
Two like magnetic poles of strength $10$ and $40$ Am are separated by a distance $30cm$ . The intensity of magnetic field is Zero on the line joining them.
A. At a point $10cm$ from a stronger pole
B. At a point $20cm$ from a stronger pole
C. At a mid-point
D. At infinity
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:
This problem is based on the intensity of the magnetic field and we know that if the magnetic field (B) at any point is zero, then the intensity of magnetic field (H) at that point will also be zero due as $B = \mu H$ hence, use the relation $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{m}{{{d^2}}}$to get an accurate solution to the given problem.
Formula used:
The formula used in this solution is given as: -
$B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{m}{{{d^2}}}$
Complete step by step solution:
We know that the Magnetic Induction at a point in a magnetic field is given as: -
$B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{m}{{{d^2}}}$ … (1)
The given problem can be illustrated by a diagram given as follows: -
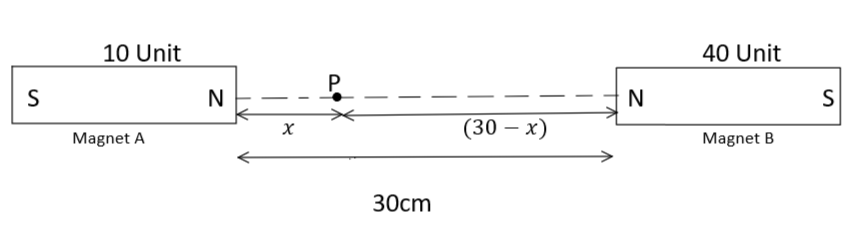
Let us consider that the magnetic field is zero at a point P which lies $x$cm from magnet A (10 units) and $(x - 30)$cm from magnet B (40 units).
So, From eq. (1)
$\therefore \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{\left( {10} \right)}}{{{x^2}}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{\left( {40} \right)}}{{{{\left( {30 - x} \right)}^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {30 - x} \right)}^2}}}{{{x^2}}} = 4$
On further Calculation, we get a quadratic equation as: -
$ \Rightarrow 900 + {x^2} - 60x = 4{x^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 3{x^2} + 60x - 900 = 0$
On Solving this equation, we get
$ \Rightarrow x = 10cm$
i.e., the distance of magnet A (10 units) from point P = $x = 10cm$
and the distance of magnet B (40 units) from point P = $30 - x = 30 - 10 = 20cm$
As, the stronger magnetic pole is B and the magnetic field is zero at a point $20cm$ from a stronger pole. Thus, the intensity of magnetic field is also zero on the line joining the magnets at a point $20cm$ from a stronger pole.
Hence, the correct option is (B) At a point $20cm$ from a stronger pole.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note:
A particular point at which resultant magnetic field intensity is zero due to earth’s magnetic field is called a neutral point. Or in other word a null point is that particular point where the magnetic field is completely neutralised by the horizontal component of the magnetic field of earth.
This problem is based on the intensity of the magnetic field and we know that if the magnetic field (B) at any point is zero, then the intensity of magnetic field (H) at that point will also be zero due as $B = \mu H$ hence, use the relation $B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{m}{{{d^2}}}$to get an accurate solution to the given problem.
Formula used:
The formula used in this solution is given as: -
$B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{m}{{{d^2}}}$
Complete step by step solution:
We know that the Magnetic Induction at a point in a magnetic field is given as: -
$B = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{m}{{{d^2}}}$ … (1)
The given problem can be illustrated by a diagram given as follows: -

Let us consider that the magnetic field is zero at a point P which lies $x$cm from magnet A (10 units) and $(x - 30)$cm from magnet B (40 units).
So, From eq. (1)
$\therefore \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{\left( {10} \right)}}{{{x^2}}} = \dfrac{{{\mu _o}}}{{4\pi }}\dfrac{{\left( {40} \right)}}{{{{\left( {30 - x} \right)}^2}}}$
$ \Rightarrow \dfrac{{{{\left( {30 - x} \right)}^2}}}{{{x^2}}} = 4$
On further Calculation, we get a quadratic equation as: -
$ \Rightarrow 900 + {x^2} - 60x = 4{x^2}$
$ \Rightarrow 3{x^2} + 60x - 900 = 0$
On Solving this equation, we get
$ \Rightarrow x = 10cm$
i.e., the distance of magnet A (10 units) from point P = $x = 10cm$
and the distance of magnet B (40 units) from point P = $30 - x = 30 - 10 = 20cm$
As, the stronger magnetic pole is B and the magnetic field is zero at a point $20cm$ from a stronger pole. Thus, the intensity of magnetic field is also zero on the line joining the magnets at a point $20cm$ from a stronger pole.
Hence, the correct option is (B) At a point $20cm$ from a stronger pole.
Therefore, the correct option is B.
Note:
A particular point at which resultant magnetic field intensity is zero due to earth’s magnetic field is called a neutral point. Or in other word a null point is that particular point where the magnetic field is completely neutralised by the horizontal component of the magnetic field of earth.
Recently Updated Pages
Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




