
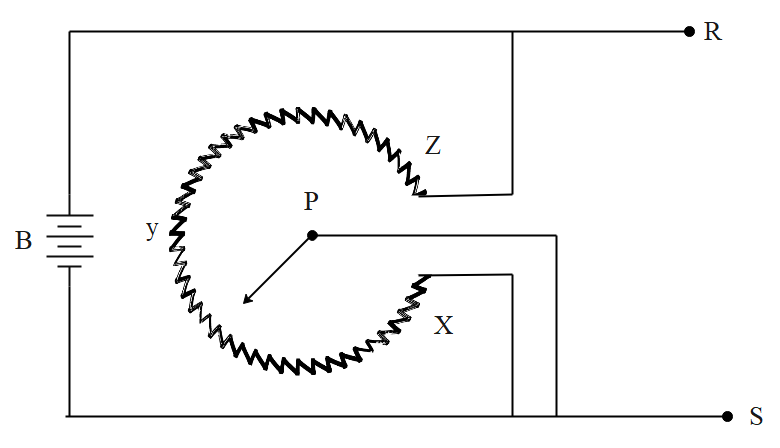
The arm PQ can revolve with uniform speed continuously about P round the circular uniform potentiometer track XYZ. The voltage between RS will vary with respect to lime:
(A) Sinusoidally
(B) Linearly
(C) Rectangularly
(D) Like saw tooth
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: We know that a potentiometer is a three-terminal resistor with a sliding or rotating contact that forms an adjustable voltage divider. If only two terminals are used, one end and the wiper, it acts as a variable resistor or rheostat. A potentiometer circuit can be used for comparing and measuring potential differences, the principle of action being that the unknown EMF is measured by balancing it against a known potential difference. Potentiometers are commonly used to control electrical devices such as volume controls on audio equipment. Potentiometers operated by a mechanism can be used as position transducers, for example, in a joystick.
Complete step-by step answer:
As the voltage between $RS\text{ }\left( V \right)\,\propto \,$Resistance between P and Z.
Arm PQ is revolving uniformly so resistance between P and Z is changing uniformly
Let resistance XZ = R.
So, we can write resistance between P and Z as the function of time is $r=R-kt$.
Where k is some constant and r is resistance between P and Z which is an equation of decreasing straight line.
As arm comes to point Z resistance r = 0 and again it stands from R as it comes to point X.
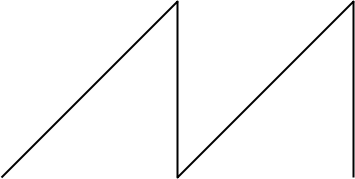
Hence, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: We should know that the sawtooth wave or we can say saw wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is so named based, particularly bowed string instruments like violins and cellos, since the slip-stick behaviour of the bow drives the strings with a sawtooth-like motion. The convention is that a sawtooth wave ramps upward and then sharply drops. In a reverse or inverse sawtooth wave, the wave ramps downward and then sharply rises. It can also be considered the extreme case of an asymmetric triangle wave. Sawtooth waves are known for their use in music. The sawtooth and square waves are among the most common waveforms used to create sounds with subtractive analog and virtual analog music synthesizers.
It should also be known to us that the sawtooth wave is the form of the vertical and horizontal deflection signals used to generate a raster on CRT-based television or monitor screens. Oscilloscopes also use a sawtooth wave for their horizontal deflection, though they typically use electrostatic deflection.
Complete step-by step answer:
As the voltage between $RS\text{ }\left( V \right)\,\propto \,$Resistance between P and Z.
Arm PQ is revolving uniformly so resistance between P and Z is changing uniformly
Let resistance XZ = R.
So, we can write resistance between P and Z as the function of time is $r=R-kt$.
Where k is some constant and r is resistance between P and Z which is an equation of decreasing straight line.
As arm comes to point Z resistance r = 0 and again it stands from R as it comes to point X.

Hence, the correct answer is Option D.
Note: We should know that the sawtooth wave or we can say saw wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform. It is so named based, particularly bowed string instruments like violins and cellos, since the slip-stick behaviour of the bow drives the strings with a sawtooth-like motion. The convention is that a sawtooth wave ramps upward and then sharply drops. In a reverse or inverse sawtooth wave, the wave ramps downward and then sharply rises. It can also be considered the extreme case of an asymmetric triangle wave. Sawtooth waves are known for their use in music. The sawtooth and square waves are among the most common waveforms used to create sounds with subtractive analog and virtual analog music synthesizers.
It should also be known to us that the sawtooth wave is the form of the vertical and horizontal deflection signals used to generate a raster on CRT-based television or monitor screens. Oscilloscopes also use a sawtooth wave for their horizontal deflection, though they typically use electrostatic deflection.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main Course 2026 - Important Updates and Details

JEE Main 2026 Session 1 Correction Window Started: Check Dates, Edit Link & Fees

Chemistry Question Pattern for JEE Main & Board Exams

Chemistry Question Paper PDF Download (2025, 2024) with Solutions

JEE Main Books 2026: Best JEE Main Books for Physics, Chemistry and Maths

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




