
The compound A with following sequence of reaction gave benzoic acid

A. Nitrobenzene
B. Aniline
C. Benzaldehyde
D. Amides
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: When aniline undergoes a reaction with nitrous acid at the temperature of 273K -278K results in the formation of benzenediazonium chloride. The production of nitrous acid is due to the reaction of sodium nitrite with hydrochloric acid.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In the given question, the reactant A undergoes reaction with \[{\rm{NaN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}/{\rm{HCl}}\] to form B. The then product formed B reacts with KCN to form C. The acidic hydrolysis of C results in the formation of benzoic acid.
Let’s understand the diazotization reaction in detail. In the diazotization reaction, the primary aromatic amine converts into diazonium salt. Here, A undergoes undergoes reaction with \[{\rm{NaN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}/{\rm{HCl}}\]. So, the reaction is,
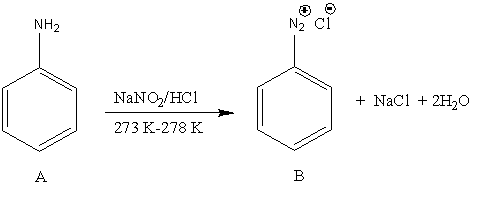
Image: Reaction of aniline with \[{\rm{NaN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}/{\rm{HCl}}\]
In the second reaction, B undergoes a reaction with KCN. The reaction of diazonium chloride with KCN results in the formation of cyanide. So, the reaction is,
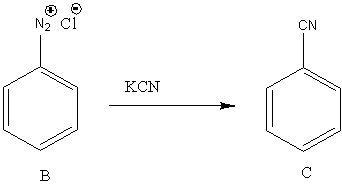
Image: Reaction of diazonium chloride with KCN
So, product C is benzonitrile.
Let’s understand the third reaction. The acidic hydrolysis of benzonitrile gives benzoic acid.
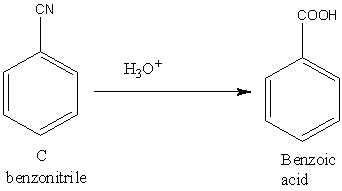
Image: Acidic hydrolysis of benzonitrile
So, the complete reaction is,
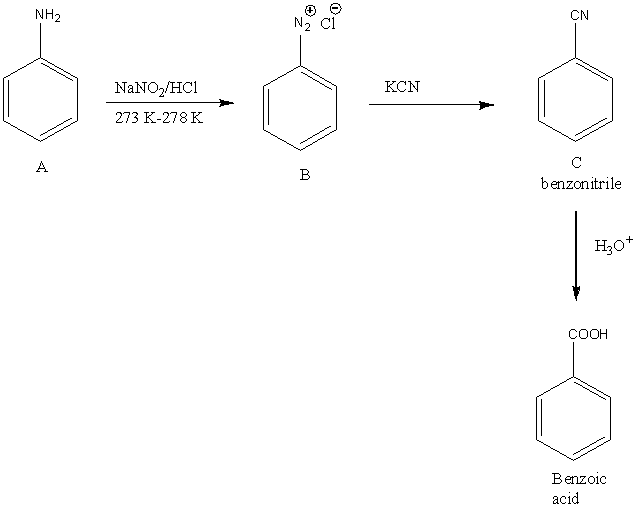
Image: The reaction of aniline to form benzoic acid
Hence, the reactant A is aniline, i.e, \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\] .
Note: The Sandmeyer reaction is the one in which chloride, bromide and cyanide ion can be introduced in the benzene ring in the presence of copper ion. And, we know, the acidic hydrolysis of cyanide gives the carboxylic acid.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In the given question, the reactant A undergoes reaction with \[{\rm{NaN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}/{\rm{HCl}}\] to form B. The then product formed B reacts with KCN to form C. The acidic hydrolysis of C results in the formation of benzoic acid.
Let’s understand the diazotization reaction in detail. In the diazotization reaction, the primary aromatic amine converts into diazonium salt. Here, A undergoes undergoes reaction with \[{\rm{NaN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}/{\rm{HCl}}\]. So, the reaction is,

Image: Reaction of aniline with \[{\rm{NaN}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{2}}}/{\rm{HCl}}\]
In the second reaction, B undergoes a reaction with KCN. The reaction of diazonium chloride with KCN results in the formation of cyanide. So, the reaction is,

Image: Reaction of diazonium chloride with KCN
So, product C is benzonitrile.
Let’s understand the third reaction. The acidic hydrolysis of benzonitrile gives benzoic acid.

Image: Acidic hydrolysis of benzonitrile
So, the complete reaction is,

Image: The reaction of aniline to form benzoic acid
Hence, the reactant A is aniline, i.e, \[{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{5}}}{\rm{N}}{{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}\] .
Note: The Sandmeyer reaction is the one in which chloride, bromide and cyanide ion can be introduced in the benzene ring in the presence of copper ion. And, we know, the acidic hydrolysis of cyanide gives the carboxylic acid.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




