
If the roots of the equation ${x^2} - 2ax + {a^2} + a - 3 = 0$ are real and less than 3, then
A. $a < 2$
B. $2 \leqslant a \leqslant 3$
C. $3 < a \leqslant 4$
D. $a > 4$
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: Check the concavity of the given quadratic equation and using this information check whether $f(3)$ is positive or negative. Also use the fact that the discriminant must be greater than or equal to 0 as real roots exist. With the two inequalities, find the range of a.
Formula used: Discriminant of the standard quadratic equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ is ${b^2} - 4ac$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let $f(x) = {x^2} - 2ax + {a^2} + a - 3$
The coefficient of ${x^2}$ in the equation ${x^2} - 2ax + {a^2} + a - 3 = 0$ is greater than 0. Therefore, it is a concave upwards graph. Since it is a concave upwards graph, $f(x)$ will be negative only when $x \in \left[ {p,q} \right]$ where $p,q$ are the roots.
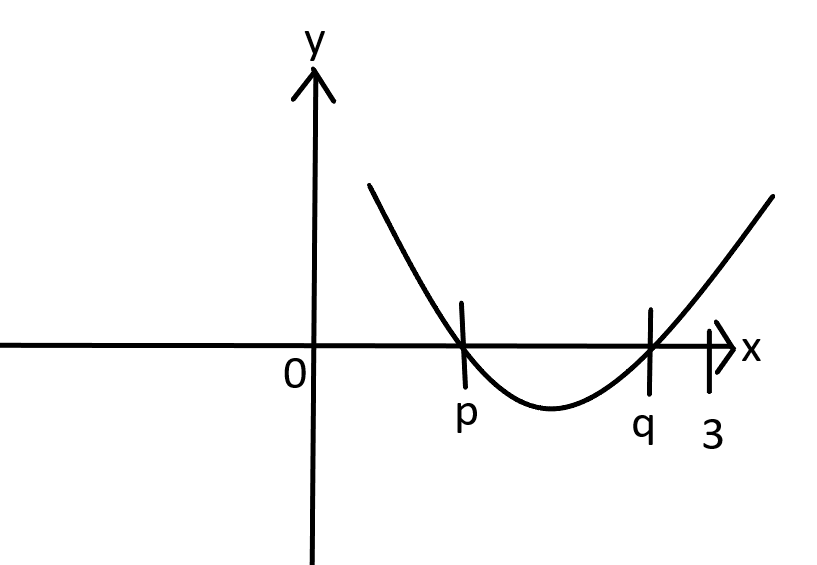
Therefore, $f(3)$ is positive. We also know that real roots exist. Therefore, the discriminant of the quadratic equation, ${x^2} - 2ax + {a^2} + a - 3 = 0$ must also be greater than or equal to 0.
Since $f(3) > 0$,
${3^2} - 2a(3) + {a^2} + a - 3 > 0$
$9 - 6a + {a^2} + a - 3 > 0$
${a^2} - 5a + 6 > 0$
Solving further we get,
${a^2} - 2a - 3a + 6 > 0$
$a\left( {a - 2} \right) - 3\left( {a - 2} \right) > 0$
$\left( {a - 2} \right)\left( {a - 3} \right) > 0$
$a \in \left( { - \infty ,2} \right) \cup \left( {3,\infty } \right)$
Since discriminant, $D \geqslant 0$,
${\left( { - 2a} \right)^2} - 4\left( 1 \right)\left( {{a^2} + a - 3} \right) \geqslant 0$
$4{a^2} - 4{a^2} - 4a + 12 \geqslant 0$
Simplifying the above inequality,
$4a \leqslant 12$
$a \leqslant 3$
$a \in ( - \infty ,3]$
Taking the intersection of $\left( { - \infty ,2} \right) \cup \left( {3,\infty } \right)$ and $( - \infty ,3]$, we get $a \in \left( { - \infty ,2} \right)$.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A. $a < 2$.
Note: Given a quadratic polynomial $a{x^2} + bx + c$, if $a > 0$ then the graph of the quadratic polynomial will be a concave upwards graph and if $a < 0$ then the graph of the quadratic polynomial will be a concave downwards graph.
Formula used: Discriminant of the standard quadratic equation $a{x^2} + bx + c = 0$ is ${b^2} - 4ac$
Complete step-by-step solution:
Let $f(x) = {x^2} - 2ax + {a^2} + a - 3$
The coefficient of ${x^2}$ in the equation ${x^2} - 2ax + {a^2} + a - 3 = 0$ is greater than 0. Therefore, it is a concave upwards graph. Since it is a concave upwards graph, $f(x)$ will be negative only when $x \in \left[ {p,q} \right]$ where $p,q$ are the roots.

Therefore, $f(3)$ is positive. We also know that real roots exist. Therefore, the discriminant of the quadratic equation, ${x^2} - 2ax + {a^2} + a - 3 = 0$ must also be greater than or equal to 0.
Since $f(3) > 0$,
${3^2} - 2a(3) + {a^2} + a - 3 > 0$
$9 - 6a + {a^2} + a - 3 > 0$
${a^2} - 5a + 6 > 0$
Solving further we get,
${a^2} - 2a - 3a + 6 > 0$
$a\left( {a - 2} \right) - 3\left( {a - 2} \right) > 0$
$\left( {a - 2} \right)\left( {a - 3} \right) > 0$
$a \in \left( { - \infty ,2} \right) \cup \left( {3,\infty } \right)$
Since discriminant, $D \geqslant 0$,
${\left( { - 2a} \right)^2} - 4\left( 1 \right)\left( {{a^2} + a - 3} \right) \geqslant 0$
$4{a^2} - 4{a^2} - 4a + 12 \geqslant 0$
Simplifying the above inequality,
$4a \leqslant 12$
$a \leqslant 3$
$a \in ( - \infty ,3]$
Taking the intersection of $\left( { - \infty ,2} \right) \cup \left( {3,\infty } \right)$ and $( - \infty ,3]$, we get $a \in \left( { - \infty ,2} \right)$.
Therefore, the correct answer is option A. $a < 2$.
Note: Given a quadratic polynomial $a{x^2} + bx + c$, if $a > 0$ then the graph of the quadratic polynomial will be a concave upwards graph and if $a < 0$ then the graph of the quadratic polynomial will be a concave downwards graph.
Recently Updated Pages
Mutually Exclusive vs Independent Events: Key Differences Explained

Area vs Volume: Key Differences Explained for Students

Area of an Octagon Formula Explained Simply

Absolute Pressure Formula Explained: Key Equation & Examples

Central Angle of a Circle Formula Explained Quickly

Difference Between Vapor and Gas: JEE Main 2026

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Jan 21 Shift 1 Question Papers with Solutions & Answer Keys – Detailed Day 1 Analysis

JEE Main Response Sheet 2026 Released – Key Dates and Official Updates by NTA

JEE Main 2026 Answer Key OUT – Download Session 1 PDF, Response Sheet & Challenge Link

JEE Main Marks vs Percentile 2026: Calculate Percentile and Rank Using Marks

JEE Main 2026 Jan 22 Shift 1 Today Paper Live Analysis With Detailed Solutions

Other Pages
Pregnancy Week and Due Date Calculator: Find How Far Along You Are

NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 11 Areas Related to Circles (2025-26)

NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes (2025-26)

All Mensuration Formulas with Examples and Quick Revision

Complete List of Class 10 Maths Formulas (Chapterwise)

NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 13 Statistics




