
Match the polymers given in column I with their repeating units given in column II.
Column I Column II (a) Acrilan (i)
(b) Polystyrene (ii)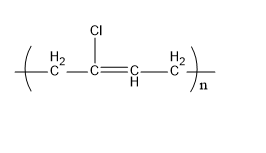
(c) Neoprene (iii)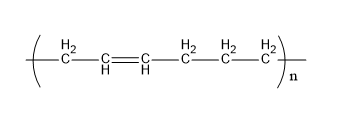
(d) Novolac (iv) 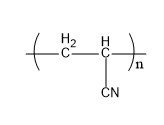
(e) Buna-N (v) 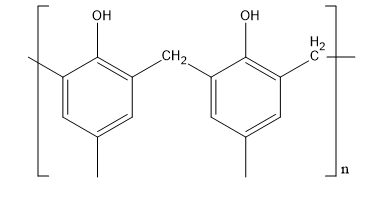 (vi)
(vi)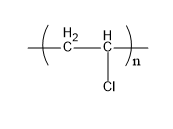
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Acrilan | (i)
 |
| (b) Polystyrene | (ii) |
| (c) Neoprene | (iii) |
| (d) Novolac | (iv)  |
| (e) Buna-N | (v)  (vi) (vi) |
Answer
238.8k+ views
Hint: Polymer defines a very large molecule made up of many small numbers of monomers. Some examples of polymer are polyethene, polyester, etc. Some of the polymers are very important in our day-to-day life.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let's understand the given polymers in detail. Acrilan is a polymer which is very hard in nature. Also, it has a very high melting point. It is also known by the name of orlon. When acrylonitrile undergoes additional polymerization, it gives acrylonitrile. Its structure is,
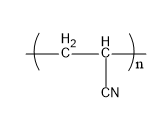
Fig: Acrilan
Therefore, A matches (iv).
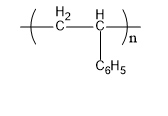
Now we will discuss polystyrene. The monomer units that form polystyrene are styrene. Its commercial manufacturing is done from petroleum. Its structure is,
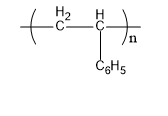
Fig: Polystyrene
Therefore, B matches (i)
Neoprene is a synthetic rubber. The monomer units that form a neoprene are chloroprene. It is formed by the polymerization process. Its structure is,
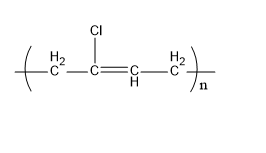
Fig:Neoprene
Therefore, C matches (ii).
Let’s discuss about novolac. This polymer is synthesised from formaldehyde and phenol. This polymer has a very molecular weight. Its polymer chain is straight. Its structure is,
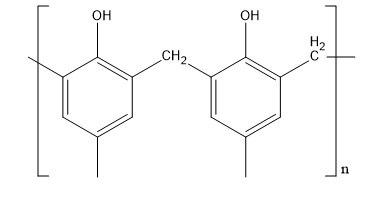
Fig:Novolac
Therefore, D matches with (v).
Buna-n is a polymer formed from acrylonitrile and 1,3-butadiene. Its structure is,
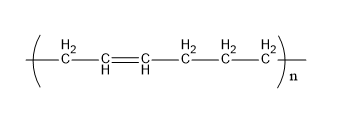
Fig:Buna-N
Therefore, E matches (iii)
Hence, the complete table is:
Note: The process of polymer formation from the monomers is termed polymerization process. For example, the polymerization of ethane gives the polymer of polyethene. There are two types, addition and condensation polymerization.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Let's understand the given polymers in detail. Acrilan is a polymer which is very hard in nature. Also, it has a very high melting point. It is also known by the name of orlon. When acrylonitrile undergoes additional polymerization, it gives acrylonitrile. Its structure is,

Fig: Acrilan
Therefore, A matches (iv).
Now we will discuss polystyrene. The monomer units that form polystyrene are styrene. Its commercial manufacturing is done from petroleum. Its structure is,

Fig: Polystyrene
Therefore, B matches (i)
Neoprene is a synthetic rubber. The monomer units that form a neoprene are chloroprene. It is formed by the polymerization process. Its structure is,

Fig:Neoprene
Therefore, C matches (ii).
Let’s discuss about novolac. This polymer is synthesised from formaldehyde and phenol. This polymer has a very molecular weight. Its polymer chain is straight. Its structure is,

Fig:Novolac
Therefore, D matches with (v).
Buna-n is a polymer formed from acrylonitrile and 1,3-butadiene. Its structure is,

Fig:Buna-N
Therefore, E matches (iii)
Hence, the complete table is:
| Column I | Column II |
| (a) Acrilan | (iv) 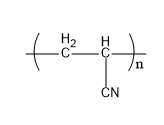 |
| (b) Polystyrene | (i)
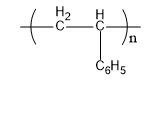 |
| (c) Neoprene | (ii)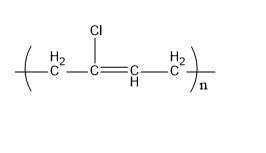 |
| (d) Novolac | (v) 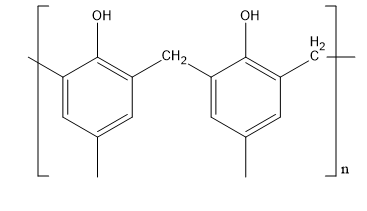 |
| (e) Buna-N | (iii)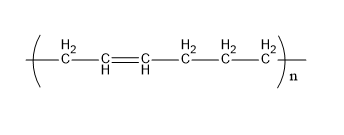 |
Note: The process of polymer formation from the monomers is termed polymerization process. For example, the polymerization of ethane gives the polymer of polyethene. There are two types, addition and condensation polymerization.
Recently Updated Pages
Types of Solutions in Chemistry: Explained Simply

JEE Main Mock Test 2025-26: Principles Related To Practical

JEE Main 2025-26 Organic Compounds Containing Nitrogen Mock Test

JEE Main 2025-26 Mock Test: Organic Compounds Containing Oxygen

JEE Main 2025-26 Redox Reactions & Electro Mock Test

JEE Main Solutions Mock Test 1-2 (2025-26): Free Practice & Answers

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

JEE Main Participating Colleges 2026 - A Complete List of Top Colleges

Understanding Electromagnetic Waves and Their Importance

Common Ion Effect: Concept, Applications, and Problem-Solving

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Electrochemistry - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The D And F Block Elements - 2025-26

CBSE Notes Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 - Solutions - 2025-26




