
Which of the following structure of carboxylic acid accounts for the acidic nature
A. R—COOH
B. R—C—(OH)2
C. R—CHO
D. None of these
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Organic compounds are those compounds that contain carbon-carbon or carbon-hydrogen bonds. Due to the catenation property of carbon, it can form long chains of compounds containing carbon and these compounds are organic compounds.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The organic compounds are classified on the basis of the carbon chain open-chain and closed-chain compounds and aromatic compounds. Organic compounds are also classified on the basis of the functional group attached to the carbon chain for example:
Alkene if there is a double bond between the carbon-carbon bond C=C
Alcohol if the functional group is —HO
Halides if the functional group is —X (Where X can be F, Cl, Br, I)
Aldehyde if the functional group is —CHO
Ketone if the functional group is —CO—
These are some functional groups and classes of organic compounds.
R—C—(OH)2 is diol because it contains two alcoholic groups ‘ol’ is used as a suffix for the alcoholic group (—OH) hence R—C—(OH)2 is a diol example of diols-
1. Methanediol or methylene glycol

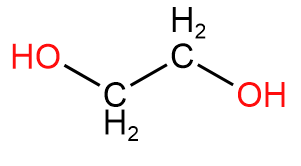
2. Ethanediol or ethylene glycol
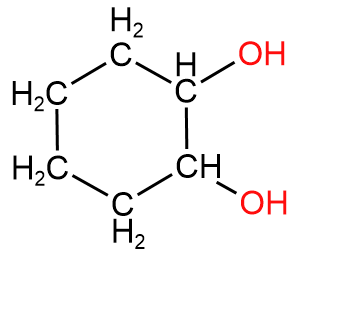
3. Cyclohexane-1,2-diol
R—CHO is an aldehydic group, it is also known as the carbonyl group as it contains the C=O group. Examples of aldehydes are-
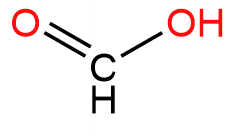
1. Methanal or Formaldehyde
2. Ethanal or Acetaldehyde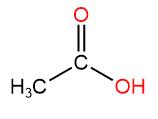
3. Benzenecarbaldehyde or benzaldehyde
R—COOH is a carboxylic acid group, it is acidic in nature because on dissociation it gives R—COO- and H+ ions in the solution:
Examples of carboxylic acid:
1. Ethanoic Acid or Acetic acid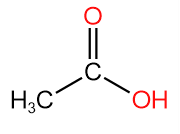
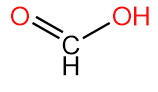
2. Methanoic Acid or Formic acid
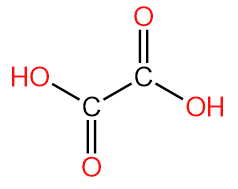
3. Oxalic Acid
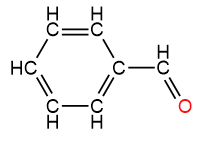
4. Salicylic Acid
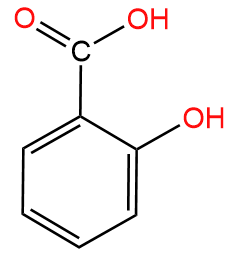
Hence we know that the carboxylic group is R—COOH.
Thus, Option (A) is correct
Note: Most of the Carboxylic acid occurs naturally for example in insects like ants formic acid is found, caprylic acid in coconuts, and oxalic acid in oxalis. Carboxylic acids are weak acids compared to inorganic acids like HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, etc.
Complete Step by Step Answer:
The organic compounds are classified on the basis of the carbon chain open-chain and closed-chain compounds and aromatic compounds. Organic compounds are also classified on the basis of the functional group attached to the carbon chain for example:
Alkene if there is a double bond between the carbon-carbon bond C=C
Alcohol if the functional group is —HO
Halides if the functional group is —X (Where X can be F, Cl, Br, I)
Aldehyde if the functional group is —CHO
Ketone if the functional group is —CO—
These are some functional groups and classes of organic compounds.
R—C—(OH)2 is diol because it contains two alcoholic groups ‘ol’ is used as a suffix for the alcoholic group (—OH) hence R—C—(OH)2 is a diol example of diols-
1. Methanediol or methylene glycol

2. Ethanediol or ethylene glycol

3. Cyclohexane-1,2-diol

R—CHO is an aldehydic group, it is also known as the carbonyl group as it contains the C=O group. Examples of aldehydes are-
1. Methanal or Formaldehyde

2. Ethanal or Acetaldehyde

3. Benzenecarbaldehyde or benzaldehyde

R—COOH is a carboxylic acid group, it is acidic in nature because on dissociation it gives R—COO- and H+ ions in the solution:
Examples of carboxylic acid:
1. Ethanoic Acid or Acetic acid

2. Methanoic Acid or Formic acid

3. Oxalic Acid

4. Salicylic Acid

Hence we know that the carboxylic group is R—COOH.
Thus, Option (A) is correct
Note: Most of the Carboxylic acid occurs naturally for example in insects like ants formic acid is found, caprylic acid in coconuts, and oxalic acid in oxalis. Carboxylic acids are weak acids compared to inorganic acids like HCl, H2SO4, HNO3, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

JEE Energetics Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




