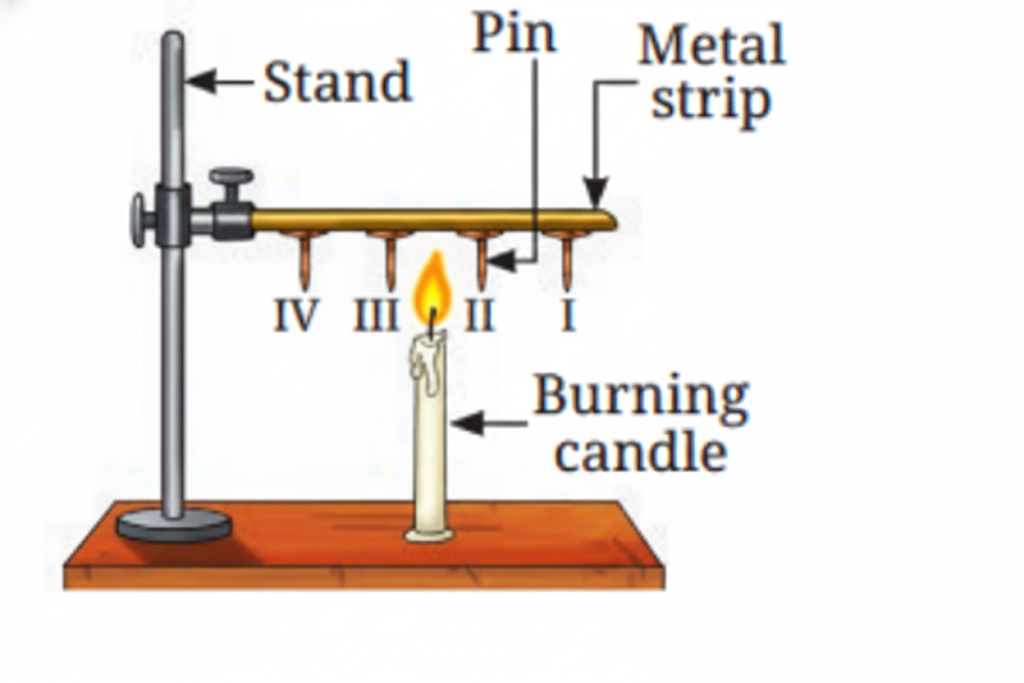
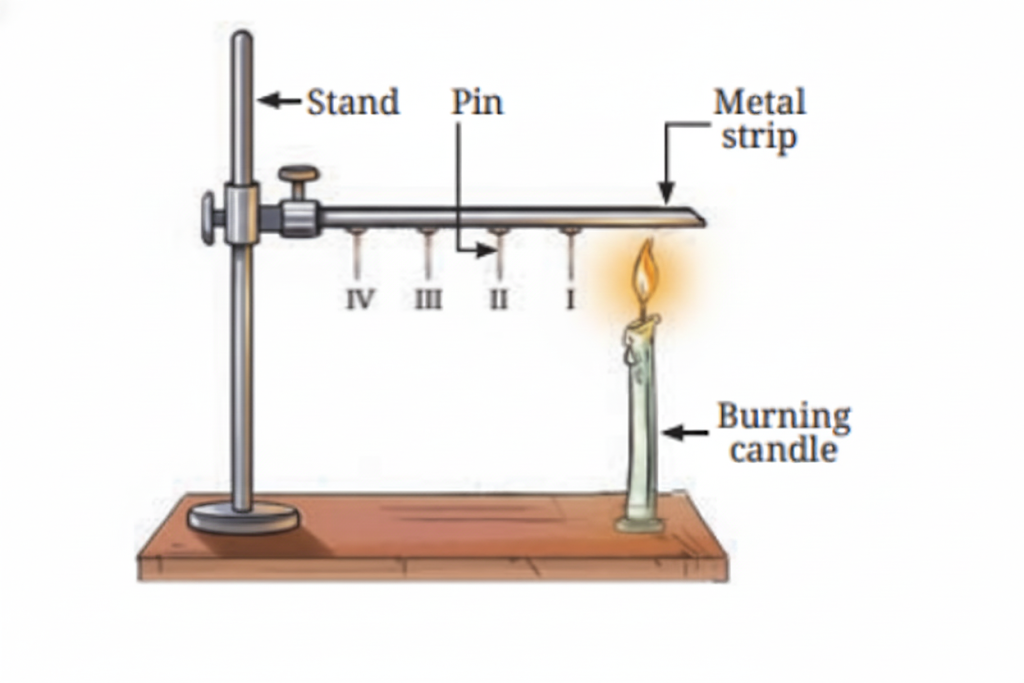
Heat is transferred through solids by conduction. During conduction, heat is passed from one particle to the next in a solid material. The particles themselves remain in place, but the heat energy moves through them.
