
If a magnet is hanged with its magnetic axis, then it stops in
A. Magnetic meridian
B. Geometric meridian
C. Angle of dip
D. None of these
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint:
In this question we have to use the concept of magnetic axis. The magnetic axis is a line that straddles the Earth's magnetic poles. The terms "magnetic meridian" and "magnetic equator" refer to a large circle that is perpendicular to the Earth's magnetic axis and a vertical plane that passes across it.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that a line joining the magnetic North Pole and the magnetic South Pole inside the earth is defined as Magnetic Meridian.
Also, in a Bar Magnet, there are two poles named ‘North-Pole’ and ‘South-Pole’ such that the magnetic field lines originate from the North pole and end at the South pole.
Since the magnetic meridian is parallel with the earth’s magnetic lines of force, therefore, whenever a magnet is freely suspended in the air along its magnetic axis then it will stop in Earth’s Magnetic Meridian.
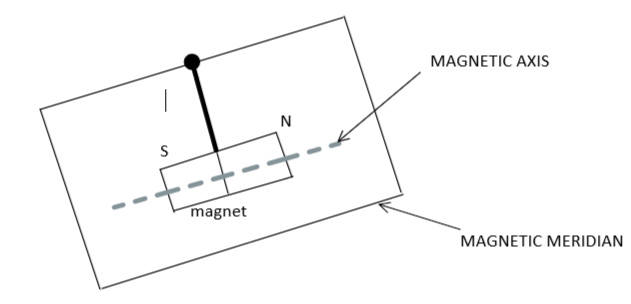
Thus, if a magnet is hanging with its magnetic axis, then it stops in the Magnetic meridian.
Hence, the correct option is (A) Magnetic meridian.
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note:
Since this is a problem related to a suspension of a bar magnet in Magnetism (conceptual problem) hence, it is essential that given options must be analyzed very carefully to give a precise explanation. While writing an explanation for this kind of conceptual problem, always keep in mind to provide the exact reasons in support of your explanation.
In this question we have to use the concept of magnetic axis. The magnetic axis is a line that straddles the Earth's magnetic poles. The terms "magnetic meridian" and "magnetic equator" refer to a large circle that is perpendicular to the Earth's magnetic axis and a vertical plane that passes across it.
Complete step by step solution:
We know that a line joining the magnetic North Pole and the magnetic South Pole inside the earth is defined as Magnetic Meridian.
Also, in a Bar Magnet, there are two poles named ‘North-Pole’ and ‘South-Pole’ such that the magnetic field lines originate from the North pole and end at the South pole.
Since the magnetic meridian is parallel with the earth’s magnetic lines of force, therefore, whenever a magnet is freely suspended in the air along its magnetic axis then it will stop in Earth’s Magnetic Meridian.

Thus, if a magnet is hanging with its magnetic axis, then it stops in the Magnetic meridian.
Hence, the correct option is (A) Magnetic meridian.
Therefore, the correct option is A.
Note:
Since this is a problem related to a suspension of a bar magnet in Magnetism (conceptual problem) hence, it is essential that given options must be analyzed very carefully to give a precise explanation. While writing an explanation for this kind of conceptual problem, always keep in mind to provide the exact reasons in support of your explanation.
Recently Updated Pages
Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




