
Which of the following is an addition polymer?
A Glucose
B Polyethylene
C Ethylene
D Terylene
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Polymers, which are formed by adding the smallest unit, monomer molecule (containing double or triple bond) again and again in some pattern is known as addition polymer. Addition polymer generated through addition reaction in the presence of free radical followed by three steps, free radical initiation chain proportion, and termination of the chain. In addition to polymerization, there is no co-generation of another product and reactions take place between unsaturated bonds of monomers, unlike condensation polymers.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Glucose: Glucose is a monosaccharide (carbohydrate) which combine with other carbohydrates during polymerization reaction to give starch and water (different product). Condensation polymerization cause monosaccharide’s conversion to products such as polysaccharides and water. As it is co-generating water during polymerization thus, glucose polymer (glucans) is not an addition polymer.
Ethylene is itself a monomer of polyethylene, which on combining repeatedly give polyethylene (polyethylene) and no other co-product. Thus, polyethylene is a addition polymer where a large number of ethylene join with a carbon-carbon double bond during polymerization in the presence of a free radical such as
Free radical initiation:
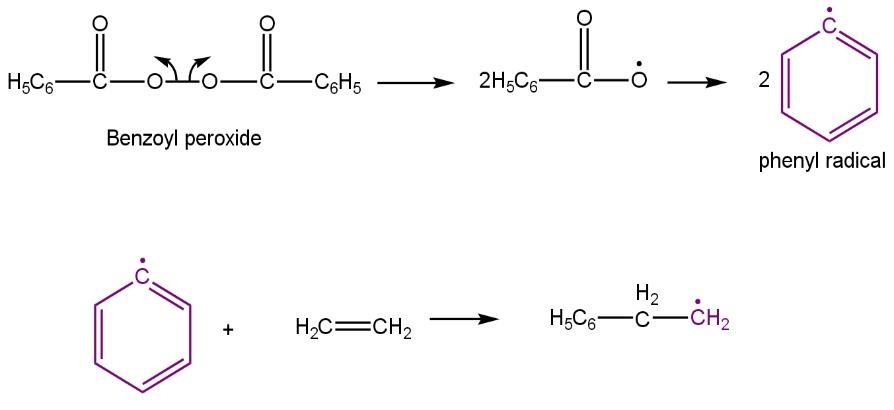
Chain propagation:
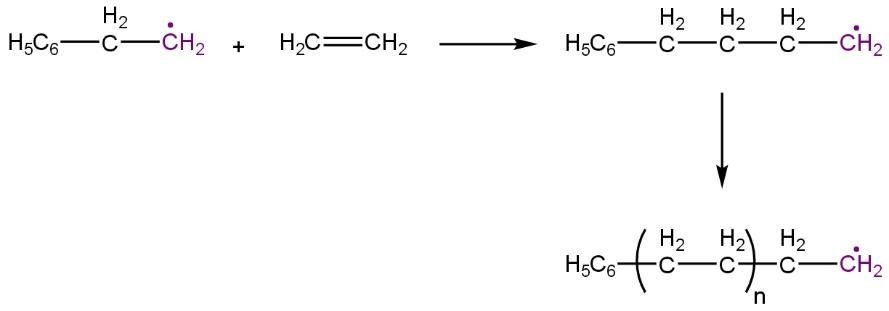
Chain termination:
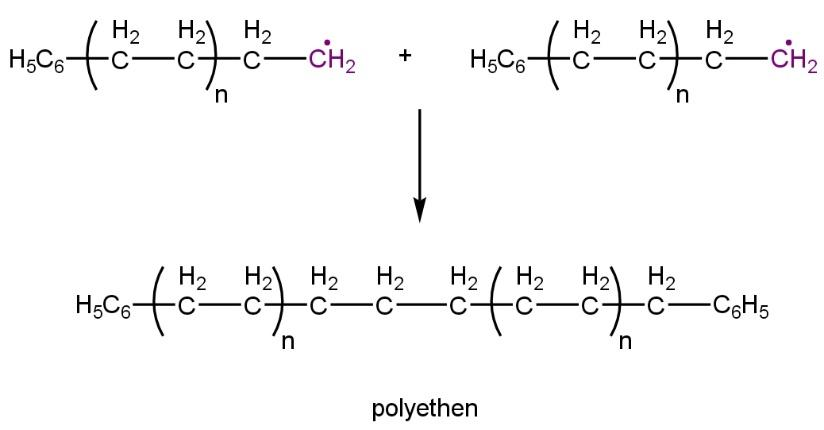
Whereas terylene is also a condensation polymer that is formed when ethylene glycol reacts with terephthalate acid during polymerization releasing out water (co-generate another product) and oxygen and carbon compounds.
Note: Polymerization is generally of two types, addition polymerization in which monomers (unsaturation) are simply joined together so that the resulting polymer contains only atoms from which it is formed which is not the case in condensation polymerization.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Glucose: Glucose is a monosaccharide (carbohydrate) which combine with other carbohydrates during polymerization reaction to give starch and water (different product). Condensation polymerization cause monosaccharide’s conversion to products such as polysaccharides and water. As it is co-generating water during polymerization thus, glucose polymer (glucans) is not an addition polymer.
Ethylene is itself a monomer of polyethylene, which on combining repeatedly give polyethylene (polyethylene) and no other co-product. Thus, polyethylene is a addition polymer where a large number of ethylene join with a carbon-carbon double bond during polymerization in the presence of a free radical such as
Free radical initiation:

Chain propagation:

Chain termination:

Whereas terylene is also a condensation polymer that is formed when ethylene glycol reacts with terephthalate acid during polymerization releasing out water (co-generate another product) and oxygen and carbon compounds.
Note: Polymerization is generally of two types, addition polymerization in which monomers (unsaturation) are simply joined together so that the resulting polymer contains only atoms from which it is formed which is not the case in condensation polymerization.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