3. Why does smoke rise?
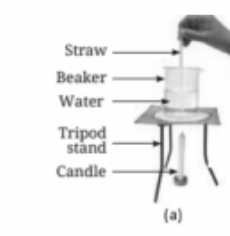
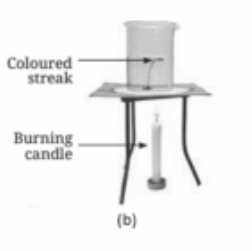
Smoke rises because hot air is lighter than cooler air. As the smoke consists of warm gases, it rises upward due to convection, where the warmer, lighter air rises and is replaced by cooler, denser air.
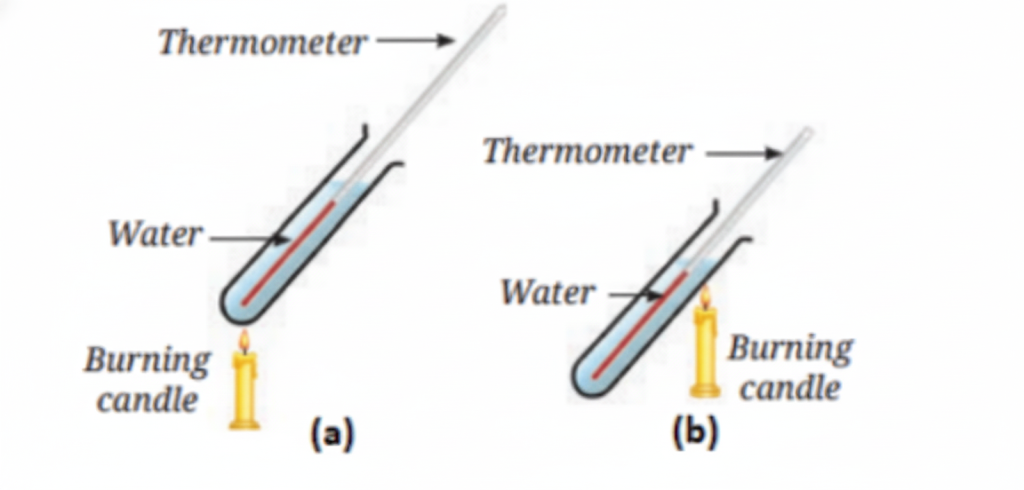
4. Why is water a better conductor of heat than air?
Water is a better conductor of heat than air because water molecules are closer together, allowing heat to transfer more efficiently between them. Air, on the other hand, has large spaces between its molecules, making it a poor conductor of heat.
5. How does heat transfer through liquids?
Heat in liquids is transferred through convection. As a liquid is heated, the warmer, less dense part rises, and the cooler, denser part sinks, creating a circular movement of the liquid known as convection currents.
6. How does heat from the Sun reach the Earth?
Heat from the Sun reaches the Earth through radiation. This process involves the transfer of energy in the form of electromagnetic waves, which can travel through the vacuum of space.
