
Ethylene is converted to X on passing through a mixture of an acidified aqueous solution of palladium chloride and cupric chloride. Which of the following reagents readily take part in addition reaction with X
A.\[B{r_2}\]
B. HBr
C. HCl
D. HCN
Answer
233.1k+ views
Hint: Ethylene when treated by passing through a mixture of an acidified aqueous solution of palladium chloride and cupric chloride, the reaction is called the Wacker process. This chemical reaction is a type of homogeneous catalysis.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Ethene and oxygen are treated in a reaction tower at high temperatures and pressure.
The catalyst used in this reaction is an aqueous solution of\[PdC{l_2}\] and\[CuC{l_2}\].
Acetaldehyde or ethanal is produced in this reaction. So, X is acetaldehyde.
In this question, we have to find out which of the following given compounds will take part in an addition reaction with acetaldehyde.
Due to the difference in electronegativity of carbon and oxygen in the carbonyl group present in acetaldehyde, it gives addition reactions.
Carbon acquires a partial positive charge and oxygen develops a partial negative charge.
A. \[B{r_2}\]
Bromine will not take part in addition to reaction with acetaldehyde.
It rather takes part in a substitution reaction.
Aldehydes and ketones can transfer an α-hydrogen for a halogen in an acidic medium.
Acetaldehyde undergoes tautomerization to form an enol which then reacts with bromine.
Enol is nucleophilic.
The reaction is as follows:
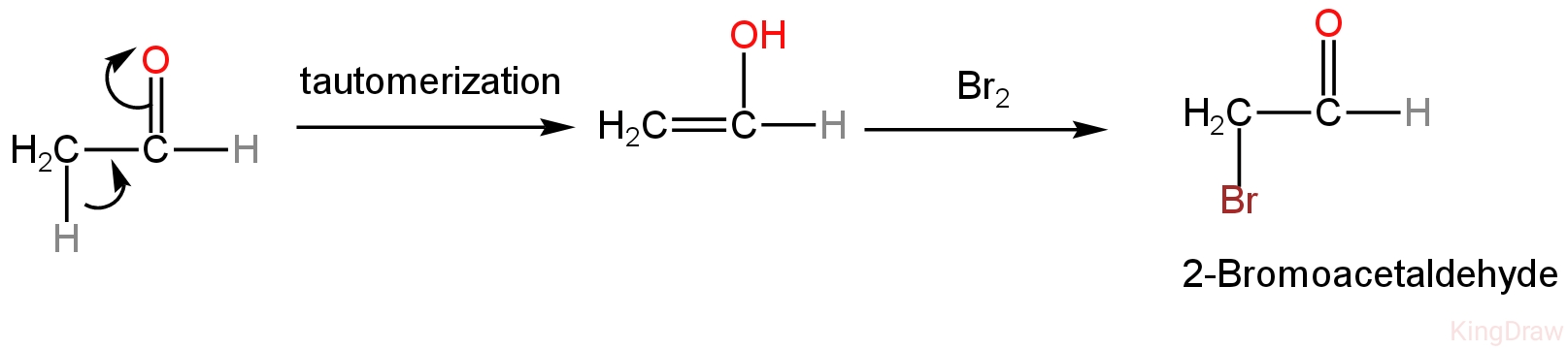
Image: Reaction of acetaldehyde with bromine.
So, A is incorrect.
B. HBr
When acetaldehyde is treated with HBr, it will give enol.
Enol can't attack the nucleophile bromide or bromine can attack enol as both the enol and bromine are negatively charged.
So, it will not take part in an addition reaction.
So, B is incorrect.
C. HCl
When acetaldehyde is treated with HCl, it will give enol.
Enol can't attack the chloride nor chloride can attack enol as both the enol and chloride are negatively charged.
So, it will not take part in an addition reaction.
So, C is incorrect.
D. HCN
It will take part in addition reaction with acetaldehyde by forming cyanohydrin.
In the initial step of the mechanism, the cyanide ion works as a nucleophile and constructs a carbon-carbon bond with the electrophilic carbonyl carbon constructing a tetrahedral alkoxide ion intermediate.
In the second step, the alkoxide ion is protonated by HCN which regenerates the cyanide ion.
The reaction happens as follows:-
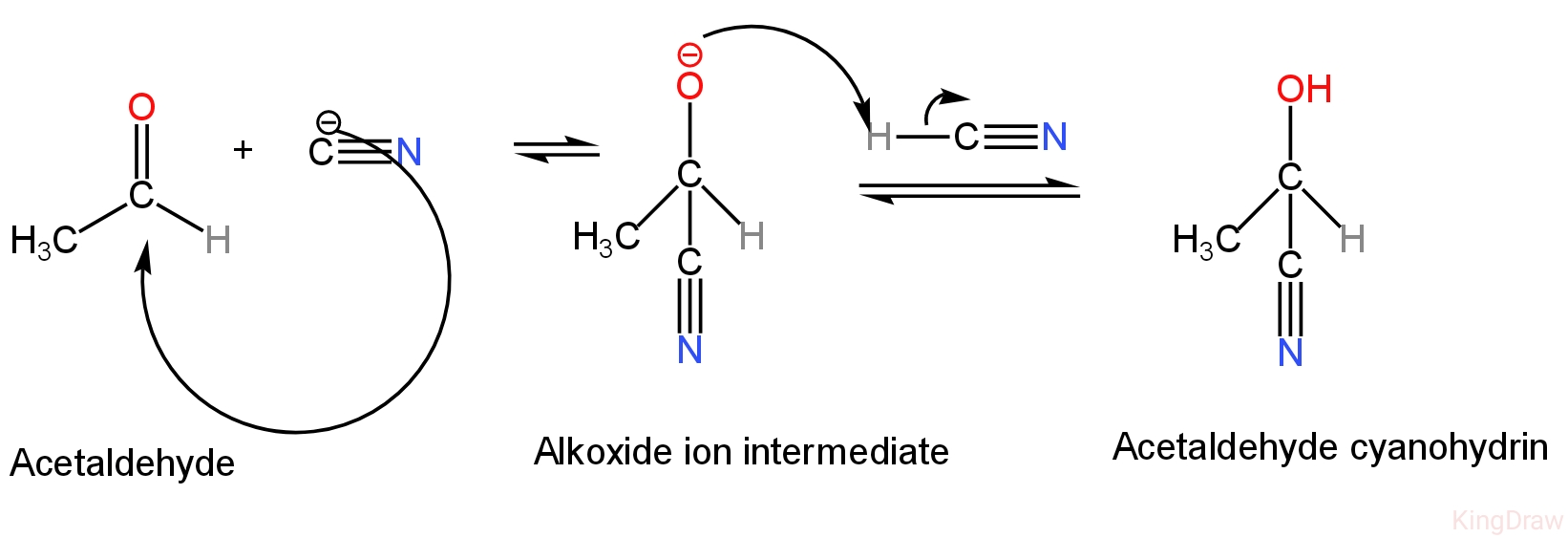
Image: Formation of cyanohydrin
So, HCN will take part in the addition reaction with acetaldehyde.
So, option D is correct.
Note: A cyanohydrin compound is a compound in which cyano and a hydroxyl group are linked to the same carbon atom. The general formula is R2C(OH)CN, where R can be Hydrogen, alkyl, or aryl group. It can be created by treating a ketone or an aldehyde with hydrogen cyanide (HCN) in the presence of extra quantities of sodium cyanide (NaCN) as a catalyst.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
Ethene and oxygen are treated in a reaction tower at high temperatures and pressure.
The catalyst used in this reaction is an aqueous solution of\[PdC{l_2}\] and\[CuC{l_2}\].
Acetaldehyde or ethanal is produced in this reaction. So, X is acetaldehyde.
In this question, we have to find out which of the following given compounds will take part in an addition reaction with acetaldehyde.
Due to the difference in electronegativity of carbon and oxygen in the carbonyl group present in acetaldehyde, it gives addition reactions.
Carbon acquires a partial positive charge and oxygen develops a partial negative charge.
A. \[B{r_2}\]
Bromine will not take part in addition to reaction with acetaldehyde.
It rather takes part in a substitution reaction.
Aldehydes and ketones can transfer an α-hydrogen for a halogen in an acidic medium.
Acetaldehyde undergoes tautomerization to form an enol which then reacts with bromine.
Enol is nucleophilic.
The reaction is as follows:

