
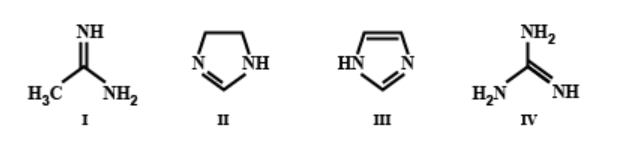
The order of basicity among the following compounds is:
A ) I > IV > III > II
B ) II >I IV > III
C ) IV > I > II > III
D ) IV > II > III > i
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Consider various factors such as number of amino groups and number of double bonds. Greater is the number of amino groups, greater is the basicity.
Complete step by step answer:
In compound IV, three amino groups are present, whereas in all the remaining compounds, only two amino groups are present. Greater is the number of amino groups, greater is the basicity. Also, in compound IV, when a proton is accepted, the stabilisation of the positive charge in the conjugate acid involves resonance with two different amino groups. However, in case of compound I, this resonance is with only one amino group. Greater is the number of amino groups, greater is the number of resonance structures and greater is the delocalisation. Hence, compound IV is more basic than compound I.
In compound II, only one double bond is present whereas in compound III, two double bonds are present. Hence, the extent of delocalisation is greater in compound III than in compound II. Greater is the delocalisation, lesser is the availability of lone pairs of electrons for donation to suitable acid. Hence, II is more basic than compound III.
Hence, the option C ) is the correct answer.
Note:
If the extent of delocalisation of electrons is greater, then lower is the basicity.
Complete step by step answer:
In compound IV, three amino groups are present, whereas in all the remaining compounds, only two amino groups are present. Greater is the number of amino groups, greater is the basicity. Also, in compound IV, when a proton is accepted, the stabilisation of the positive charge in the conjugate acid involves resonance with two different amino groups. However, in case of compound I, this resonance is with only one amino group. Greater is the number of amino groups, greater is the number of resonance structures and greater is the delocalisation. Hence, compound IV is more basic than compound I.
In compound II, only one double bond is present whereas in compound III, two double bonds are present. Hence, the extent of delocalisation is greater in compound III than in compound II. Greater is the delocalisation, lesser is the availability of lone pairs of electrons for donation to suitable acid. Hence, II is more basic than compound III.
Hence, the option C ) is the correct answer.
Note:
If the extent of delocalisation of electrons is greater, then lower is the basicity.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




