
The ring B is coaxial with a solenoid A as shown in figure. As the switch S is closed
at $t=0,$ the ring B
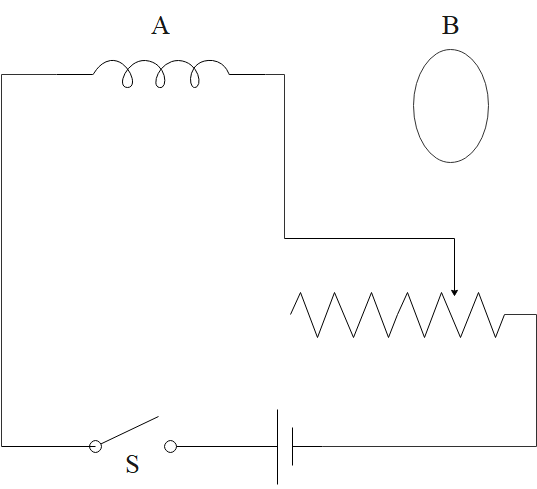
(A) is attracted towards A
(B) is repelled by A
(C) is initially repelled and then attracted
(D) is initially attracted and then repelled
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We know that a solenoid is the generic term for a coil of wire used as an electromagnet. It also refers to any device that converts electrical energy to mechanical energy using a solenoid. The device creates a magnetic field from electric current and uses the magnetic field to create linear motion. It is used as a device consisting of a coil of wire, the housing and a moveable plunger (armature). When an electrical current is introduced, a magnetic field forms around the coil which draws the plunger in. More simply, a solenoid converts electrical energy into mechanical work. Based on this we have to answer this question.
Complete step by step answer
It is known that Lenz's law, in electromagnetism, states that an induced electric current flows in a direction such that the current opposes the change that induced it. Lenz's law states that the direction of an induced e.m.f. will be such that if it were to cause a current to flow in a conductor in an external circuit, then that current would generate a field that would oppose the change that created it. This illustrates that Lenz's law is a result of energy conservation
We can say that according to Lenz's law, when an electromagnetic field is generated by a change in magnetic flux, the polarity of the induced electromagnetic field produces an induced current whose magnetic field opposes the initial changing magnetic field which produced it.
Current increases with time. So, flux passing through B will increase with time. From Lenz's law, it should have a tendency to move away from the coil to decrease flux.
Hence, we can say that the correct answer is option A.
Note It is required to know that electromagnetism is a branch of physics involving the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. It deals with the electromagnetic force that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces and exhibits electromagnetic fields such as magnetic fields, electric fields, and light. Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, electromechanical solenoids, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment.
Complete step by step answer
It is known that Lenz's law, in electromagnetism, states that an induced electric current flows in a direction such that the current opposes the change that induced it. Lenz's law states that the direction of an induced e.m.f. will be such that if it were to cause a current to flow in a conductor in an external circuit, then that current would generate a field that would oppose the change that created it. This illustrates that Lenz's law is a result of energy conservation
We can say that according to Lenz's law, when an electromagnetic field is generated by a change in magnetic flux, the polarity of the induced electromagnetic field produces an induced current whose magnetic field opposes the initial changing magnetic field which produced it.
Current increases with time. So, flux passing through B will increase with time. From Lenz's law, it should have a tendency to move away from the coil to decrease flux.
Hence, we can say that the correct answer is option A.
Note It is required to know that electromagnetism is a branch of physics involving the study of the electromagnetic force, a type of physical interaction that occurs between electrically charged particles. It deals with the electromagnetic force that occurs between electrically charged particles. The electromagnetic force is one of the four fundamental forces and exhibits electromagnetic fields such as magnetic fields, electric fields, and light. Electromagnets are widely used as components of other electrical devices, such as motors, generators, electromechanical solenoids, relays, loudspeakers, hard disks, MRI machines, scientific instruments, and magnetic separation equipment.
Recently Updated Pages
Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




