
What is the nature of the graph between the separation of the slits and fringe width in case of young’s double slit experiment ?
A) Straight line with negative slope.
B) Straight line with positive slope.
C) Rectangular hyperbola
D) None of these
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Young’s double slit experiment is a demonstration that light and matter can display characteristics of both classically defined waves and particles. he observed that as the difference /distance between the slits is decreased the fringe width obtained has more width, he concluded that both have inverse relationship as \[fringe\;width(\beta ) \propto \dfrac{1}{{separation\;between\;slits}}\]and when he plotted the data collected this was resembling a shape called rectangular hyperbola.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that the fringe width (\[\beta \]) in case of young’s double slit experiment is given by \[fringe\;width(\beta ) = \lambda \dfrac{D}{d}\] ,
From this equation we conclude that,
\[fringe\;width(\beta ) \propto \dfrac{1}{{separation\;between\;slits}}\]
\[fringe\;width(\beta ) \propto \dfrac{1}{d}\] ; separation between the slits = d.
It means that ;
\[ \Rightarrow \beta d = \]constant.
As we know the graph of \[xy = \]constant is a rectangular hyperbola. Here is the graph between the fringe-width and the separation between slits in Young's double slit experiment.
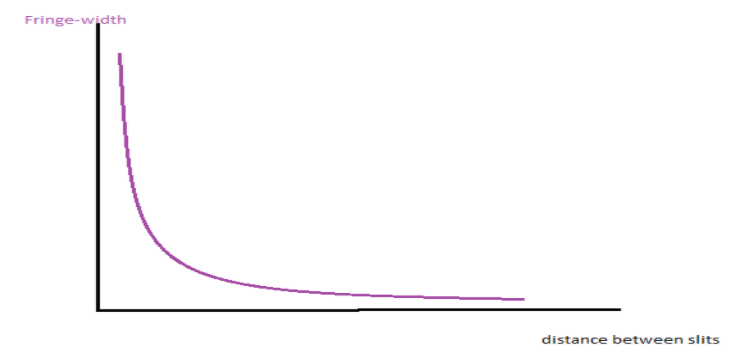
Hence option (C) is the correct answer.
Historically, Young's double slit experiment was first carried out by Young in 1801. This experiment demonstrated that light was a wave.
Young’s double slit experiment uses two coherent sources of light placed at a small distance apart, usually only a few orders of magnitude greater than the wavelength of light is used. Young’s double-slit experiment helped in understanding the wave theory of light which was proposed by Huygens .
Note: The double slit experiment was later conducted using electrons, and the pattern which generated was similar as expected with light. This surprised the world and it changed our understanding of matter and particles, forcing us to accept that matter like light also behaves like a wave.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that the fringe width (\[\beta \]) in case of young’s double slit experiment is given by \[fringe\;width(\beta ) = \lambda \dfrac{D}{d}\] ,
From this equation we conclude that,
\[fringe\;width(\beta ) \propto \dfrac{1}{{separation\;between\;slits}}\]
\[fringe\;width(\beta ) \propto \dfrac{1}{d}\] ; separation between the slits = d.
It means that ;
\[ \Rightarrow \beta d = \]constant.
As we know the graph of \[xy = \]constant is a rectangular hyperbola. Here is the graph between the fringe-width and the separation between slits in Young's double slit experiment.

Hence option (C) is the correct answer.
Historically, Young's double slit experiment was first carried out by Young in 1801. This experiment demonstrated that light was a wave.
Young’s double slit experiment uses two coherent sources of light placed at a small distance apart, usually only a few orders of magnitude greater than the wavelength of light is used. Young’s double-slit experiment helped in understanding the wave theory of light which was proposed by Huygens .
Note: The double slit experiment was later conducted using electrons, and the pattern which generated was similar as expected with light. This surprised the world and it changed our understanding of matter and particles, forcing us to accept that matter like light also behaves like a wave.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance




