
Which of the following compounds cannot be acetylated?
(A) $C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}$
(B) ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}NH$
(C) ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}N$
(D) None of these
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: The chemical process of adding an acetyl functional group to a chemical molecule is known as acetylation. When treated with acid chloride, anhydride, or esters, aliphatic and aromatic primary and secondary amines undergo acetylation reactions via nucleophilic substitution. This process occurs in the presence of a strong base like pyridine. When an amine reacts with acid chloride, it releases $HCl$ . This $HCl$ shifts the equilibrium to the right hand side of the reaction.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
For compounds to get acetylated, it is necessary to have $\alpha $ – hydrogen. In this case, methyl amine ($C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}$ ), a primary amine, has two -hydrogens, while dimethyl amine (${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}NH$) , a secondary amine, has one. So, these compounds can be acetylated easily with acid chloride, anhydride, or esters. However, because there is no $\alpha $ -hydrogen attached to $N$ in trimethylamine (${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}N$ ), a tertiary amine, it cannot be acetylated.
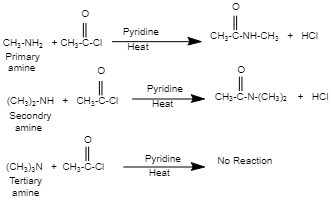 Correct option: (C) ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}N$.
Correct option: (C) ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}N$.
Additional Information: The process of amines reacting with benzoyl chloride is known as benzoylation. Deacetylation, which means removing an acetyl group from a chemical compound, can be considered the opposite reaction to acetylation.
Note: The hydrogen attached to nitrogen is analysed and not with carbon as the hydrogen attached to nitrogen gets released in the form of $HCl$ , which shifts the equilibrium to the right hand side of the reaction. So, there should be at least one hydrogen attached to nitrogen in an amine to undergo acetylation.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
For compounds to get acetylated, it is necessary to have $\alpha $ – hydrogen. In this case, methyl amine ($C{{H}_{3}}N{{H}_{2}}$ ), a primary amine, has two -hydrogens, while dimethyl amine (${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}NH$) , a secondary amine, has one. So, these compounds can be acetylated easily with acid chloride, anhydride, or esters. However, because there is no $\alpha $ -hydrogen attached to $N$ in trimethylamine (${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}N$ ), a tertiary amine, it cannot be acetylated.
 Correct option: (C) ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}N$.
Correct option: (C) ${{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{3}}N$.Additional Information: The process of amines reacting with benzoyl chloride is known as benzoylation. Deacetylation, which means removing an acetyl group from a chemical compound, can be considered the opposite reaction to acetylation.
Note: The hydrogen attached to nitrogen is analysed and not with carbon as the hydrogen attached to nitrogen gets released in the form of $HCl$ , which shifts the equilibrium to the right hand side of the reaction. So, there should be at least one hydrogen attached to nitrogen in an amine to undergo acetylation.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




