
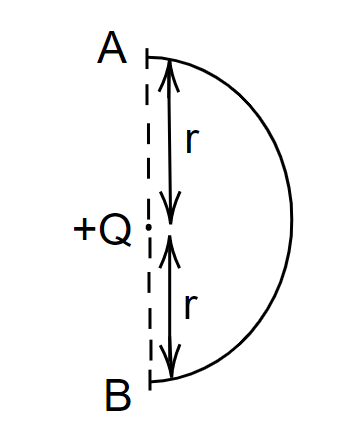
The work done in slowly moving an electron of charge e and mass m from A to B along a semi-circular path (as shown in the figure) in a vertical plane in the field of charge Q is
A. \[ - 2mgr\]
B. \[ - \dfrac{{Qe}}{r}\]
C. \[2mgr + \dfrac{{Qe}}{r}\]
D. Zero
Answer
240k+ views
Hint:Before we proceed with the problem, it is important to know about the work done by a charge and electric potential energy. It is defined as the force applied on a charge leading to a certain displacement in it. Electric potential energy can be defined as the total potential energy a unit charge will possess if located at any point in outer space.
Formula Used:
By the formula of electric potential energy we have,
\[V = \dfrac{{KQ}}{R}\]
Where, Q is the point charge and R is the distance between any point around the charge to the point charge.
Complete step by step solution:
Now we can able to solve the problem step by step as follows.
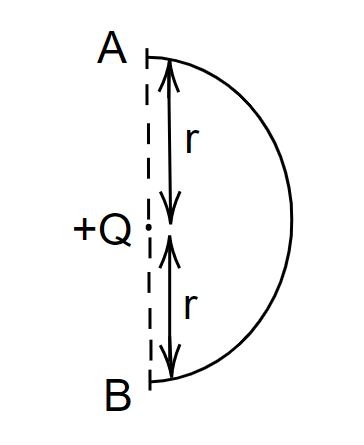
Image: An electron of charge e and mass m moving along a circular path.
We can say that the electric force acts on an electron when it is taken from point A to point B. Then the work has to be done by the electrostatic field and also the work has to be done against the gravitational field. So, work done in the electrostatic field is given by,
\[{W_{AB}} = q\left( {{V_B} - {V_A}} \right)\]
\[{W_{AB}} = e\left( {\dfrac{{KQ}}{R} - \dfrac{{KQ}}{R}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = 0\]
Then the work done against the gravitational field is
\[{W_{AB}} = mg\left( { - 2R} \right)\]
\[{W_{AB}} = - 2mgR\]
Hence, the net work done is,
\[{W_{AB}} = 0 + \left( { - 2mgR} \right)\]
\[ \therefore {W_{AB}} = - 2mgR\]
Therefore, the work done by the electric force will be equal \[ - 2mgr\] from point A to point B along this semi-circular path in the field of charge.
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Note:When an electron moves in a circular path, the magnitude of velocity, acceleration, and electric field remains the same but the direction will change continuously and the electric force is always perpendicular to the displacement.
Formula Used:
By the formula of electric potential energy we have,
\[V = \dfrac{{KQ}}{R}\]
Where, Q is the point charge and R is the distance between any point around the charge to the point charge.
Complete step by step solution:
Now we can able to solve the problem step by step as follows.

Image: An electron of charge e and mass m moving along a circular path.
We can say that the electric force acts on an electron when it is taken from point A to point B. Then the work has to be done by the electrostatic field and also the work has to be done against the gravitational field. So, work done in the electrostatic field is given by,
\[{W_{AB}} = q\left( {{V_B} - {V_A}} \right)\]
\[{W_{AB}} = e\left( {\dfrac{{KQ}}{R} - \dfrac{{KQ}}{R}} \right)\]
\[ \Rightarrow {W_{AB}} = 0\]
Then the work done against the gravitational field is
\[{W_{AB}} = mg\left( { - 2R} \right)\]
\[{W_{AB}} = - 2mgR\]
Hence, the net work done is,
\[{W_{AB}} = 0 + \left( { - 2mgR} \right)\]
\[ \therefore {W_{AB}} = - 2mgR\]
Therefore, the work done by the electric force will be equal \[ - 2mgr\] from point A to point B along this semi-circular path in the field of charge.
Hence, option A is the correct answer.
Note:When an electron moves in a circular path, the magnitude of velocity, acceleration, and electric field remains the same but the direction will change continuously and the electric force is always perpendicular to the displacement.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

JEE Main 2025-26 Electronic Devices Mock Test: Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26 Atoms and Nuclei Mock Test – Free Practice Online

JEE Main 2025-26: Magnetic Effects of Current & Magnetism Mock Test

JEE Main Mock Test 2025: Properties of Solids and Liquids

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Clemmensen and Wolff Kishner Reductions Explained for JEE & NEET

Degree of Dissociation: Meaning, Formula, Calculation & Uses

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/2/3) 2025: PDF, Answer Key & Solutions

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 3 (55/1/3) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper Set 1 (55/1/1) 2025 – PDF, Solutions & Marking Scheme




