
If one of the lines of the pair $a{{x}^{2}}+2bxy+b{{y}^{2}}=0$ bisects the angle between x-axis and y-axis, then
[a] a+b = 12b
[b] a+b = -2b
[c] a+b = 2b
[d] ${{\left( a-b \right)}^{2}}=4{{b}^{2}}$
Answer
243.3k+ views
Hint: Use the fact that the pair of straight lines represented by the homogeneous equation $a{{x}^{2}}+2hxy+c{{y}^{2}}=0$ pass through the origin. Use the fact that any line passing through the origin is of the form $y=mx$. Use the fact that the slope of a line bisecting the coordinate axis is either 1 or -1. Hence find the required relation.
Complete step-by-step solution -
We have $a{{x}^{2}}+2bxy+b{{y}^{2}}=0$
Dividing both sides by ${{x}^{2}}$, we get
$a+2b\left( \dfrac{y}{x} \right)+b{{\left( \dfrac{y}{x} \right)}^{2}}=0$
We know that the equation of the line passing through origin is y = mx.
Hence we have $m=\dfrac{y}{x}$
Hence we get
$a+2bm+b{{m}^{2}}=0$
The above equation has either m = 1 or m = -1 as its root.
If m = 1, we have
$\begin{align}
& a+2b+b=0 \\
& \Rightarrow a+3b=0 \\
\end{align}$
If m = -1, we have
$\begin{align}
& a-2b+b=0 \\
& \Rightarrow a=b \\
\end{align}$
Hence options [b] and [c] are correct.
Note: When a = b, the equation becomes
$b{{x}^{2}}+2bxy+b{{y}^{2}}=0$
Dividing both sides by b, we get
${{x}^{2}}+2xy+{{y}^{2}}=0$
The graph of this pair is shown below
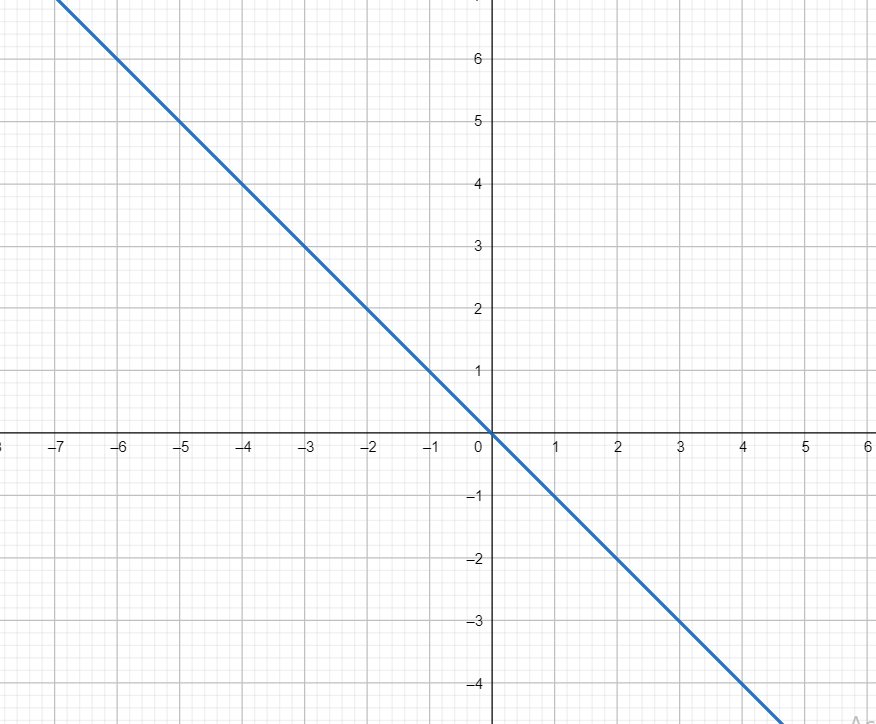
Which is a pair of coincident lines
Observe that the lines are bisecting the angle between x-axis and y-axis.
When a = -3b, the equation becomes
$-3b{{x}^{2}}+2bxy+b{{y}^{2}}=0$
Dividing both sides by b, we get
$-3{{x}^{2}}+2xy+{{y}^{2}}=0$
The graph of this pair is shown below
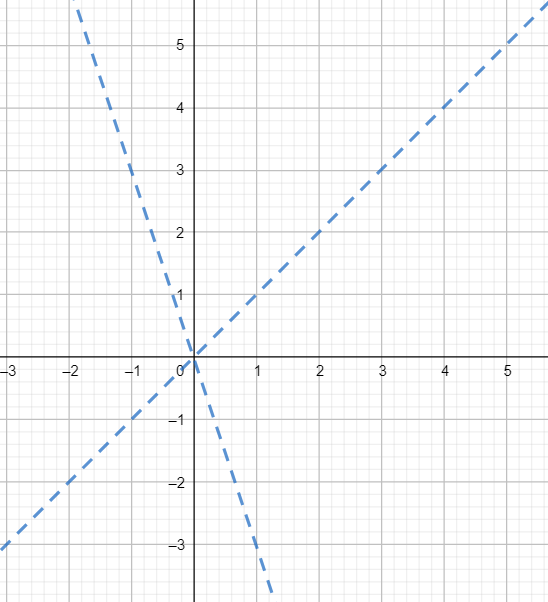
Observe that one line is bisecting the angle between x-axis and y-axis.
Complete step-by-step solution -
We have $a{{x}^{2}}+2bxy+b{{y}^{2}}=0$
Dividing both sides by ${{x}^{2}}$, we get
$a+2b\left( \dfrac{y}{x} \right)+b{{\left( \dfrac{y}{x} \right)}^{2}}=0$
We know that the equation of the line passing through origin is y = mx.
Hence we have $m=\dfrac{y}{x}$
Hence we get
$a+2bm+b{{m}^{2}}=0$
The above equation has either m = 1 or m = -1 as its root.
If m = 1, we have
$\begin{align}
& a+2b+b=0 \\
& \Rightarrow a+3b=0 \\
\end{align}$
If m = -1, we have
$\begin{align}
& a-2b+b=0 \\
& \Rightarrow a=b \\
\end{align}$
Hence options [b] and [c] are correct.
Note: When a = b, the equation becomes
$b{{x}^{2}}+2bxy+b{{y}^{2}}=0$
Dividing both sides by b, we get
${{x}^{2}}+2xy+{{y}^{2}}=0$
The graph of this pair is shown below

Which is a pair of coincident lines
Observe that the lines are bisecting the angle between x-axis and y-axis.
When a = -3b, the equation becomes
$-3b{{x}^{2}}+2bxy+b{{y}^{2}}=0$
Dividing both sides by b, we get
$-3{{x}^{2}}+2xy+{{y}^{2}}=0$
The graph of this pair is shown below

Observe that one line is bisecting the angle between x-axis and y-axis.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2026 Session 2 City Intimation Slip & Exam Date: Expected Date, Download Link

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Application Form: Reopened Registration, Dates & Fees

JEE Main 2026 Session 2 Registration (Reopened): Last Date, Fees, Link & Process

WBJEE 2026 Registration Started: Important Dates Eligibility Syllabus Exam Pattern

Geometry of Complex Numbers Explained

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 1 Results Out and Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

Ideal and Non-Ideal Solutions Explained for Class 12 Chemistry

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Understanding Differential Equations: A Complete Guide

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

JEE Advanced 2026 - Exam Date (Released), Syllabus, Registration, Eligibility, Preparation, and More

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Understanding the Block and Tackle System

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




