
Plot a graph showing the variation of undecayed nuclei $N$ versus time $t$. From the graph, find out how one can determine the half-life and average life of the radioactive nuclei.
Answer
243k+ views
Hint: Radioactive decay is the process of slow disintegration of radioactive elements by releasing their energy in the form of radiation. The radioactive materials have unstable nuclei and therefore the nuclei breakdowns take place in the form of radiation. The radioactivity is given by the formula:
$A = - \dfrac{{dN}}{{dt}}$
where $A = $ total activity
$N = $ number of particles
$t = $ time
Complete step by step solution:
In radioactive decay, the rate of radioactive decay is proportional to the number of nuclei present. The number of nuclei in radioactive decay degrades and exponentially decreases with time. As per the radioactive decay law, the disintegration equation is given by:
$N = {N_0}{e^{ - \lambda t}}$
Where, $N = $ number of radioactive atoms at any random time.
${N_0} = $ number of radioactive atoms present initially.
$\lambda = $ decay constant
$t = $ time
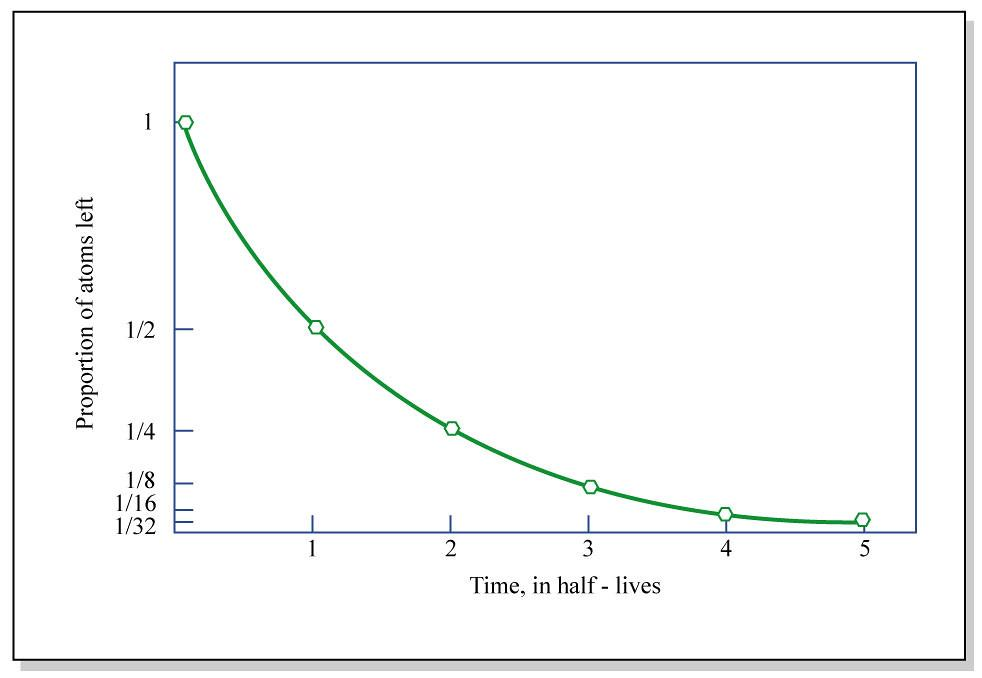
The above plot depicts the variation of the number of nuclei disintegrate with time. $N$ gradually decreases with increase in time and there comes a state where the nuclei are completely depleted at a given time. The rate of disintegration of nuclei is directly proportional to the nuclei available i.e. $ - \dfrac{{dN}}{{dt}} \propto N$
$ \Rightarrow - \dfrac{{dN}}{{dt}} = \lambda N$
The negative sign represents the gradual decrease of the number of nuclei with time.
The half-life of the radioactive element is the time required for its activity to decrease by one-half. So after one half-life, 50% of the initial activity remains and after two half-lives only 25% of the initial activity remains and after three half-lives, only 12.5% is present and so forth.
The half-life of a given nuclei can be derived as follows:
In half-life of a nuclei, the given lifespan of the nuclei is completed by 50% and it is denoted as ${t_{1/2}}$.
Therefore, the half-life of an atomic nuclei can be given by substituting $t = {t_{1/2}}$and $N = \dfrac{{{N_0}}}{2}$ in $N = {N_0}{e^{ - \lambda {t_{1/2}}}}$
Which gives, $\dfrac{{{N_0}}}{2} = {N_0}{e^{ - \lambda {t_{1/2}}}}$ $ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = {e^{ - \lambda {t_{1/2}}}}$
Taking log on both side, we get ${\log _e}(2) = \lambda {t_{1/2}}$
$ \Rightarrow 0.693 = \lambda {t_{1/2}}$ $ \Rightarrow {t_{1/2}} = \dfrac{{0.693}}{\lambda }$
The average life of a nuclei atom is the amount of time required for the nuclei to decay to $36.8\% $ of the total amount. Therefore $N = 0.368{N_0}$ and $t$ changes as
$0.368{N_0} = {N_0}{e^{ - \lambda {t_{avg}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow 0.368 = {e^{ - \lambda {t_{avg}}}}$
Taking log on both sides,
${\log _e}(0.368) = - \lambda {t_{avg}}$
Which gives, $0.434 = \lambda {t_{avg}}$
$ \Rightarrow {t_{avg}} = \dfrac{{0.434}}{\lambda }$
Note: The unstable nuclei in radioactive samples do not decay simultaneously. Instead the decay of a given nucleus is an entirely random event. The rate of nuclei disintegration is insulated by surrounding electrons and hence the disintegration of the radioactive element is independent of temperature, pressure and doesn't follow any mass law or any other law that explains the physical and chemical change.
$A = - \dfrac{{dN}}{{dt}}$
where $A = $ total activity
$N = $ number of particles
$t = $ time
Complete step by step solution:
In radioactive decay, the rate of radioactive decay is proportional to the number of nuclei present. The number of nuclei in radioactive decay degrades and exponentially decreases with time. As per the radioactive decay law, the disintegration equation is given by:
$N = {N_0}{e^{ - \lambda t}}$
Where, $N = $ number of radioactive atoms at any random time.
${N_0} = $ number of radioactive atoms present initially.
$\lambda = $ decay constant
$t = $ time