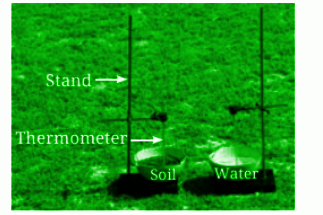
7. How do large water bodies affect the temperature of nearby regions?
Large water bodies like oceans and seas moderate the temperatures of nearby regions. During the day, water absorbs heat, keeping coastal areas cooler. At night, water releases heat, preventing drastic temperature drops in the surrounding areas.
8. Why do hollow bricks keep houses cooler in hot regions?
Hollow bricks trap air in their cavities. Since air is a poor conductor of heat, it acts as an insulator, preventing the transfer of heat from outside to inside, thus keeping the house cooler.
9. How does water seep through the Earth's surface?
Water seeps into the Earth through a process called infiltration. Water moves through the soil and porous rock layers and collects in underground reservoirs called aquifers.
10. What is the process of convection in liquids and gases?
Convection in liquids and gases occurs when warmer, less dense regions rise and cooler, denser regions sink, creating a continuous cycle of movement. This helps distribute heat evenly throughout the substance.
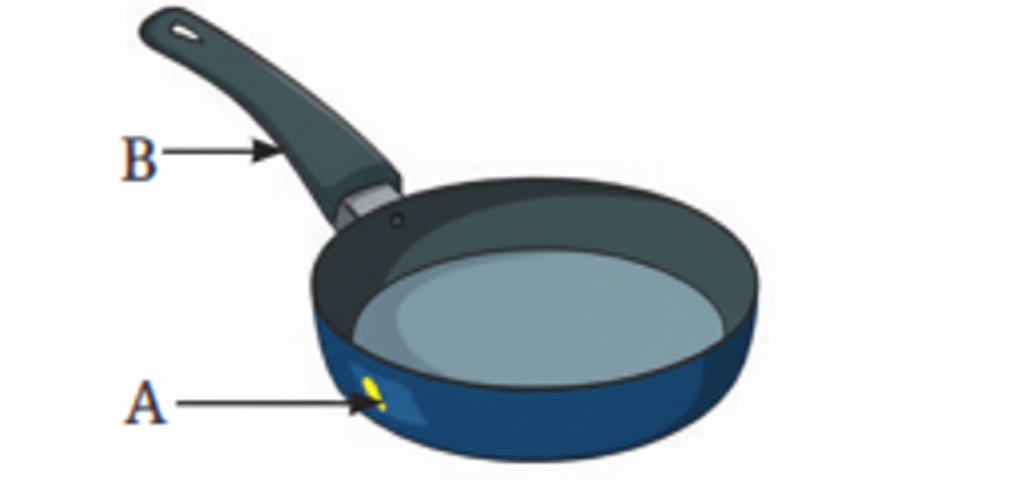
11. What are good and poor conductors of heat?
Good conductors of heat include metals like aluminum and steel. Poor conductors (insulators) include materials like wood, plastic, and bakelite. Good conductors allow heat to pass through them quickly, while poor conductors slow down heat transfer.
12. What is the difference between conduction, convection, and radiation?
Conduction transfers heat through direct contact between particles in solids. Convection transfers heat in fluids (liquids and gases) through the movement of the fluid. Radiation transfers heat through electromagnetic waves without requiring a medium (like in the case of heat from the Sun).
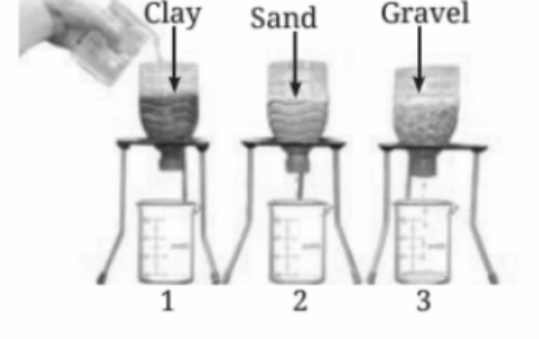
13. How do the size of particles in soil affect the flow of water?
The flow of water through soil depends on the size of the particles. Smaller particles like clay have tiny pores that allow water to seep slowly, while larger particles like gravel have bigger spaces between them, allowing water to pass through more quickly.