
The angle of depression of the top and the bottom of a building 50m high are observed from the top of a tower are \[30^\circ \] and \[60^\circ \] respectively. Find the height of the tower and also the horizontal distance between the building and the tower.
Answer
535.7k+ views
Hint: Draw the diagram of the given problem statement for a better understanding of the situation. Use the trigonometric ratios, that are $\sin \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Opposite}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}$ and $\tan \theta = \dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}$ in the physical triangle formed to find the height of the tower and horizontal distance between the building and the tower.
Complete step by step answer:
Since it is given that the angle observed from the top of the tower to the top and bottom of the building are \[30^\circ \] and \[60^\circ \]respectively, we can draw a diagram representing the condition.
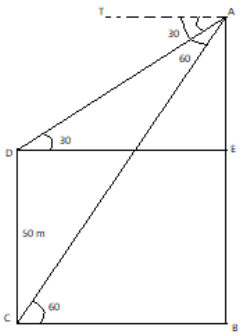
In the diagram, A represents the top of the tower, AB represents the height of the tower, DC represents the building of height 50 metres.
It is given in the question that the angle $\angle TAD$ is \[30^\circ \] and the angle $\angle TAC$ is \[60^\circ \].
By the property of the corresponding angles of the parallel lines, we can say that the angle $\angle ADE$is \[30^\circ \] and the angle $\angle ACB$ is \[60^\circ \].
In the triangle $ADE$, we can say
\[\tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{{{\text{AE}}}}{{DE}}\]
On further simplifying
$
\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{{\text{AE}}}}{{DE}} \\
\sqrt 3 {\text{AE = DE}} \\
$
Similarly, in the triangle ${\text{ACB}}$
\[\tan {60^ \circ } = \dfrac{{{\text{AB}}}}{{{\text{BC}}}}\]
On further simplifying
$
\sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{{\text{AB}}}}{{{\text{BC}}}} \\
\sqrt 3 {\text{BC = AB}} \\
$
From the figure we infer that,
${\text{BC = DE}}$
$
{\text{AB = AE + EB}} \\
{\text{EB = CD = 50}} \\
{\text{AB = AE + 50}} \\
$
Substituting the value ${\text{AE + 50}}$ for ${\text{AB}}$ and ${\text{DE}}$ for ${\text{BC}}$ in the equation \[\sqrt 3 {\text{BC = AB}}\], we get
\[\sqrt 3 {\text{DE = AE + 50}}\]
Also, \[\sqrt 3 {\text{AE = DE}}\]
Thus the expression becomes \[\sqrt 3 \left( {\sqrt 3 {\text{AE}}} \right){\text{ = AE + 50}}\]
We can solve the expression to find the value of ${\text{AE}}$
$
3{\text{AE = AE + 50}} \\
{\text{2AE = 50}} \\
{\text{AE = 25}} \\
$
Substituting the value 25 for ${\text{AE}}$ in the equation ${\text{AB = AE + 50}}$ to find the height of the tower, and in the equation \[\sqrt 3 {\text{AE = DE}}\] to find the horizontal distance between the building and the tower.
$
{\text{AB = 25 + 50}} \\
{\text{AB = 75}} \\
$
\[{\text{DE}} = \sqrt 3 \left( {25} \right)\]
Thus the height of the tower is 75 m, and the horizontal distance between the building and the tower is $25\sqrt 3 $m.
Note: In a right angled triangle, the $\tan \theta $ is the equal to $\dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}$, where perpendicular is the side opposite to the angle $\theta $, and $\sin \theta $ is the equal to $\dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}$, where perpendicular is the side opposite to the angle $\theta $.
Complete step by step answer:
Since it is given that the angle observed from the top of the tower to the top and bottom of the building are \[30^\circ \] and \[60^\circ \]respectively, we can draw a diagram representing the condition.

