
Which of the following is a non-linear molecule?
(A) $C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$
(B) $C{{O}_{2}}$
(C) $C{{S}_{2}}$
(D) $BeC{{l}_{2}}$
Answer
242.1k+ views
Hint: Firstly, the hybridization of each of the molecules in the options is determined. The hybridization is calculated by calculating the number of bond pairs and lone pairs in a molecule. Hybridization is the idea of combining the two atomic orbitals to form a new type of hybridised orbital. This mixing creates hybrid orbitals with entirely different energies and shapes.
Formula Used: Hybridization is calculated as:
Hybridization=$12(V+M-C+A)$
Where $V$= number of valence electrons of the central atom
$M$= number of monovalent atoms
$C$= positive charge
$A$= negative charge
Complete Step by Step Answer:
(A) $C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$
Hybridization=$\frac{1}{2}(4+0-0+2)=3$
The hybridization of $C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$is$s{{p}^{2}}$. Hence, $C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$is non-linear in shape.
(B) $C{{O}_{2}}$
Hybridization=$\frac{1}{2}(4+0-0+0)=2$
The hybridization of $C{{O}_{2}}$is$sp$. Hence, $C{{O}_{2}}$is linear in shape.
(C) $C{{S}_{2}}$
Hybridization=$\frac{1}{2}(4+0-0+0)=2$
The hybridization of $C{{S}_{2}}$is$sp$. Hence, $C{{S}_{2}}$is linear in shape.
(D) $BeC{{l}_{2}}$
Hybridization=$\frac{1}{2}(2+2-0+0)=2$
The hybridization of $BeC{{l}_{2}}$is$sp$. Hence, $BeC{{l}_{2}}$is linear in shape.
All the other molecules in the options except $C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$are $sp$ hybridised and thus, linear in shape.
The structures of all the molecules are shown below:
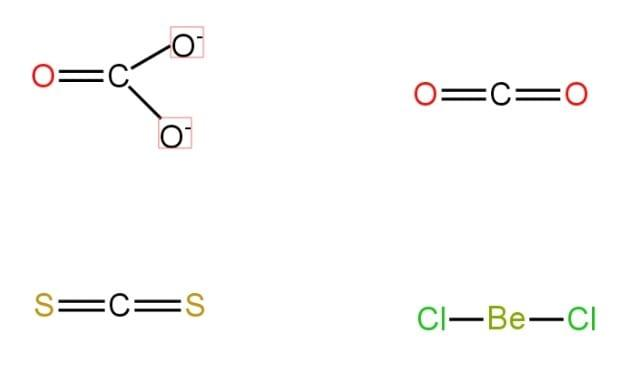
Thus, $C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$is a non-linear molecule.
Correct Option: (A) $C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$.
Note: The central atom in the geometry described by linear molecular geometry is bonded to two other atoms (or ligands) at a bond angle of${{180}^{o}}$. All the linear molecules must be $sp$ hybridized. Non-linear molecules have bond angles other than ${{180}^{o}}$, depending upon the shape of the molecule. The shape of the molecule may be bent, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, etc.
Formula Used: Hybridization is calculated as:
Hybridization=$12(V+M-C+A)$
Where $V$= number of valence electrons of the central atom
$M$= number of monovalent atoms
$C$= positive charge
$A$= negative charge
Complete Step by Step Answer:
(A) $C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$
Hybridization=$\frac{1}{2}(4+0-0+2)=3$
The hybridization of $C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$is$s{{p}^{2}}$. Hence, $C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$is non-linear in shape.
(B) $C{{O}_{2}}$
Hybridization=$\frac{1}{2}(4+0-0+0)=2$
The hybridization of $C{{O}_{2}}$is$sp$. Hence, $C{{O}_{2}}$is linear in shape.
(C) $C{{S}_{2}}$
Hybridization=$\frac{1}{2}(4+0-0+0)=2$
The hybridization of $C{{S}_{2}}$is$sp$. Hence, $C{{S}_{2}}$is linear in shape.
(D) $BeC{{l}_{2}}$
Hybridization=$\frac{1}{2}(2+2-0+0)=2$
The hybridization of $BeC{{l}_{2}}$is$sp$. Hence, $BeC{{l}_{2}}$is linear in shape.
All the other molecules in the options except $C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$are $sp$ hybridised and thus, linear in shape.
The structures of all the molecules are shown below:

Thus, $C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$is a non-linear molecule.
Correct Option: (A) $C{{O}_{3}}^{2-}$.
Note: The central atom in the geometry described by linear molecular geometry is bonded to two other atoms (or ligands) at a bond angle of${{180}^{o}}$. All the linear molecules must be $sp$ hybridized. Non-linear molecules have bond angles other than ${{180}^{o}}$, depending upon the shape of the molecule. The shape of the molecule may be bent, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, etc.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2026 PDF Download (All Sets) with Answer Key

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More




