
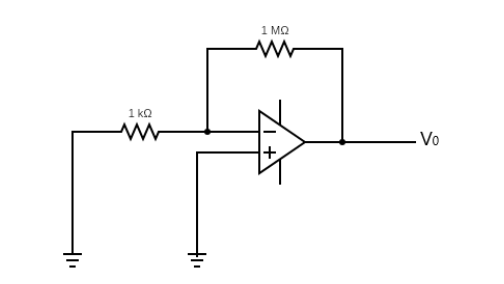
An op amp has an offset voltage of 1mV and is ideal in all other respects. If this op amp is used in the circuit shown in figure the output voltage would be:
(A) 1 mV
(B) 1 V
(C) \[0.1{\text{V}}\]
(D) 0 V.
Answer
232.8k+ views
Hint: In such a circuit, the offset voltage (also known as the input offset voltage) is the input voltage to the op amp. The ratio of the output voltage to the input voltage is equal to the ratio of the resistance across the op amp and the input resistance of the op amp
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
\[{V_{out}} = \dfrac{{{R_F}}}{{{R_{in}}}}{V_{off}}\] where \[{V_{out}}\] is the output voltage of the op amp, \[{R_F}\] is the resistance connected across the op amp, \[{R_{in}}\] is the input resistance usually connected to the negative part terminal of the op amp, and \[{V_{off}}\] is the offset voltage.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
To solve the above question, as told, we note that the op amp is ideal. This means that for such a circuit the offset voltage would be amplified. This offset voltage is a parameter of an amplifier which gives information about the required input voltage for the operation of the amplifier.
Generally, the ratio of the output voltage to the input voltage is equal to the ratio of the resistance across the op amp and the input resistance of the op amp
\[{V_{out}} = \dfrac{{{R_F}}}{{{R_{in}}}}{V_{off}}\] where \[{V_{out}}\] is the output voltage of the op amp, \[{R_F}\] is the resistance connected across the op amp, \[{R_{in}}\] is the input resistance usually connected to the negative part terminal of the op amp, and \[{V_{off}}\] is the offset voltage.
By inserting known values, we have
\[{V_{out}} = \dfrac{{1000k\Omega }}{{1k\Omega }}0.001{\text{V}} = 1{\text{V}}\]
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: As seen from the diagram, there is no input signal in the system as both the negative and positive are grounded. Hence, why the offset voltage is used as the input. Also, this is ideal, an non-ideal op amp may give a zero volt at output even at a non zero offset voltage.
Formula used: In this solution we will be using the following formulae;
\[{V_{out}} = \dfrac{{{R_F}}}{{{R_{in}}}}{V_{off}}\] where \[{V_{out}}\] is the output voltage of the op amp, \[{R_F}\] is the resistance connected across the op amp, \[{R_{in}}\] is the input resistance usually connected to the negative part terminal of the op amp, and \[{V_{off}}\] is the offset voltage.
Complete Step-by-Step solution:
To solve the above question, as told, we note that the op amp is ideal. This means that for such a circuit the offset voltage would be amplified. This offset voltage is a parameter of an amplifier which gives information about the required input voltage for the operation of the amplifier.
Generally, the ratio of the output voltage to the input voltage is equal to the ratio of the resistance across the op amp and the input resistance of the op amp
\[{V_{out}} = \dfrac{{{R_F}}}{{{R_{in}}}}{V_{off}}\] where \[{V_{out}}\] is the output voltage of the op amp, \[{R_F}\] is the resistance connected across the op amp, \[{R_{in}}\] is the input resistance usually connected to the negative part terminal of the op amp, and \[{V_{off}}\] is the offset voltage.
By inserting known values, we have
\[{V_{out}} = \dfrac{{1000k\Omega }}{{1k\Omega }}0.001{\text{V}} = 1{\text{V}}\]
Hence, the correct option is B.
Note: As seen from the diagram, there is no input signal in the system as both the negative and positive are grounded. Hence, why the offset voltage is used as the input. Also, this is ideal, an non-ideal op amp may give a zero volt at output even at a non zero offset voltage.
Recently Updated Pages
Circuit Switching vs Packet Switching: Key Differences Explained

JEE General Topics in Chemistry Important Concepts and Tips

JEE Extractive Metallurgy Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Amino Acids and Peptides Important Concepts and Tips for Exam Preparation

JEE Atomic Structure and Chemical Bonding important Concepts and Tips

Electricity and Magnetism Explained: Key Concepts & Applications

Trending doubts
JEE Main 2026: Session 2 Registration Open, City Intimation Slip, Exam Dates, Syllabus & Eligibility

JEE Main 2026 Application Login: Direct Link, Registration, Form Fill, and Steps

JEE Main Marking Scheme 2026- Paper-Wise Marks Distribution and Negative Marking Details

Understanding the Angle of Deviation in a Prism

Hybridisation in Chemistry – Concept, Types & Applications

How to Convert a Galvanometer into an Ammeter or Voltmeter

Other Pages
JEE Advanced Marks vs Ranks 2025: Understanding Category-wise Qualifying Marks and Previous Year Cut-offs

Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter Class 12 Physics Chapter 11 CBSE Notes - 2025-26

Understanding Uniform Acceleration in Physics

Understanding the Electric Field of a Uniformly Charged Ring

JEE Advanced Weightage 2025 Chapter-Wise for Physics, Maths and Chemistry

Derivation of Equation of Trajectory Explained for Students