In the diagram, A represents the top of the tower, AB represents the height of the tower, DC represents the building of height 50 metres.
It is given in the question that the angle $\angle TAD$ is \[30^\circ \] and the angle $\angle TAC$ is \[60^\circ \].
By the property of the corresponding angles of the parallel lines, we can say that the angle $\angle ADE$is \[30^\circ \] and the angle $\angle ACB$ is \[60^\circ \].
In the triangle $ADE$, we can say
\[\tan {30^ \circ } = \dfrac{{{\text{AE}}}}{{DE}}\]
On further simplifying
$
\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} = \dfrac{{{\text{AE}}}}{{DE}} \\
\sqrt 3 {\text{AE = DE}} \\
$
Similarly, in the triangle ${\text{ACB}}$
\[\tan {60^ \circ } = \dfrac{{{\text{AB}}}}{{{\text{BC}}}}\]
On further simplifying
$
\sqrt 3 = \dfrac{{{\text{AB}}}}{{{\text{BC}}}} \\
\sqrt 3 {\text{BC = AB}} \\
$
From the figure we infer that,
${\text{BC = DE}}$
$
{\text{AB = AE + EB}} \\
{\text{EB = CD = 50}} \\
{\text{AB = AE + 50}} \\
$
Substituting the value ${\text{AE + 50}}$ for ${\text{AB}}$ and ${\text{DE}}$ for ${\text{BC}}$ in the equation \[\sqrt 3 {\text{BC = AB}}\], we get
\[\sqrt 3 {\text{DE = AE + 50}}\]
Also, \[\sqrt 3 {\text{AE = DE}}\]
Thus the expression becomes \[\sqrt 3 \left( {\sqrt 3 {\text{AE}}} \right){\text{ = AE + 50}}\]
We can solve the expression to find the value of ${\text{AE}}$
$
3{\text{AE = AE + 50}} \\
{\text{2AE = 50}} \\
{\text{AE = 25}} \\
$
Substituting the value 25 for ${\text{AE}}$ in the equation ${\text{AB = AE + 50}}$ to find the height of the tower, and in the equation \[\sqrt 3 {\text{AE = DE}}\] to find the horizontal distance between the building and the tower.
$
{\text{AB = 25 + 50}} \\
{\text{AB = 75}} \\
$
\[{\text{DE}} = \sqrt 3 \left( {25} \right)\]
Thus the height of the tower is 75 m, and the horizontal distance between the building and the tower is $25\sqrt 3 $m.
Note: In a right angled triangle, the $\tan \theta $ is the equal to $\dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Base}}}}$, where perpendicular is the side opposite to the angle $\theta $, and $\sin \theta $ is the equal to $\dfrac{{{\text{Perpendicular}}}}{{{\text{Hypotenuse}}}}$, where perpendicular is the side opposite to the angle $\theta $.
Recently Updated Pages
Area vs Volume: Key Differences Explained for Students

Mutually Exclusive vs Independent Events: Key Differences Explained

Know The Difference Between Fluid And Liquid

Dimensions of Charge: Dimensional Formula, Derivation, SI Units & Examples

How to Calculate Moment of Inertia: Step-by-Step Guide & Formulas

Difference Between Crystalline and Amorphous Solid: Table & Examples

Trending doubts
JEE Mains Result 2026 OUT Check Scorecard Percentile Cutoff and Toppers

JEE Main Marks vs Percentile 2026: Calculate Percentile and Rank Using Marks

JEE Main 2026 Expected Cutoff Category Wise Qualifying Marks & Percentile

JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Jan 21 Shift 1 Question Papers with Solutions & Answer Keys – Detailed Day 1 Analysis

JEE Mains Marks vs Rank 2026 – Estimate Your Rank with JEE Scores

Other Pages
CBSE Class 10 Maths Question Paper 2026 OUT Download PDF with Solutions

CBSE Class 10 Maths 2025 Set 1 Question Paper (Standard)

CBSE Class 10 Maths Question Paper Set 3 2025 (Standard) – PDF, Solutions & Analysis

Complete List of Class 10 Maths Formulas (Chapterwise)

NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Area And Volume - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 10 Maths Chapter 11 Areas Related To Circles - 2025-26




