
The number of isomers possible for square planar complex ${{K}_{2}}\left[ PdClB{{r}_{2}}\left( SCN \right) \right]$ is:
A) 2
B) 3
C) 4
D) 6
Answer
233.4k+ views
Hint: The given complex is a square planar complex of type $\left[ MA{{B}_{2}}C \right]$ i.e., it can show geometrical isomerism and the complex consist of $SC{{N}^{-}}$ ligand which is an ambidentate ligand i.e., it can donate electrons to the central metal ion from both nitrogen as well as sulphur which means it can also show structural isomerism.
Complete answer:Structural Isomerism: When the molecular formula of the two complexes is the same but differs in the bonding of ligands, then the complexes are categorized under structural isomerism. Structural isomerism is further divided into four types as per the following chart.
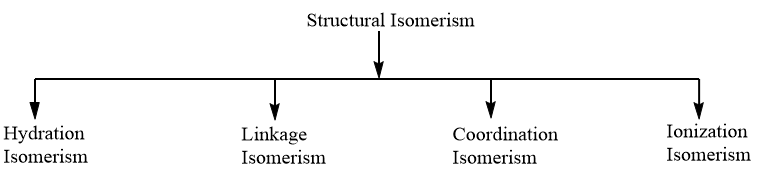
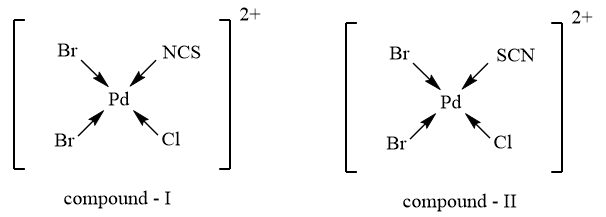
As the given complex consists of an ambidentate ligand i.e., $SC{{N}^{-}}$ which has the tendency to donate electrons through sulphur, as well as nitrogen atom, therefore, the compound, will exhibit Linkage isomerism and the possible structures for the complex showing linkage isomerism are as follows:
Geometrical isomerism: In coordination compounds, the complexes which consist of the same molecular form and the connectivity or bonding between the atoms are the same but differ in the spatial arrangement of atoms is known as geometrical isomers. It is only exhibited by octahedral and square planar complexes and tetrahedral complexes do not show geometrical isomerism.
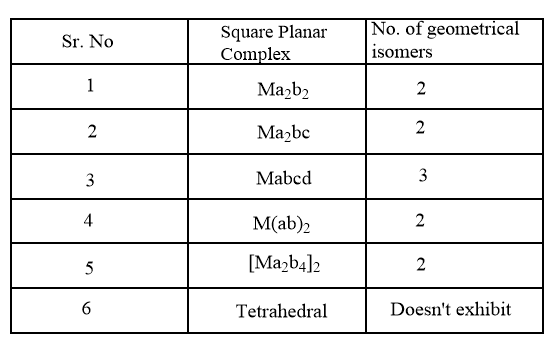
For square planar complexes, the number of geometrical isomers is summarized in the following table:
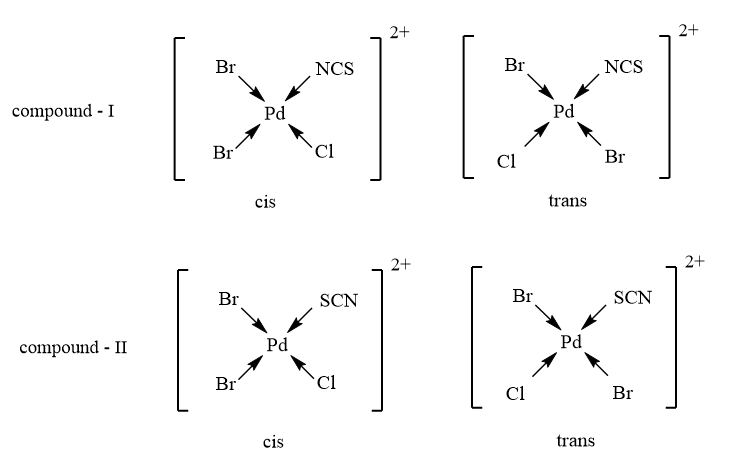
As the given complex is of the second type, therefore, it will exhibit 2 geometrical isomers as follows:
Therefore, the total number of possible isomers for ${{K}_{2}}\left[ PdClB{{r}_{2}}\left( SCN \right) \right]$ is $4$.
option (C) is correct.
Note: It is important to note that the square planar complexes do not show optical isomerism due to the presence of a plane of symmetry. Also, the important point to remember is that the cis isomers are identical to the linkage isomers, so the total number of isomers is 4 instead of 6.
Complete answer:Structural Isomerism: When the molecular formula of the two complexes is the same but differs in the bonding of ligands, then the complexes are categorized under structural isomerism. Structural isomerism is further divided into four types as per the following chart.

As the given complex consists of an ambidentate ligand i.e., $SC{{N}^{-}}$ which has the tendency to donate electrons through sulphur, as well as nitrogen atom, therefore, the compound, will exhibit Linkage isomerism and the possible structures for the complex showing linkage isomerism are as follows:

Geometrical isomerism: In coordination compounds, the complexes which consist of the same molecular form and the connectivity or bonding between the atoms are the same but differ in the spatial arrangement of atoms is known as geometrical isomers. It is only exhibited by octahedral and square planar complexes and tetrahedral complexes do not show geometrical isomerism.
For square planar complexes, the number of geometrical isomers is summarized in the following table:

As the given complex is of the second type, therefore, it will exhibit 2 geometrical isomers as follows:

Therefore, the total number of possible isomers for ${{K}_{2}}\left[ PdClB{{r}_{2}}\left( SCN \right) \right]$ is $4$.
option (C) is correct.
Note: It is important to note that the square planar complexes do not show optical isomerism due to the presence of a plane of symmetry. Also, the important point to remember is that the cis isomers are identical to the linkage isomers, so the total number of isomers is 4 instead of 6.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