The above plot depicts the variation of the number of nuclei disintegrate with time. $N$ gradually decreases with increase in time and there comes a state where the nuclei are completely depleted at a given time. The rate of disintegration of nuclei is directly proportional to the nuclei available i.e. $ - \dfrac{{dN}}{{dt}} \propto N$
$ \Rightarrow - \dfrac{{dN}}{{dt}} = \lambda N$
The negative sign represents the gradual decrease of the number of nuclei with time.
The half-life of the radioactive element is the time required for its activity to decrease by one-half. So after one half-life, 50% of the initial activity remains and after two half-lives only 25% of the initial activity remains and after three half-lives, only 12.5% is present and so forth.
The half-life of a given nuclei can be derived as follows:
In half-life of a nuclei, the given lifespan of the nuclei is completed by 50% and it is denoted as ${t_{1/2}}$.
Therefore, the half-life of an atomic nuclei can be given by substituting $t = {t_{1/2}}$and $N = \dfrac{{{N_0}}}{2}$ in $N = {N_0}{e^{ - \lambda {t_{1/2}}}}$
Which gives, $\dfrac{{{N_0}}}{2} = {N_0}{e^{ - \lambda {t_{1/2}}}}$ $ \Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{2} = {e^{ - \lambda {t_{1/2}}}}$
Taking log on both side, we get ${\log _e}(2) = \lambda {t_{1/2}}$
$ \Rightarrow 0.693 = \lambda {t_{1/2}}$ $ \Rightarrow {t_{1/2}} = \dfrac{{0.693}}{\lambda }$
The average life of a nuclei atom is the amount of time required for the nuclei to decay to $36.8\% $ of the total amount. Therefore $N = 0.368{N_0}$ and $t$ changes as
$0.368{N_0} = {N_0}{e^{ - \lambda {t_{avg}}}}$
$ \Rightarrow 0.368 = {e^{ - \lambda {t_{avg}}}}$
Taking log on both sides,
${\log _e}(0.368) = - \lambda {t_{avg}}$
Which gives, $0.434 = \lambda {t_{avg}}$
$ \Rightarrow {t_{avg}} = \dfrac{{0.434}}{\lambda }$
Note: The unstable nuclei in radioactive samples do not decay simultaneously. Instead the decay of a given nucleus is an entirely random event. The rate of nuclei disintegration is insulated by surrounding electrons and hence the disintegration of the radioactive element is independent of temperature, pressure and doesn't follow any mass law or any other law that explains the physical and chemical change.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Tests: Free Practice Papers & Solutions

JEE Main 2025-26 Experimental Skills Mock Test – Free Practice

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Other Pages
CBSE Class 12 Physics Question Paper 2026: Download SET-wise PDF with Answer Key & Analysis

JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring




