
Which pair of polymers have similar properties?
(A) Nylon, PVC
(B) PAN,PTFE
(C) PCTFE,PTFE
(D) Bakelite, alkyl resin
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Any of a group of organic or synthetic compounds known as polymers are made up of macromolecules, or very large molecules, which are just multiples of simpler chemical building blocks known as monomers. Numerous natural and man-made materials, as well as a large portion of the components in living things, are composed of polymers.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In polymer chemistry, polymerization is the process of joining monomer molecules to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks by a chemical reaction. Different techniques exist to classify the various types of polymerization. Due to the functional groups contained in the reactants and their inherent steric effects, polymerization in chemical compounds can take place through a variety of reaction processes that vary in complexity.
Numerous applications can be found for polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene.
Polytetrafluoroethylene, a high-molecular-weight polymer made entirely of fluorine and carbon, is a fluorocarbon solid. Due to the strong electronegativity of fluorine in fluorocarbons, which exhibits reduced London dispersion forces, PTFE is hydrophobic, meaning that neither water nor things containing water can wet it. One of the lowest coefficients of friction of any substance is found in PTFE.
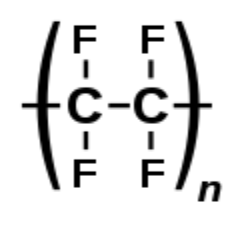
The thermoplastic chlorofluoropolymer known as polychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE or PTFCE) has the molecular formula \[{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CClF}}} \right)_{\text{n}}}\], where n is the number of monomer units in the polymer molecule. It is comparable to polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE), except instead of tetrafluoroethene, it is a homopolymer of chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE). Of all plastics, it transmits water vapour at the slowest rate.
The carbon backbone of both PCTFE and PTFE is the same, so they might have the same chemical properties.
Hence option (C) is correct.
Note: Due to the functional groups contained in the reactants and their inherent steric effects, polymerization in chemical compounds can take place through a variety of reaction processes that vary in complexity. Alkenes undergo comparatively straightforward radical reactions to create polymers in more straightforward polymerizations; in contrast, substitution reactions at a carbonyl group need more complicated synthesis because of the way the reactants polymerize. The polymerization of alkanes is also possible, but only with the aid of potent acids.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In polymer chemistry, polymerization is the process of joining monomer molecules to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks by a chemical reaction. Different techniques exist to classify the various types of polymerization. Due to the functional groups contained in the reactants and their inherent steric effects, polymerization in chemical compounds can take place through a variety of reaction processes that vary in complexity.
Numerous applications can be found for polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene.
Polytetrafluoroethylene, a high-molecular-weight polymer made entirely of fluorine and carbon, is a fluorocarbon solid. Due to the strong electronegativity of fluorine in fluorocarbons, which exhibits reduced London dispersion forces, PTFE is hydrophobic, meaning that neither water nor things containing water can wet it. One of the lowest coefficients of friction of any substance is found in PTFE.
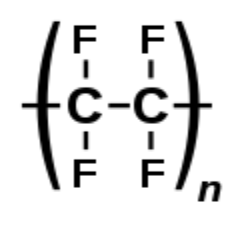
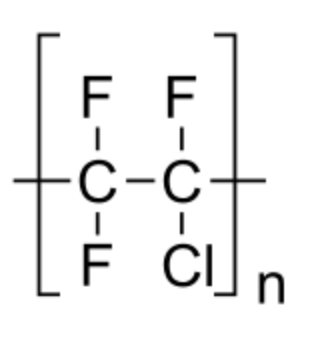
The thermoplastic chlorofluoropolymer known as polychlorotrifluoroethylene (PCTFE or PTFCE) has the molecular formula \[{\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{F}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{CClF}}} \right)_{\text{n}}}\], where n is the number of monomer units in the polymer molecule. It is comparable to polytetrafluoroethene (PTFE), except instead of tetrafluoroethene, it is a homopolymer of chlorotrifluoroethylene (CTFE). Of all plastics, it transmits water vapour at the slowest rate.

The carbon backbone of both PCTFE and PTFE is the same, so they might have the same chemical properties.
Hence option (C) is correct.
Note: Due to the functional groups contained in the reactants and their inherent steric effects, polymerization in chemical compounds can take place through a variety of reaction processes that vary in complexity. Alkenes undergo comparatively straightforward radical reactions to create polymers in more straightforward polymerizations; in contrast, substitution reactions at a carbonyl group need more complicated synthesis because of the way the reactants polymerize. The polymerization of alkanes is also possible, but only with the aid of potent acids.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




