
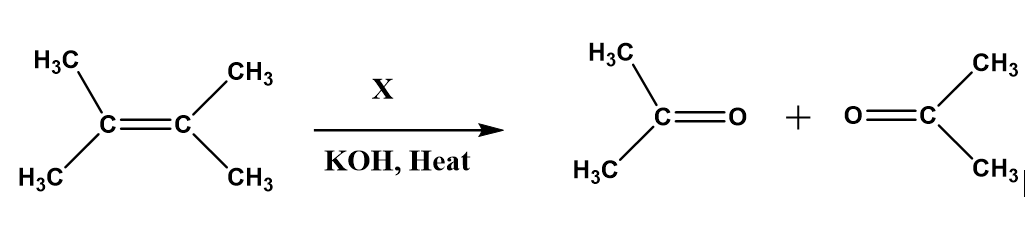
X in the above reaction is?
(a) \[HN{O_3}\]
(b) \[{O_2}\]
(c) \[{O_3}\]
(d) \[KMn{O_4}\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The cold, acidic and alkaline potassium permanganate (\[KMn{O_4}\]) can form various products by reacting with alkene. The alkaline \[KMn{O_4}\] can oxidise alkene into ketone or carboxylic acid compounds.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The carbon-carbon double bond in an alkene is considered highly reactive due to its electron density. Because of high electron density, the double bond of an alkene can be easily polarised by various reagents.
The alkaline potassium permanganate (\[KMn{O_4}\]) is used for the oxidation of unsaturated hydrocarbons (alkene and alkynes) to produce alcohol and then convert these alcohols to ketone and finally into carboxylic acids.
The substituted alkene with alkaline potassium permanganate (\[KMn{O_4}\]) can undergo oxidation and as a result formation of a carboxylic acid is observed.
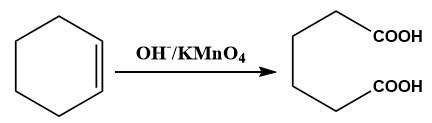
Image: Oxidation of alkene to acid
Whereas the more substituted alkenes with alkaline potassium permanganate (\[KMn{O_4}\]) are ended with the ketone as a final product.
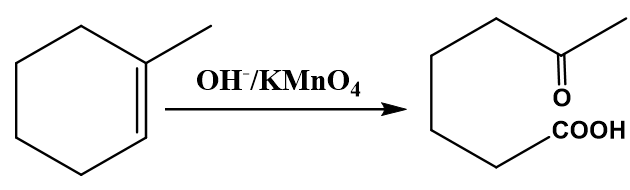
Image: Oxidation of alkene to ketone
During the oxidation of alkene by \[KMn{O_4}\]a cyclic diester of manganese is formed as an intermediate which leads to the formation of glycols or diols by means of syn addition.
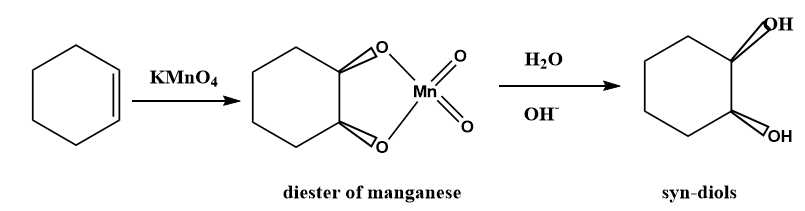
Image: Synthesis of syn-diol
Therefore, from the above discussion, it is quite clear that potassium permanganate (\[KMn{O_4}\]) is the best candidate to cleave the carbon-carbon double bond. Hence option (d) will be the correct answer.
Note: Potassium permanganate (\[KMn{O_4}\]) is also called Beyer’s reagent and it is used for unsaturated hydrocarbons or for the formation of vicinal glycols. \[KMn{O_4}\]occurs in purple crystalline form.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The carbon-carbon double bond in an alkene is considered highly reactive due to its electron density. Because of high electron density, the double bond of an alkene can be easily polarised by various reagents.
The alkaline potassium permanganate (\[KMn{O_4}\]) is used for the oxidation of unsaturated hydrocarbons (alkene and alkynes) to produce alcohol and then convert these alcohols to ketone and finally into carboxylic acids.
The substituted alkene with alkaline potassium permanganate (\[KMn{O_4}\]) can undergo oxidation and as a result formation of a carboxylic acid is observed.

Image: Oxidation of alkene to acid
Whereas the more substituted alkenes with alkaline potassium permanganate (\[KMn{O_4}\]) are ended with the ketone as a final product.

Image: Oxidation of alkene to ketone
During the oxidation of alkene by \[KMn{O_4}\]a cyclic diester of manganese is formed as an intermediate which leads to the formation of glycols or diols by means of syn addition.

Image: Synthesis of syn-diol
Therefore, from the above discussion, it is quite clear that potassium permanganate (\[KMn{O_4}\]) is the best candidate to cleave the carbon-carbon double bond. Hence option (d) will be the correct answer.
Note: Potassium permanganate (\[KMn{O_4}\]) is also called Beyer’s reagent and it is used for unsaturated hydrocarbons or for the formation of vicinal glycols. \[KMn{O_4}\]occurs in purple crystalline form.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




