
Which of the following is an example of metallic crystalline solids?
(a) \[C\]
(b) \[W\]
(c) \[Si\]
(d) \[AgCl\]
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: The solid is a state of matter, in which the constituent particles remain closely packed with the minimum amount of kinetic energy. Generally, solids are recognized for their rigid and hard nature. In most cases they have cubic crystal structures.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In metallic solids the constituents’ particles i.e., metal atoms are fused together by metallic bonds.
In metallic solids, the positively charged ions are evenly distributed in the crystal and surrounded by free mobile electrons.
In metallic solid the mobile electrons are not held between a couple of atoms i.e., they can delocalize. On the other hand, the metallic solid possesses a sea of electrons everywhere (Image 1).
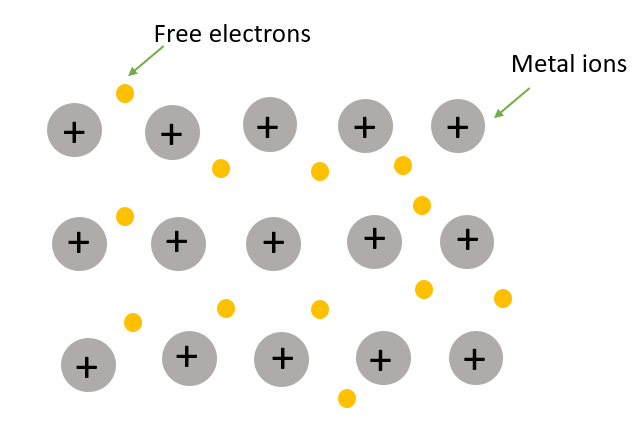
Image 1: Structure of metallic solid.
In metallic solid each atom can share one or more electrons to the sea of mobile electrons. These behaviours cause an increase in the electrical and thermal conductivity of metallic solids.
Metallic crystalline solids are malleable and ductile i.e., they can easily convert into sheets and wires respectively.
Unlike covalent solids, they are stiff or brittle in nature because the cations can slide into the sea of electrons without breaking any bond.
Metallic solids such as copper, gold, zinc, tungsten, etc. are examples of such solids.
Therefore, option (b) will be the correct answer because silicon, carbon and \[AgCl\] are not metals. While \[W\] is a metal.
Note: The metallic solid can be pure, or they can be the combination of two or more than two metals. Bronze is alloy and it has the mixture of two metals i.e., copper and tin.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In metallic solids the constituents’ particles i.e., metal atoms are fused together by metallic bonds.
In metallic solids, the positively charged ions are evenly distributed in the crystal and surrounded by free mobile electrons.
In metallic solid the mobile electrons are not held between a couple of atoms i.e., they can delocalize. On the other hand, the metallic solid possesses a sea of electrons everywhere (Image 1).

Image 1: Structure of metallic solid.
In metallic solid each atom can share one or more electrons to the sea of mobile electrons. These behaviours cause an increase in the electrical and thermal conductivity of metallic solids.
Metallic crystalline solids are malleable and ductile i.e., they can easily convert into sheets and wires respectively.
Unlike covalent solids, they are stiff or brittle in nature because the cations can slide into the sea of electrons without breaking any bond.
Metallic solids such as copper, gold, zinc, tungsten, etc. are examples of such solids.
Therefore, option (b) will be the correct answer because silicon, carbon and \[AgCl\] are not metals. While \[W\] is a metal.
Note: The metallic solid can be pure, or they can be the combination of two or more than two metals. Bronze is alloy and it has the mixture of two metals i.e., copper and tin.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