Image: Reaction of acetaldehyde with bromine.
So, A is incorrect.
B. HBr
When acetaldehyde is treated with HBr, it will give enol.
Enol can't attack the nucleophile bromide or bromine can attack enol as both the enol and bromine are negatively charged.
So, it will not take part in an addition reaction.
So, B is incorrect.
C. HCl
When acetaldehyde is treated with HCl, it will give enol.
Enol can't attack the chloride nor chloride can attack enol as both the enol and chloride are negatively charged.
So, it will not take part in an addition reaction.
So, C is incorrect.
D. HCN
It will take part in addition reaction with acetaldehyde by forming cyanohydrin.
In the initial step of the mechanism, the cyanide ion works as a nucleophile and constructs a carbon-carbon bond with the electrophilic carbonyl carbon constructing a tetrahedral alkoxide ion intermediate.
In the second step, the alkoxide ion is protonated by HCN which regenerates the cyanide ion.
The reaction happens as follows:-

Image: Formation of cyanohydrin
So, HCN will take part in the addition reaction with acetaldehyde.
So, option D is correct.
Note: A cyanohydrin compound is a compound in which cyano and a hydroxyl group are linked to the same carbon atom. The general formula is R2C(OH)CN, where R can be Hydrogen, alkyl, or aryl group. It can be created by treating a ketone or an aldehyde with hydrogen cyanide (HCN) in the presence of extra quantities of sodium cyanide (NaCN) as a catalyst.
Recently Updated Pages
JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 April 6 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 (January 31 Evening Shift) Question Paper with Solutions [PDF]

JEE Main 2023 January 30 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 25 Shift 1 Question Paper with Answer Key

JEE Main 2023 January 24 Shift 2 Question Paper with Answer Key

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions (2025-26)

Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4 The d and f Block Elements (2025-26)

Biomolecules Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Biomolecules (2025-26)




